Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachelard H. S., Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Pratt O. E. The transport of glucose into the brain of the rat in vivo. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Feb 27;183(1070):71–82. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E. Inhibition of entry of some amino acids into the brain, with observations on mental retardation in the aminoacidurias. Psychol Med. 1974 Aug;4(3):262–269. doi: 10.1017/s003329170004294x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E. The influx of amino acids into the brain of the rat in vivo: the essential compared with some non-essential amino acids. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Feb 27;183(1070):59–70. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E. The movement of amino acids between blood and skeletal muscle in the rat. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(2):459–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E. The requirements of the brain for some amino acids. J Physiol. 1975 Apr;246(3):539–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Pratt O. E. Saturation of a shared mechanism which transports L-arginine and L-lysine into the brain of the living rat. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(1):29–41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Pratt O. E. The effect of age upon the entry of some amino acids into the brain, and their incorporation into cerebral protein. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1978 Jun;20(3):335–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1978.tb15223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Aoki T. T. Starvation and body nitrogen. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1971;82:43–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Pratt O. E. Insulin-stimulated entry of glucose into muscle in vivo as a major factor in the regulation of blood glucose. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):273–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Pratt O. E. The effect of age upon the influx of glucose into the brain. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:141–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Pratt O. E. Thyroid hormones and the movement of amino acids between skeletal muscle and the blood [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:73P–73P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Pratt O. E., Spargo E. Storage and homoeostatic functions of the skeletal muscles in muscular dystrophy [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:41P–42P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Pratt O. E., Spargo E., Taylor D. E. Effect of bilateral hind-limb ischaemia upon the patterns of free amino acids in the circulation in the rat [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;272(1):103P–104P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Pratt O. E., Spargo E. The effects of fasting compared with those of a reduced protein intake on the movement of amino acids between skeletal muscle and blood [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):50P–51P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Pratt O. E., Spargo E. The mechanism by which glucagon induces the release of amino acids from muscle and its relevance to fasting. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Mar 18;196(1124):347–365. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
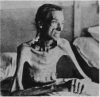
- Daniel P. M. The metabolic homoeostatic role of muscle and its function as a store of protein. Lancet. 1977 Aug 27;2(8035):446–448. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90622-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Aoki T. T., Pozefsky T., Most A. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Muscle and splanchnic glutmine and glutamate metabolism in postabsorptive andstarved man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):814–817. doi: 10.1172/JCI106552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J. Protein turnover in skeletal muscle. II. The effect of starvation and a protein-free diet on the synthesis and catabolism of skeletal muscle proteins in comparison to liver. Clin Sci. 1970 Nov;39(5):591–603. doi: 10.1042/cs0390591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozefsky T., Felig P., Tobin J. D., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid balance across tissues of the forearm in postabsorptive man. Effects of insulin at two dose levels. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2273–2282. doi: 10.1172/JCI106193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spargo E., Pratt O. E., Daniel P. M. The effects of murine muscular dystrophy on the metabolic and homeostatic functions of the skeletal muscles. J Neurol Sci. 1979 Oct;43(2):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick R. W., Song H. Turnover rates of various muscle proteins. J Anim Sci. 1974 May;38(5):1150–1157. doi: 10.2527/jas1974.3851150x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]