Abstract
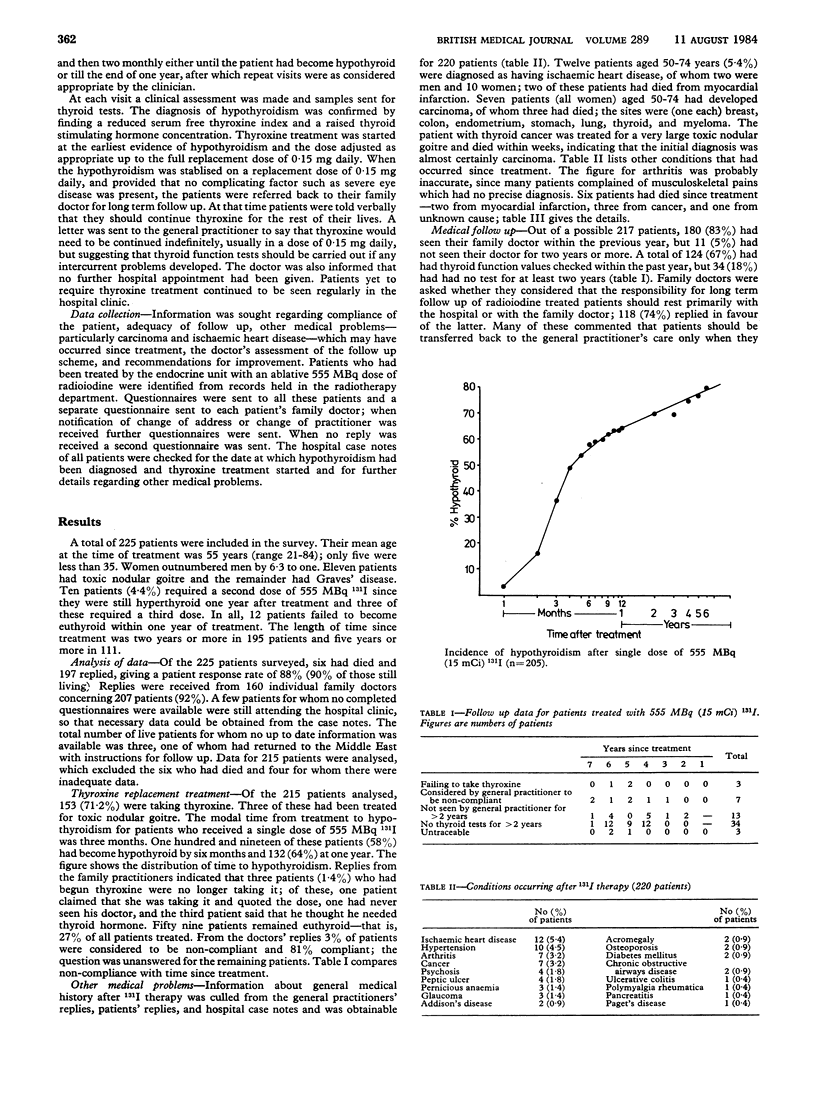
A total of 225 patients were treated for hyperthyroidism with 555 MBq (15 mCi) radioiodine to ablate the thyroid and induce early hypothyroidism. The efficacy of this treatment in eradicating hyperthyroidism and problems of follow up were assessed one to six years later from case records and questionnaires. Information was received from 197 out of 219 live patients (90%) and from 160 doctors concerning 207 patients (92%). Only three patients were not traced and six had died since treatment. The modal time to hypothyroidism was three months, and 64% of patients were hypothyroid at one year; 5.6% had failed to become euthyroid within one year. Ninety five per cent of patients had been seen by the doctor and 82% had had a thyroid test done within the past two years. Most doctors preferred patients to be returned to their care once thyroxine treatment was stabilised. An ablative dose of 131I is recommended as an effective means of treatment which has clear advantages over conventional methods. Good communications and effective follow up should ensure success.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOMFIELD G. W., ECKERT H., FISHER M., MILLER H., MUNRO D. S., WILSON G. M. Treatment of thyrotoxicosis with 131 I; a review of 500 cases. Br Med J. 1959 Jan 10;1(5114):63–74. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5114.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN J. T., CHAPMAN E. M. RISING INCIDENCE OF HYPOTHYROIDISM AFTER RADIOACTIVE-IODINE THERAPY IN THYROTOXICOSIS. N Engl J Med. 1964 Nov 12;271:1037–1042. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196411122712004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns B. M., Sheline G. E., Workman J. B., Tompkins E. A., McConahey W. M., Becker D. V. Malignant and benign neoplasms of the thyroid in patients treated for hyperthyroidism: a report of the cooperative thyrotoxicosis therapy follow-up study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Jun;38(6):976–998. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-6-976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig W. R. Radioactive iodine therapy for thyrotoxicosis. Br J Surg. 1973 Oct;60(10):758–765. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800601003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halnan K. E. Risks from radioiodine treatment of thyrotoxicosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Dec 17;287(6408):1821–1822. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6408.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. J., Hedley A. J., Curtis B., Allison S. P., Woolfson A. M., Steele R., Bewsher P. D., Weir R. D. Do we need thyroid follow-up registers? A cost-effective study. Lancet. 1982 May 29;1(8283):1229–1233. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92348-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell D. R., Jr, Bell J. H., Good R. G., Moyer D. L. The intrauterine device: a bacteriologic study of the endometrial cavity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1966 Sep 1;96(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)34650-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nofal M. M., Beierwaltes W. H., Patno M. E. Treatment of hyperthyroidism with sodium iodide I-131. JAMA. 1966 Aug 22;197(8):605–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skangalis M., Mahoney C. J., O'Leary W. M. Microbial presence in the uterine cavity as affected by varieties of intrauterine contraceptive devices. Fertil Steril. 1982 Feb;37(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)46050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. N., Wilson G. M. Clinical trial of different doses of 131-I in treatment of thyrotoxicosis. Br Med J. 1967 Jan 21;1(5533):129–132. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5533.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessey M. P., Yeates D., Flavel R., McPherson K. Pelvic inflammatory disease and the intrauterine device: findings in a large cohort study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Mar 14;282(6267):855–857. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6267.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise P. H., Burnet R. B., Ahmad A., Harding P. E. Intentional radioiodine ablation in Graves' disease. Lancet. 1975 Dec 20;2(7947):1231–1233. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


