Abstract
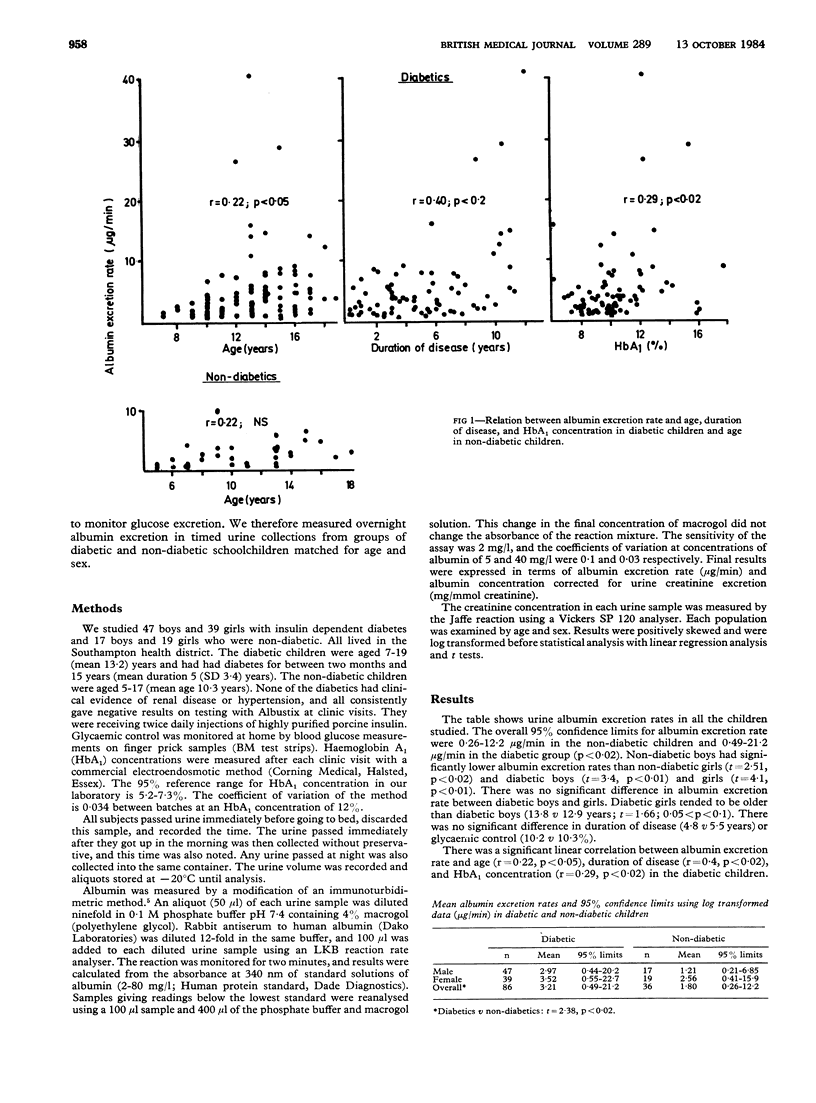
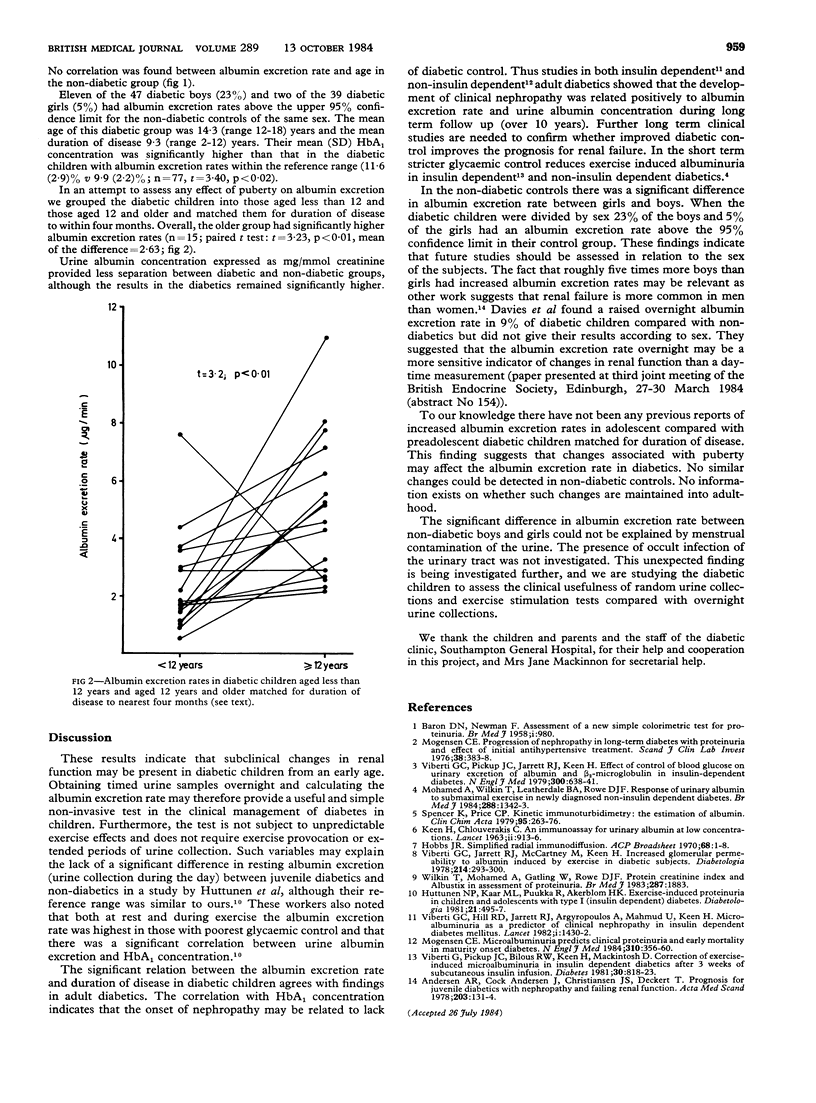
Urine albumin excretion rates were measured in overnight timed samples from diabetic and non-diabetic schoolchildren. The excretion rates in the diabetics were significantly higher than those in the controls and were positively correlated with age, duration of diabetes, and glycaemic control. Diabetic children aged 12 years and older had significantly higher albumin excretion rates than younger diabetic children matched for duration of disease. Among the non-diabetic controls there was no correlation between albumin excretion rate and age and the girls excreted significantly more albumin than the boys. Measurement of the overnight albumin excretion rate may provide a useful early indicator of the progression to clinical proteinuria in diabetes and is free from random variations such as that due to exercise.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen A. R., Andersen J. K., Christiansen J. S., Deckert T. Prognosis for juvenile diabetics with nephropathy and failing renal function. Acta Med Scand. 1978;203(1-2):131–134. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1978.tb14843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON D. N., NEWMAN F. Assessment of a new simple colorimetric test for proteinuria. Br Med J. 1958 Apr 26;1(5077):980–981. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5077.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen N. P., Kär M., Puukka R., Akerblom H. K. Exercise-induced proteinuria in children and adolescents with type 1 (insulin dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia. 1981 Nov;21(5):495–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00257792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEEN H., CHLOUVERAKIS C. AN IMMUNOASSAY METHOD FOR URINARY ALBUMIN AT LOW CONCENTRATIONS. Lancet. 1963 Nov 2;2(7314):913–914. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90620-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 9;310(6):356–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402093100605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Progression of nephropathy in long-term diabetics with proteinuria and effect of initial anti-hypertensive treatment. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976 Jul;36(4):383–388. doi: 10.1080/00365517609055274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed A., Wilkin T., Leatherdale B. A., Rowe D. Response of urinary albumin to submaximal exercise in newly diagnosed non-insulin dependent diabetes. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 May 5;288(6427):1342–1343. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6427.1342-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer K., Price C. P. Kinetic immunoturbidimetry: the estimation of albumin. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Jul 16;95(2):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90368-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Hill R. D., Jarrett R. J., Argyropoulos A., Mahmud U., Keen H. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1982 Jun 26;1(8287):1430–1432. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92450-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Jarrett R. J., McCartney M., Keen H. Increased glomerular permeability to albumin induced by exercise in diabetic subjects. Diabetologia. 1978 May;14(5):293–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01223019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Pickup J. C., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Effect of control of blood glucose on urinary excretion of albumin and beta2 microglobulin in insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 22;300(12):638–641. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903223001202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G., Pickup J. C., Bilous R. W., Keen H., Mackintosh D. Correction of exercise-induced microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetics after 3 weeks of subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):818–823. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin T., Mohamed A., Gatling W., Rowe D. Protein creatinine index and Albustix in assessment of proteinuria. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Dec 17;287(6408):1883–1883. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6408.1883-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


