Abstract
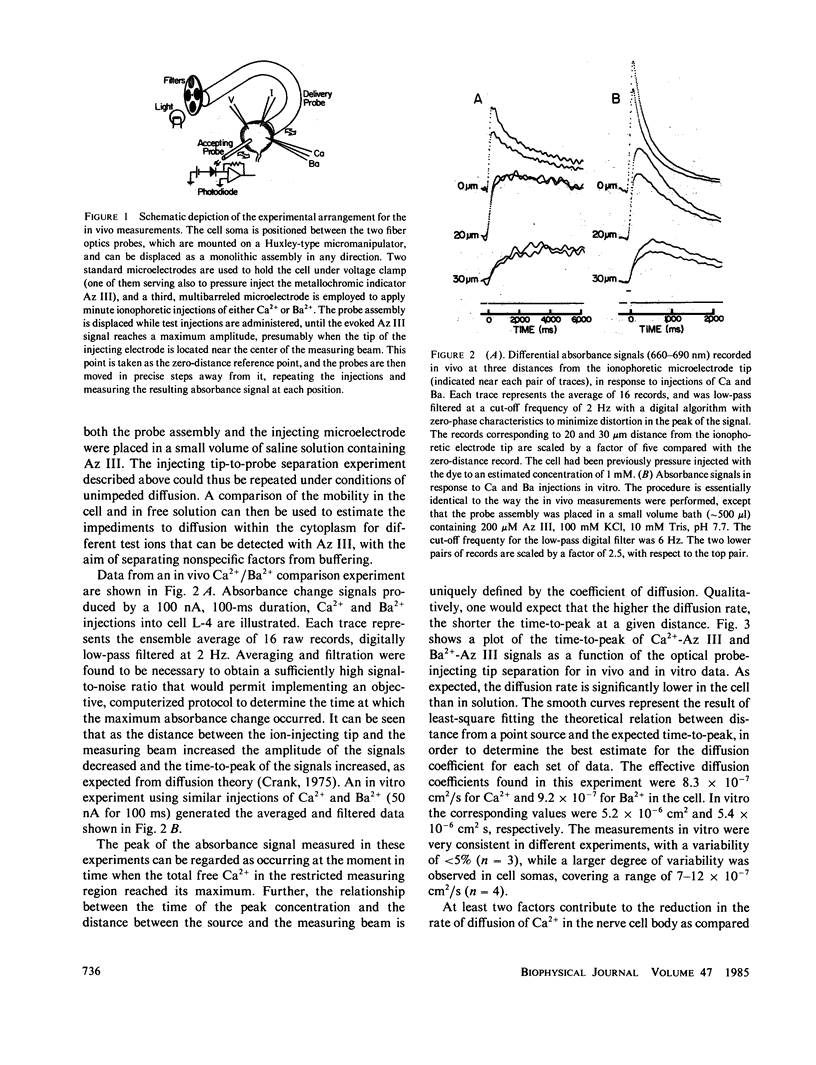
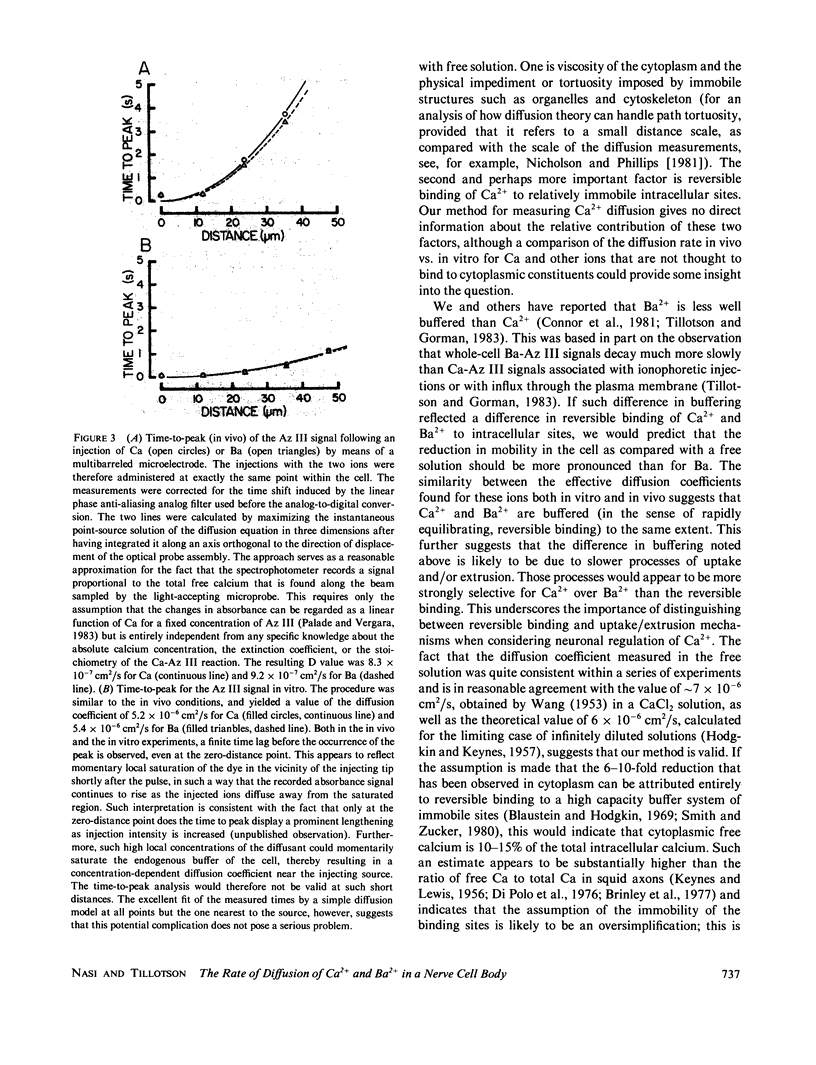
A spectrophotometric method was developed to directly measure the diffusion rate of Ca2+ and some other ions in nerve cell bodies, using pulsed ionophoretic injections and an optical microprobe to record locally absorbance changes of the dye arsenazo III. We report here that Ca2+ and Ba2+ diffuse at approximately the same rate in nerve soma cytoplasm, having effective diffusion coefficients in the range of 7-12 X 10(-7) cm2/s, while identical measurements conducted in an electrolytic solution yielded values of 5.2 X 10(-6) cm2/s for Ca and 5.4 X 10(-6) cm2/s for Ba. The results are discussed in relation to the mechanisms that regulate the intracellular concentration of free Ca.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L. The effect of cyanide on the efflux of calcium from squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):497–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Tiffert T., Scarpa A., Mullins L. J. Intracellular calcium buffering capacity in isolated squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Sep;70(3):355–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R., Requena J., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J., Scarpa A., Tiffert T. Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):433–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Hermann A. Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:393–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Changes in the intracellular concentration of free calcium ions in a pace-maker neurone, measured with the metallochromic indicator dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., LEWIS P. R. The intracellular calcium contents of some invertebrate nerves. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):399–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Nicholson C. Calcium role in depolarization-secretion coupling: an aequorin study in squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):187–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson C., Phillips J. M. Ion diffusion modified by tortuosity and volume fraction in the extracellular microenvironment of the rat cerebellum. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:225–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade P., Vergara J. Stoichiometries of arsenazo III-Ca complexes. Biophys J. 1983 Sep;43(3):355–369. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84359-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Aequorin response facilitation and intracellular calcium accumulation in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:167–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. L., Gorman A. L. Localization of neuronal Ca2+ buffering near plasma membrane studied with different divalent cations. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1983 Dec;3(4):297–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00734712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


