Abstract
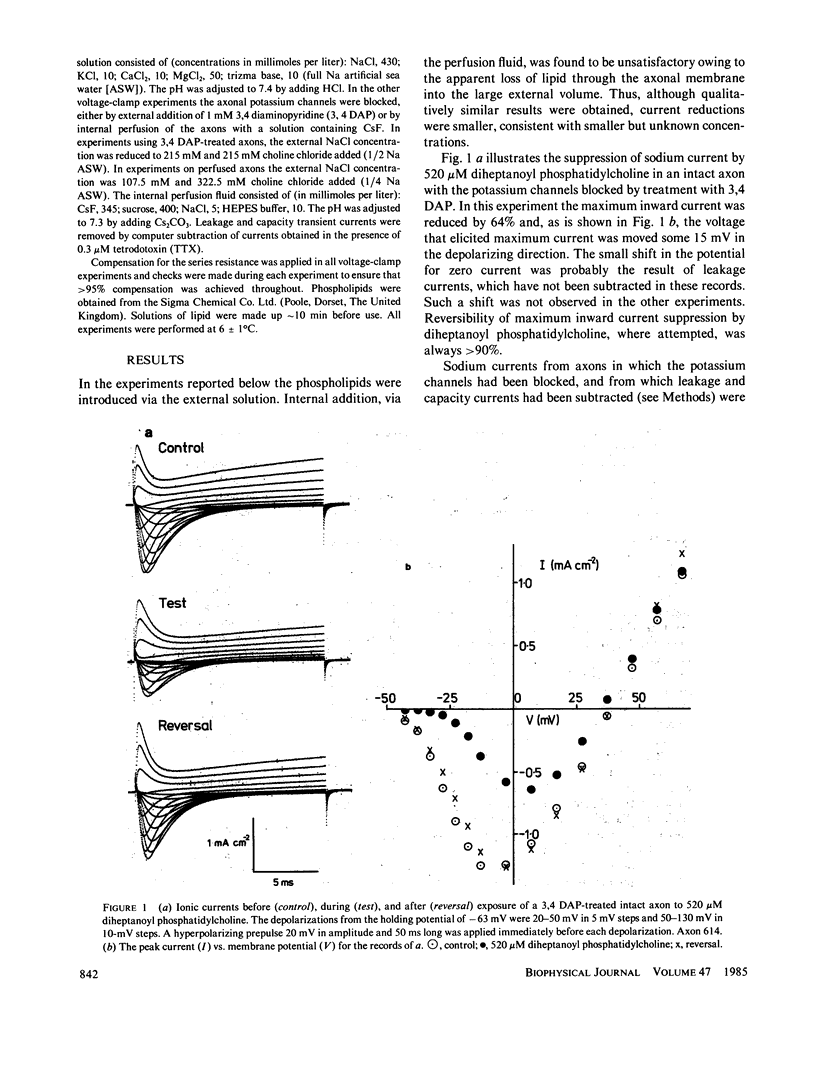
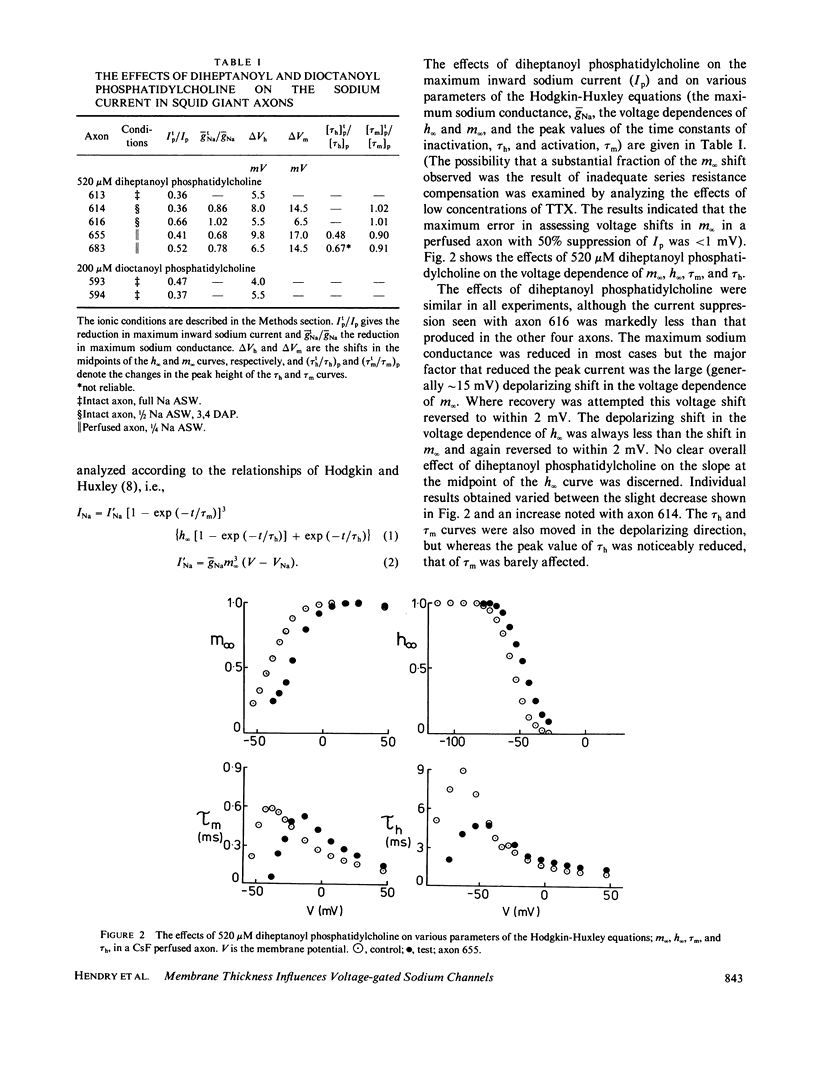
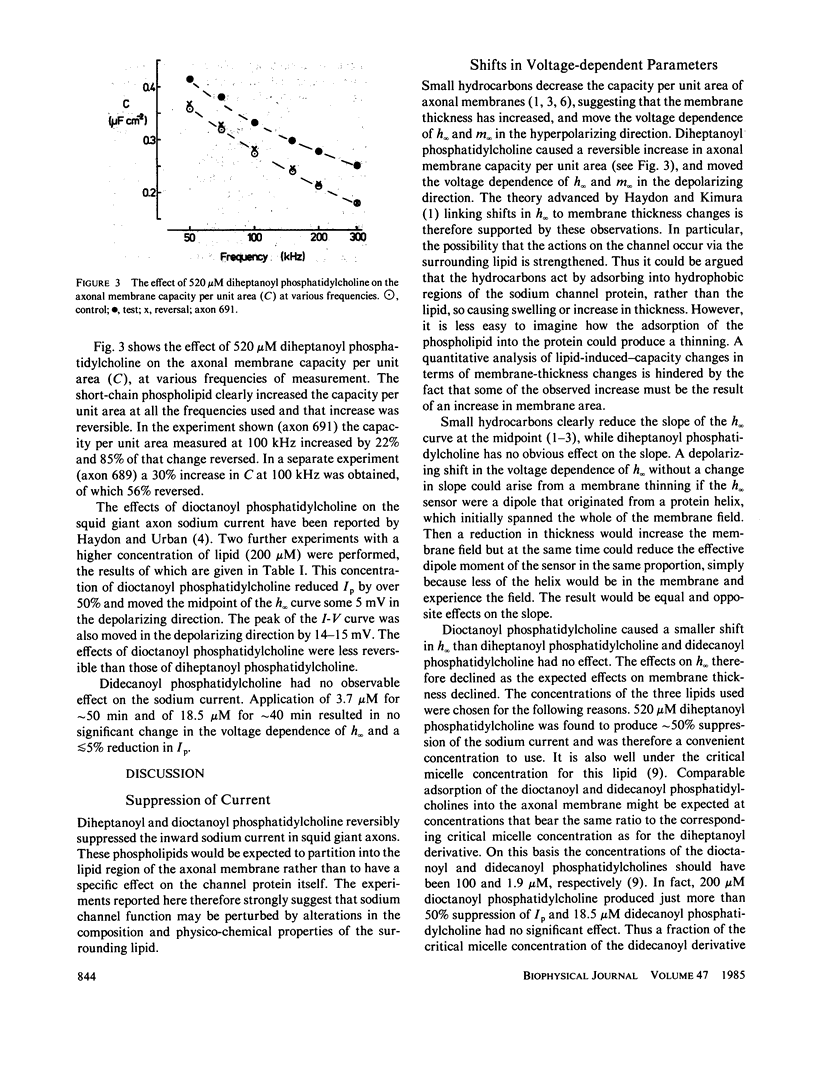
The short-chain phospholipid, diheptanoyl phosphatidylcholine, at 520 microM, reduced the maximum inward sodium current in voltage-clamped squid giant axons by greater than 50%. Analysis of these currents by means of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations showed this reduction to be mainly the result of a large depolarizing shift in the voltage dependence of the steady state activation parameter, m infinity. The voltage dependence of the steady state inactivation parameter, h infinity, was also moved in the depolarizing direction and the axonal membrane capacitance per unit area measured at 100 kHz was increased. A longer chain length derivative, didecanoyl phosphatidylcholine, had no significant effect on the axonal sodium current at concentrations of 3.7 and 18.5 microM. Dioctanoyl phosphatidylcholine was intermediate in its effects, 200 microM producing approximately the same current suppression as 520 microM diheptanoyl phosphatidylcholine, together with depolarizing shifts in m infinity and h infinity. These effects may be contrasted with those of the normal and cyclic alkanes (1-3), which tend to move both m infinity and h infinity in the hyperpolarizing direction and to reduce the capacitance per unit area at 100 kHz. The above results are all consistent with the hypothesis that small hydrocarbons thicken, while short-chain phospholipids thin, the axonal membrane. Thus membrane thickness changes may be of considerable importance in determining the behavior of the voltage-gated sodium channel.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elliott J. R., Needham D., Dilger J. P., Haydon D. A. The effects of bilayer thickness and tension on gramicidin single-channel lifetime. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 26;735(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahin R., Campbell D. T. Simple shifts in the voltage dependence of sodium channel gating caused by divalent cations. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Dec;82(6):785–805. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.6.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Kimura J. E. Some effects of n-pentane on the sodium and potassium currents of the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:57–70. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Requena J., Urban B. W. Some effects of aliphatic hydrocarbons on the electrical capacity and ionic currents of the squid giant axon membrane. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:229–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Urban B. W. The action of alcohols and other non-ionic surface active substances on the sodium current of the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:411–427. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Urban B. W. The action of hydrocarbons and carbon tetrachloride on the sodium current of the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1983 May;338:435–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Urban B. W. The admittance of the squid giant axon at radio frequencies and its relation to membrane structure. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:275–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Urban B. W. The effects of some inhalation anaesthetics on the sodium current of the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:429–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


