Abstract
Lanthanide-shifted 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has been used to compare the structure in solution of the EF-hand calcium-binding domains of four parvalbumins (isoelectric pH[pI] 3.95, 4.25, and 4.37 from carp, and pI from buffalo fish). These four parvalbumins are shown by NMR to have very similar structures at the level of resolution typical of x-ray structures. At the higher resolution possible by the lanthanide NMR technique, specific differences are noted between the pI 3.95 isoprotein from carp and the other two carp isoproteins, and the buffalo fish parvalbumin is shown to be different from all three carp isoproteins. The differences are estimated to correspond to changes of the order of 0.2 A in the positions of some of the nuclei surrounding the EF calcium site.
Full text
PDF
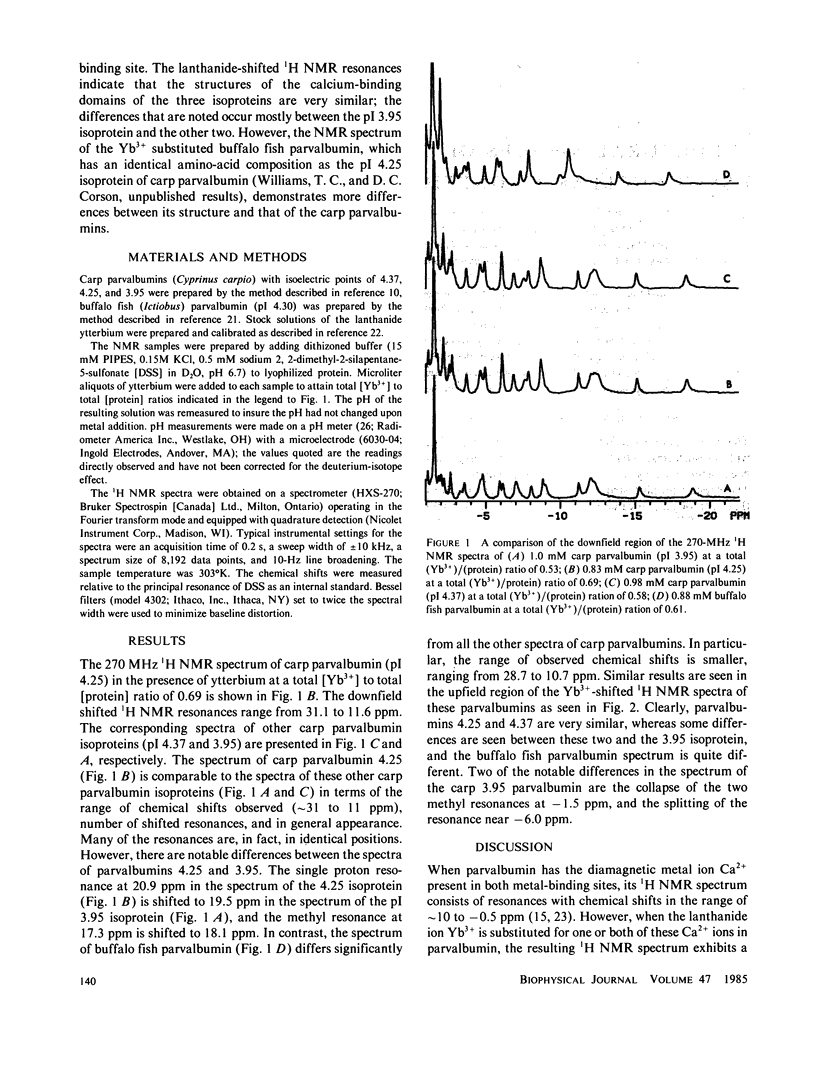

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaum E. R., Sykes B. D. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of a Ca2+-binding fragment of troponin C. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4965–4971. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffee C. J., Bradshaw R. A. Carp muscle calcium-binding protein. I. Characterization of the tryptic peptides and the complete amino acid sequence of component B. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3305–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffee C. J., Bradshaw R. A., Kretsinger R. H. The coordination of calcium ions by carp muscle calcium binding proteins A, B and C. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;48(0):211–233. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0943-7_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corson D. C., Lee L., McQuaid G. A., Sykes B. D. An optical stopped-flow and 1H and 113Cd nuclear magnetic resonance study of the kinetics and stoichiometry of the interaction of the lanthanide Yb3+ with carp parvalbumin. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;61(8):860–867. doi: 10.1139/o83-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corson D. C., Williams T. C., Sykes B. D. Calcium binding proteins: optical stopped-flow and proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the binding of the lanthanide series of metal ions to parvalbumin. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 6;22(25):5882–5889. doi: 10.1021/bi00294a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haiech J., Derancourt J., Pechere J. F., Demaille J. G. A new large-scale purification procedure for muscular parvalbumins. Biochimie. 1979;61(5-6):583–587. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(79)80155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann T., Kawakami M., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E., Dorrington K. J. The amino acid sequence of porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):737–748. doi: 10.1139/o79-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallfelz F. A., Taylor A. N., Wasserman R. H. Vitamin D-induced calcium binding factor in rat intestinal mucosa. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 May;125(1):54–58. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:239–266. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Dangelat D., Bryan R. F. Crystal data for low molecular weight albumins of carp. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):213–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90423-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Nockolds C. E. Carp muscle calcium-binding protein. II. Structure determination and general description. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3313–3326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L., Sykes B. D. Nuclear magnetic resonance determination of metal-protn distances in the EF site of carp parvalbumin using the susceptibility contribution to the line broadening of lanthanide-shifted resonances. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3208–3214. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L., Sykes B. D. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance determination of the sequential ytterbium replacement of calcium in carp parvalbumin. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1156–1162. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L., Sykes B. D. Strategies for the uses of lanthanide NMR shift probes in the determination of protein structure in solutio. Application to the EF calcium binding site of carp parvalbumin. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):193–210. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84933-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L., Sykes B. D. Use of lanthanide-induced nuclear magnetic resonance shifts for determination of protein structure in solution: EF calcium binding site of carp parvalbumin. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4366–4373. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moews P. C., Kretsinger R. H. Refinement of the structure of carp muscle calcium-binding parvalbumin by model building and difference Fourier analysis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):201–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moews P. C., Kretsinger R. H. Terbium replacement of calcium in carp muscle calcium-binding parvalbumin: an x-ray crystallographic study. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parello J., Cavé A., Puigdomenech P., Maury C., Capony J. P., Pechère J. F. Conformational studies on muscular parvalbumins. II. Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. Biochimie. 1974;56(1):61–76. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pechére J. F., Demaille J., Capony J. P. Muscular parvalbumins: preparative and analytical methods of general applicability. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 25;236(2):391–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee M. J., Sudnick D. R., Arkle V. K., Horrocks W. D., Jr Lanthanide ion luminescence probes. Characterization of metal ion binding sites and intermetal energy transfer distance measurements in calcium-binding proteins. 1. Parvalbumin. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3328–3334. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowadski J., Cornick G., Kretsinger R. H. Terbium replacement of calcium in parvalbumin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebenyi D. M., Obendorf S. K., Moffat K. Structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):327–332. doi: 10.1038/294327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


