Full text
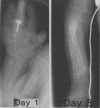
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begum R., Coutinho M. L., Dormandy T. L., Yudkin S. Maternal malabsorption presenting as congenital rickets. Lancet. 1968 May 18;1(7551):1048–1052. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosley A. R., Verrier-Jones E. R., Campbell M. J. Aetiological factors in rickets of prematurity. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Sep;55(9):683–686. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.9.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow J. F., Thomas P. S. Rachitic respiratory distress in small preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Apr;52(4):268–273. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.4.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman L. S., Haddad J. G. Human perinatal vitamin D metabolism. I. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in maternal and cord blood. J Pediatr. 1974 May;84(5):742–749. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khattab A. K., Forfar J. O. The interrelationship between calcium, phosphorus and clucose levels in mother and infant in conditions commonly associated with 'placental insufficiency'. Biol Neonate. 1971;18(1):1–16. doi: 10.1159/000240341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovar I., Mayne P., Barltrop D. Plasma alkaline phosphatase activity: a screening test for rickets in preterm neonates. Lancet. 1982 Feb 6;1(8267):308–310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91569-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncrieff M., Fadahunsi T. O. Congenital rickets due to maternal vitamin D deficiency. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Oct;49(10):810–811. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.10.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sann L., David L., Frederich A., Bovier-Lapierre M., Bourgeois J., Romand-Monier M., Bethenod M. Congenital rickets. Study of the evolution of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1977 May;66(3):323–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1977.tb07901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]