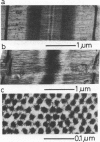
Abstract
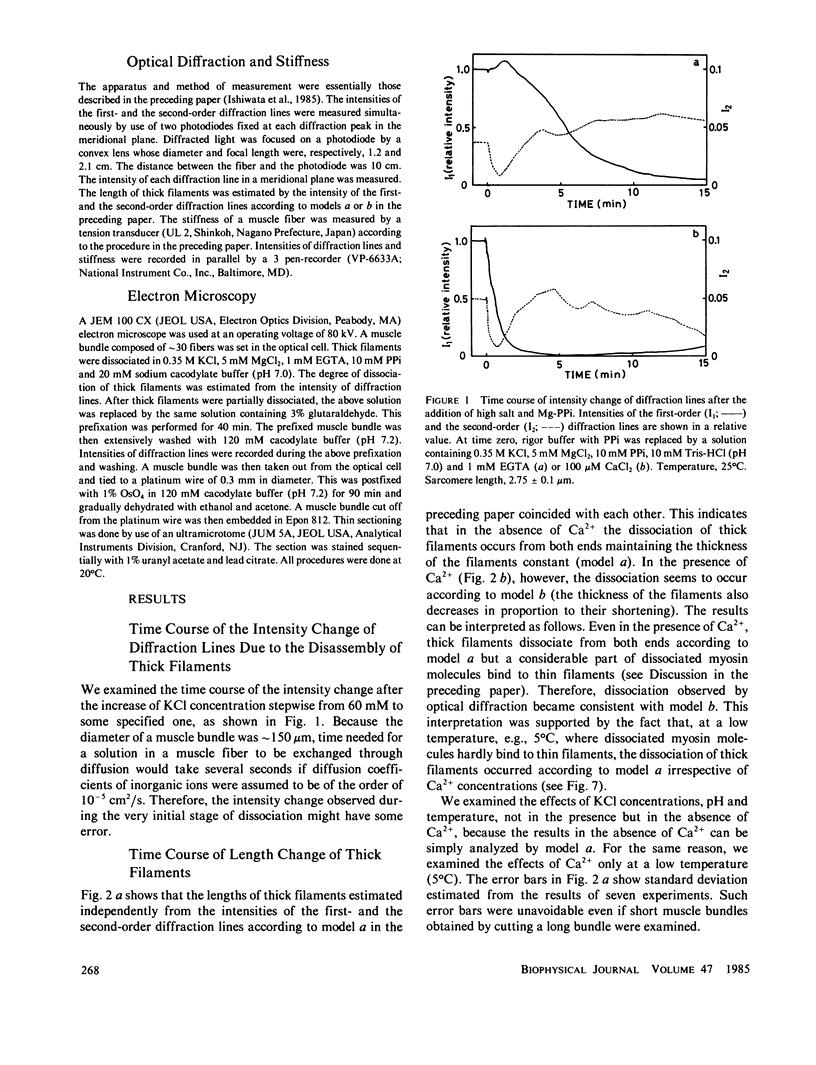
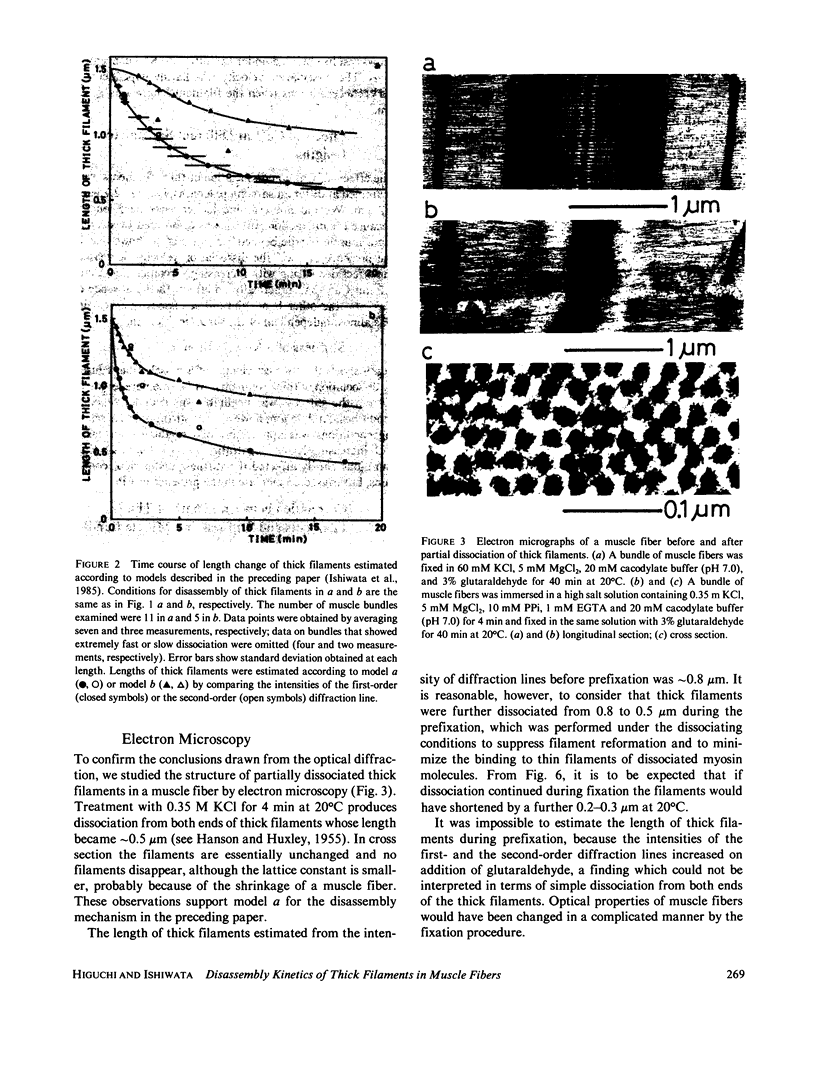
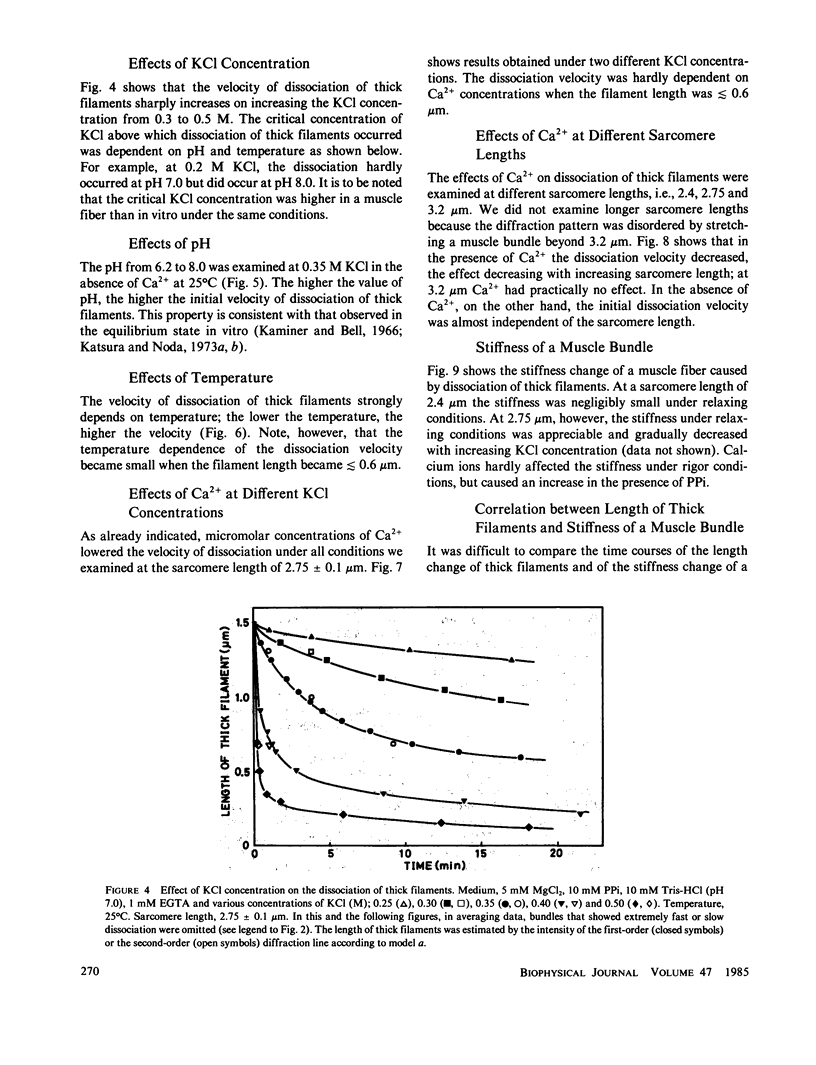
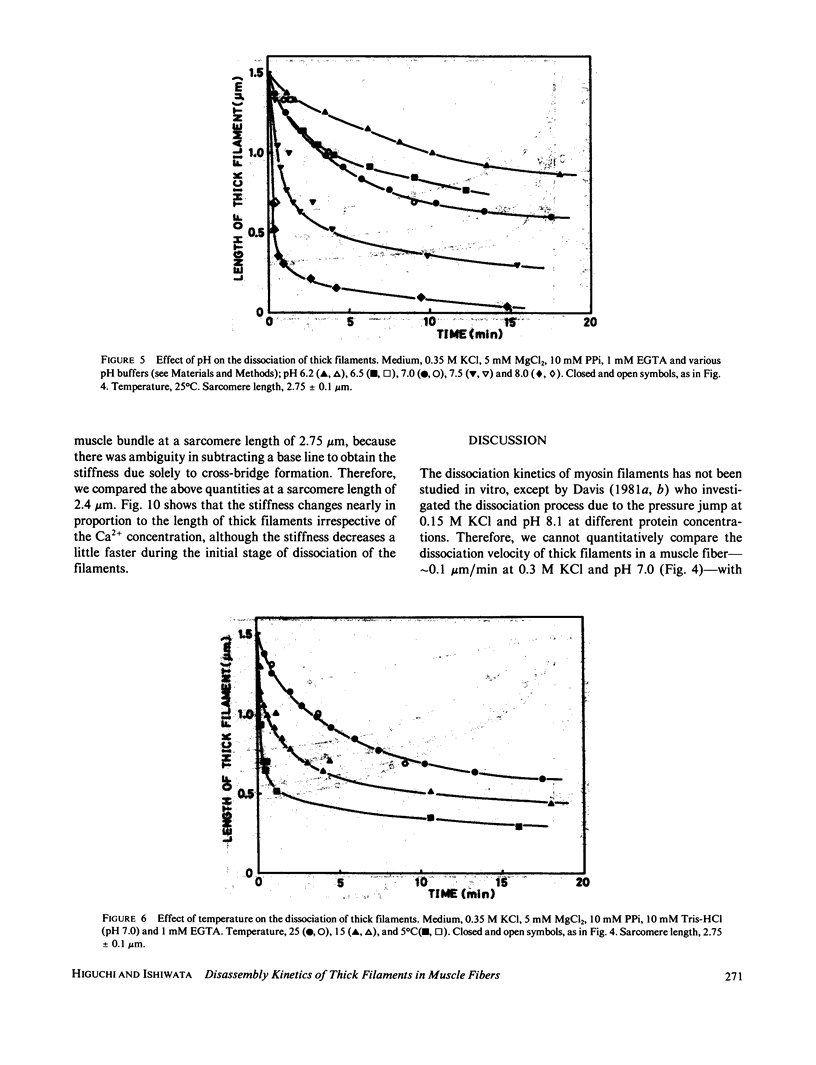
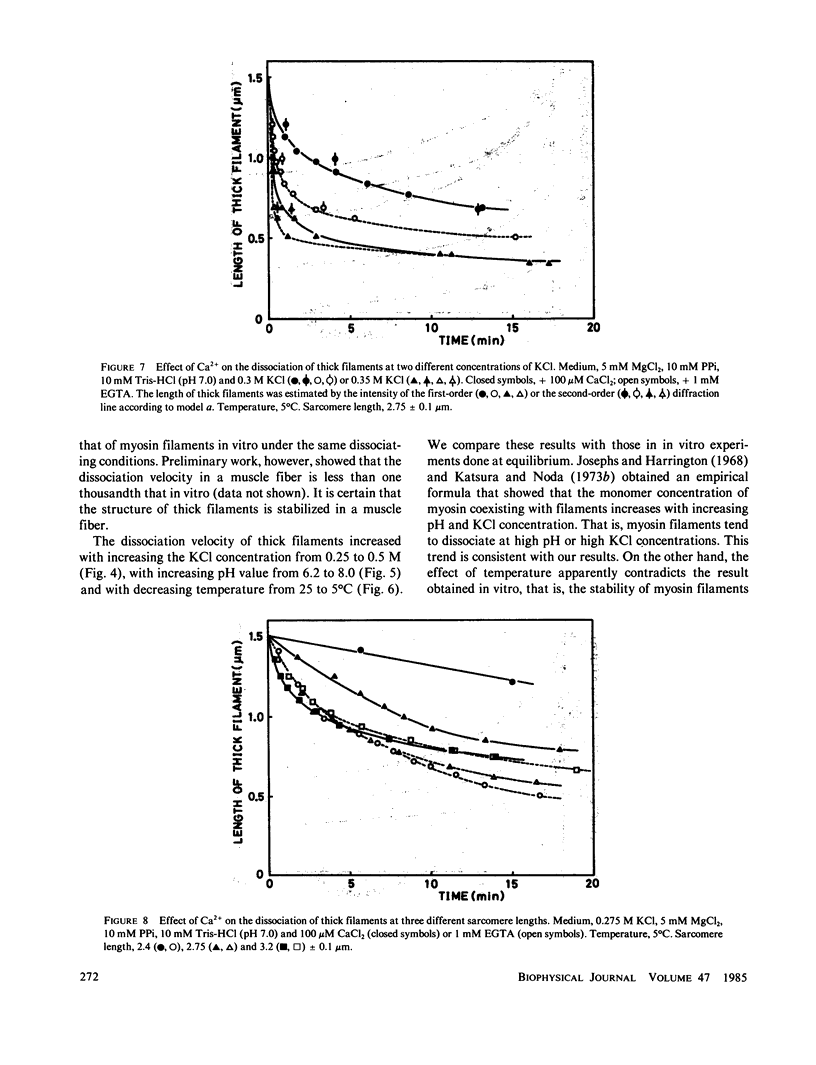
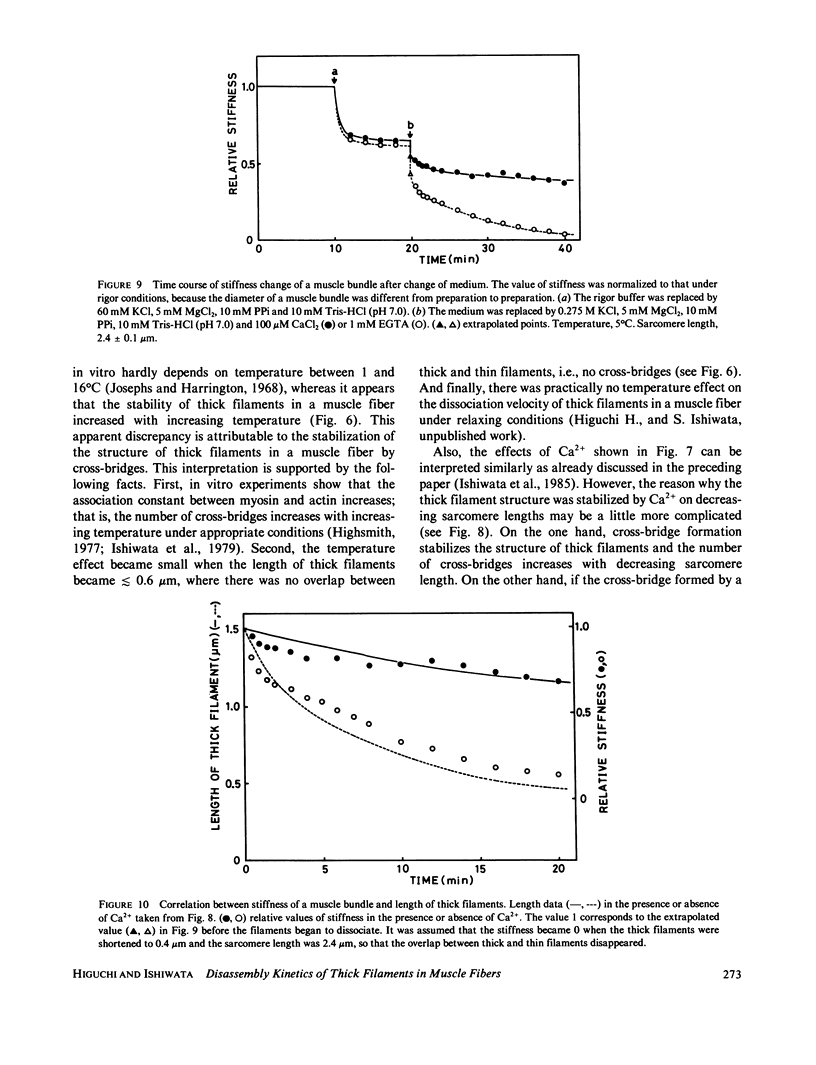
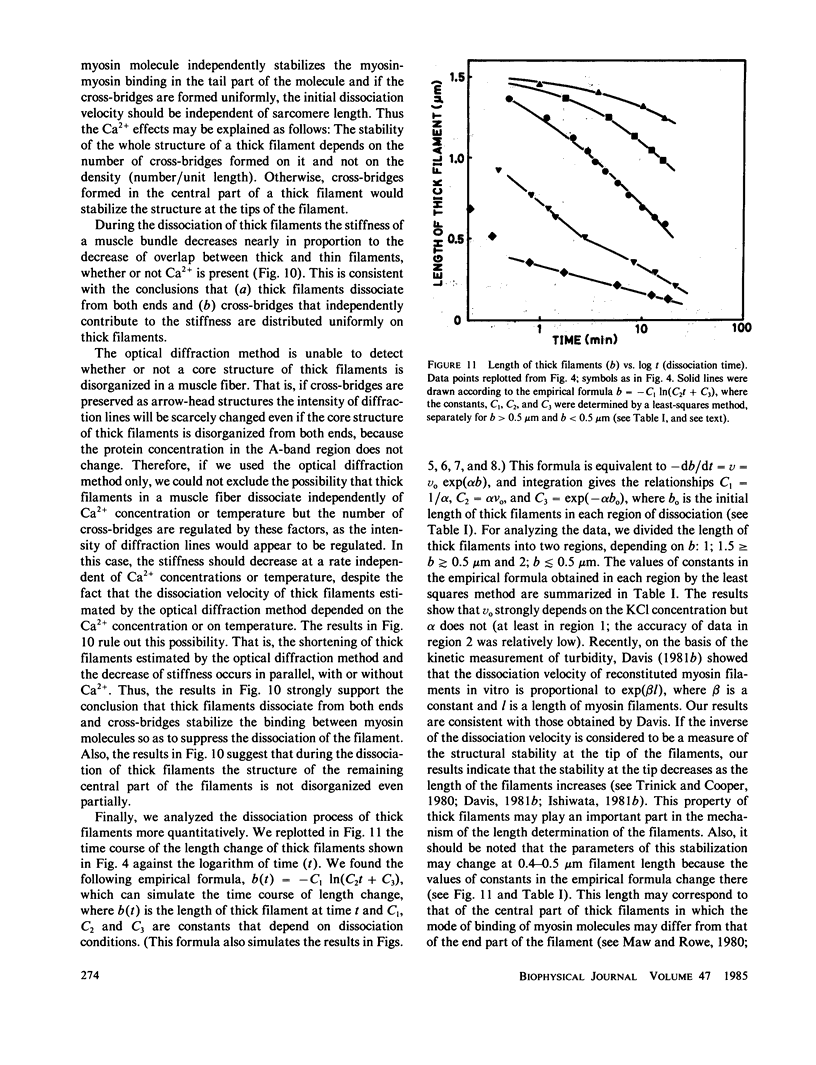
The kinetics of dissociation from both ends of thick filaments in a muscle fiber was investigated by an optical diffraction method. The dissociation velocity of thick filaments at a sarcomere length of 2.75 microns increased with increasing the KCl concentration (from 60 mM to 0.5 M), increasing the pH value (from 6.2 to 8.0) or decreasing the temperature (from 25 to 5 degrees C) in the presence of 10 mM pyrophosphate and 5 mM MgCl2. Micromolar concentrations