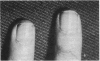
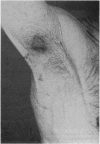
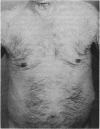
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardach H., Gebhart W., Niebauer G. "Lumpy-bumpy" elastic fibers in the skin and lungs of a patient with a penicillamine-induced elastosis perforans serpiginosa. J Cutan Pathol. 1979 Aug;6(4):243–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1979.tb01131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer W. E., Cooke K. B. Epidermolysis bullosa induced by penicillamine. Br J Dermatol. 1967 Feb;79(2):123–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1967.tb11471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWHALL J. C., SCOWEN E. F., WATTS R. W. Effect of penicillamine on cystinuria. Br Med J. 1963 Mar 2;1(5330):588–590. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5330.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlebois G., Cadotte M., Barbeau A. Cutis hyperelastica après administration prolongée de pénicillamine chez une patiente atteinte de maladie de Wilson. Union Med Can. 1972 May;101(5):893–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer K. E., Askew F. C., Richardson D. R. Skin lesions induced by penicillamine. Occurrence in a patient with hepatolenticular degeneration (Wilson Disease). Arch Dermatol. 1976 Sep;112(9):1267–1269. doi: 10.1001/archderm.112.9.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., McEvoy B., Belcher R. Ultrastructure of penicillamine-induced skin lesions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981 Mar;4(3):300–315. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(81)80176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. Penicillamine-induced skin lesions. A possible example of human lathyrism. Arch Dermatol. 1967 Feb;95(2):196–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch N., Hukill P. B. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa induced by penicillamine. Arch Dermatol. 1977 May;113(5):630–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapiere C. H. The molecular basis of connective tissue pathology. Br J Dermatol. 1973 Jul;89(1):87–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1973.tb01922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D., Bailey A. J. Covalent cross-links in collagen. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D. Estimation of types I and III collagens in whole tissue by quantitation of CNBr peptides on SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 18;702(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Martin G. R., Mecca C. E., Piez K. A. The biosynthesis of elastin cross-links. The effect of copper deficiency and a lathyrogen. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3623–3627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass F., Goldfischer S., Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa during penicillamine therapy for Wilson disease. Arch Dermatol. 1973 Nov;108(5):713–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco V., De Angelis E., De Luca M., Pisani M., Prota G. Specific incorporation of penicillamine into the epidermis of mice: an autoradiographic study. Br J Dermatol. 1983 Apr;108(4):441–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb04596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARCHER B., HILL C. H., MATRONE G. IMPORTANCE OF DIETARY COPPER IN THE FORMATION OF AORTIC ELASTIN. J Nutr. 1964 Mar;82:318–322. doi: 10.1093/jn/82.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Weissman N., Carnes W. H. Cardiovascular studies on copper deficient swine. XII. Partial purification of a soluble protein resembling elastin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 May 10;31(3):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90476-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlieb I., Fisher M., Scheinberg I. H. Penicillamine-induced skin lesions. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1981 Jan-Feb;7:149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]