Abstract
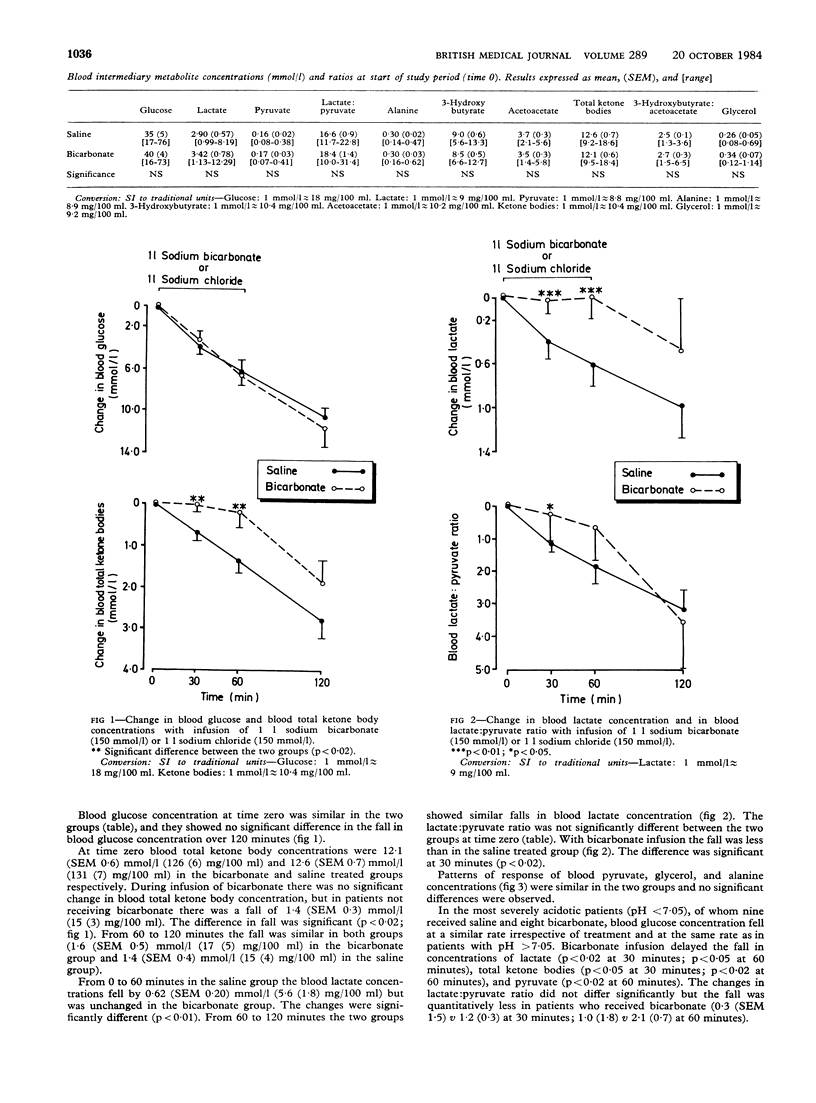
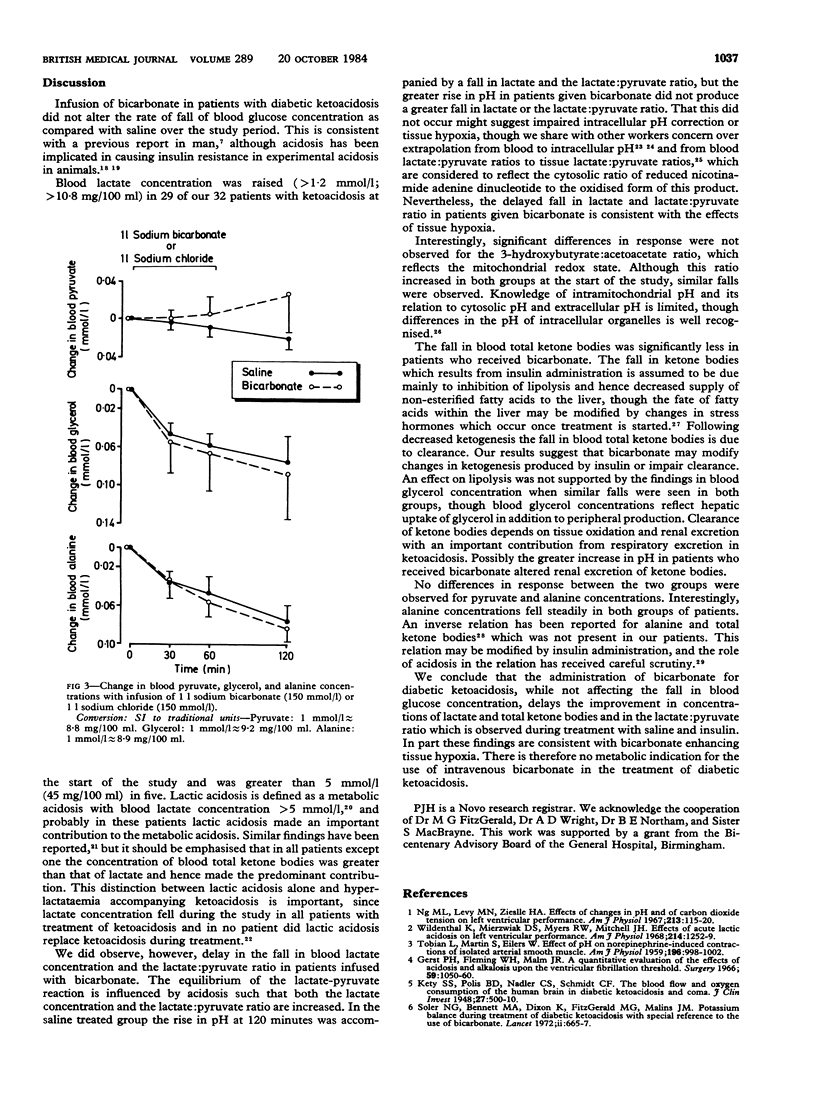
The effect of intravenous bicarbonate on the changes in intermediary metabolites during the initial treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis was examined in 16 patients. The results were compared with the changes seen in 16 patients receiving intravenous saline. Infusion of 150 mmol (mEq) bicarbonate significantly delayed the fall in blood lactate, lactate:pyruvate ratio, and total ketone bodies observed in the saline treated group. No difference in the rate of fall of blood glucose concentration was found. There is no metabolic indication for the use of intravenous bicarbonate in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assal J. P., Aoki T. T., Manzano F. M., Kozak G. P. Metabolic effects of sodium bicarbonate in management of diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes. 1974 May;23(5):405–411. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.5.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellingham A. J., Detter J. C., Lenfant C. The role of hemoglobin affinity for oxygen and red-cell 2,3-diphosphoglycerate in the management of diabetic ketoacidosis. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1970;83:113–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R., Benesch R. E. Intracellular organic phosphates as regulators of oxygen release by haemoglobin. Nature. 1969 Feb 15;221(5181):618–622. doi: 10.1038/221618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bureau M. A., Bégin R., Berthiaume Y., Shapcott D., Khoury K., Gagnon N. Cerebral hypoxia from bicarbonate infusion in diabetic acidosis. J Pediatr. 1980 Jun;96(6):968–973. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80619-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. D. Disorders of lactic acid metabolism. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Nov;5(3):613–625. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(76)80043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditzel J., Standl E. The oxygen transport system of red blood cells during diabetic ketoacidosis and recovery. Diabetologia. 1975 Aug;11(4):255–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00422388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulop M., Hoberman H. D., Rascoff J. H., Bonheim N. A., Dreyer N. P., Tannenbaum H. Lactic acidosis in diabetic patients. Arch Intern Med. 1976 Sep;136(9):987–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Féry F., Balasse E. O. Differential effects of sodium acetoacetate and acetoacetic acid infusions on alanine and glutamine metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):323–331. doi: 10.1172/JCI109860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerst P. H., Fleming W. H., Malm J. R. A quantitative evaluation of the effects of acidosis and alkalosis upon the ventricular fibrillation threshold. Surgery. 1966 Jun;59(6):1050–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Polis B. D., Nadler C. S., Schmidt C. F. THE BLOOD FLOW AND OXYGEN CONSUMPTION OF THE HUMAN BRAIN IN DIABETIC ACIDOSIS AND COMA. J Clin Invest. 