Figure 2.
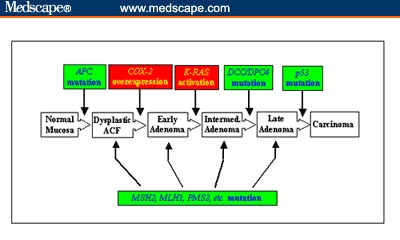
The genetic paradigm of colorectal cancer. The formation of CRC requires the sequential mutation of several genes. This includes the inactivation of TSGs (in green) and activation of oncogenes (in red). There are 2 independent pathways that can cause CRC, depending upon which TSG is first inactivated. Inactivation of the APC gene is found in about 85% of sporadic CRC, and inactivation of the mismatch repair genes, including MSH2, MLH1, and PMS2, is found in the remaining 15%.
Key: COX-2 = cyclo-oxygenase-2.