of Ca2+ suppressed the dissociation velocity markedly at shorter sarcomere lengths. The dissociation velocity, v, decreased as thick filaments became shorter, and v = -db/dt = vo exp (alpha b), where b is the length of the thick filament at time t and vo and alpha are constants. The vo value was largely dependent on the KCl concentration but the alpha value was not. The stiffness of a muscle fiber decreased nearly in proportion to the decrease of overlap between thick and thin filaments induced by the dissociation of thick filaments. This indicates that cross-bridges are uniformly distributed and contribute independently to the stiffness of a muscle fiber during the dissociation of thick filaments.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis J. S. Pressure-jump studies on the length-regulation kinetics of the self-assembly of myosin from vertebrate skeletal muscle into thick filament. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):309–314. doi: 10.1042/bj1970309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S. The influence of pressure on the self-assembly of the thick filament from the myosin of vertebrate skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):301–308. doi: 10.1042/bj1970301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujime S. An intensity expression of optical diffraction from striated muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Oct;5(5):577–587. doi: 10.1007/BF00713262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujime S. Optical diffraction study of muscle fibers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 30;379(1):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujime S., Yoshino S. Optical diffraction study of muscle fibers. I. A theoretical basis. Biophys Chem. 1978 Sep;8(4):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(78)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S. The effects of temperature and salts on myosin subfragment-1 and F-actin association. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Apr 30;180(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata S., Muramatsu K., Higuchi H. Disassembly from both ends of thick filaments in rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. An optical diffraction study. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):257–266. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83915-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs R., Harrington W. F. On the stability of myosin filaments. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2834–2847. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs R., Harrington W. F. Studies on the formation and physical chemical properties of synthetic myosin filaments. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3474–3487. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminer B., Bell A. L. Myosin filamentogenesis: effects of pH and ionic concentration. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsura I., Noda H. Further studies on the formation of reconstituted myosin filaments. J Biochem. 1973 Feb;73(2):245–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maw M. C., Rowe A. J. Fraying of A-filaments into three subfilaments. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):412–414. doi: 10.1038/286412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman R., Peters L. K. Native bare zone assemblage nucleates myosin filament assembly. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):505–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90404-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisler E., Smith C., Seegan G. Myosin minifilaments. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):129–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinick J., Cooper J. Sequential disassembly of vertebrate muscle thick filaments. J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 15;141(3):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]