1948 Jul;27(4):500–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI101997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd B., Burrin J., Smythe P., Alberti K. G. Enzymic fluorometric continuous-flow assays for blood glucose, lactate, pyruvate, alanine, glycerol, and 3-hydroxybutyrate. Clin Chem. 1978 Oct;24(10):1724–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd M. H., Iles R. A., Simpson B. R., Strunin J. M., Layton J. M., Cohen R. D. The effect of simulated metabolic acidosis on intracellular pH and lactate metabolism in the isolated perfused rat liver. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Oct;45(4):543–549. doi: 10.1042/cs0450543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKLER B., LICHTENSTEIN H., GUEST G. M. Effects of ammonium chloride acidosis on the action of insulin in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1951 Jul;166(1):191–198. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.166.1.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGillivray M. H., Bruck E., Voorhess M. L. Acute diabetic ketoacidosis in children: role of the stress hormones. Pediatr Res. 1981 Feb;15(2):99–106. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198102000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz R. Rationale for not using bicarbonate. N Y State J Med. 1976 Aug;76(8):1299–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng M. L., Levy M. N., Zieske H. A. Effects of changes of pH and of carbon dioxide tension on left ventricular performance. Am J Physiol. 1967 Jul;213(1):115–120. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park R., Arieff A. I. Lactic acidosis: current concepts. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jul;12(2):339–358. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(83)80045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. P., Llyod B., Alberti G. M. A kinetic spectrophotometric assay for rapid determination of acetoacetate in blood. Clin Chem. 1977 Oct;23(10):1893–1897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Hendler R. G., Felig P. Effect of ketone infusions on amino acid and nitrogen metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1382–1390. doi: 10.1172/JCI108057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler N. G., Bennett M. A., Dixon K., FitzGerald M. G., Malins J. M. Potassium balance during treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis with special reference to the use of bicarbonate. Lancet. 1972 Sep 30;2(7779):665–667. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIAN L., MARTIN S., EILERS W. Effect of pH on norepinephrine-induced contractions of isolated arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1959 May;196(5):998–1002. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.5.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. J., Bates R. G. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1969 Apr;49(2):285–329. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. J., Smith J. S., Fitzgerald M. G., Malins J. M. Lactic acidosis in diabetes. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 22;1(5646):744–747. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5646.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker J., Cuthbert C., Hammond V., Alberti K. G. Impaired insulin binding to isolated adipocytes in experimental diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetologia. 1981 Dec;21(6):563–568. doi: 10.1007/BF00281550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]