Abstract
The greater solubility of human insulin and its possible faster action have led to doubts about whether a sufficiently long acting formulation could be produced to provide a basal supply for diabetics. In a double blind crossover study in 18 diabetics human ultralente insulin was as effective as beef ultralente insulin in controlling basal plasma glucose concentrations (median 5.7 mmol/l (103 mg/100 ml) with human and 6.3 mmol/l (114 mg/100 ml) with beef ultralente insulin respectively). There was no significant difference between human and bovine insulin in the rise in plasma glucose concentration from 0400 to 0700 after an injection the previous morning and no difference between patients receiving an adequate or insufficient dose of human ultralente insulin. Bovine insulin antibody binding was reduced with human insulin (p less than 0.002), which suggests that human insulin is less antigenic than beef insulin. Once daily human ultralente insulin provides a suitable formulation for the basal insulin requirement of diabetics.
Full text
PDF
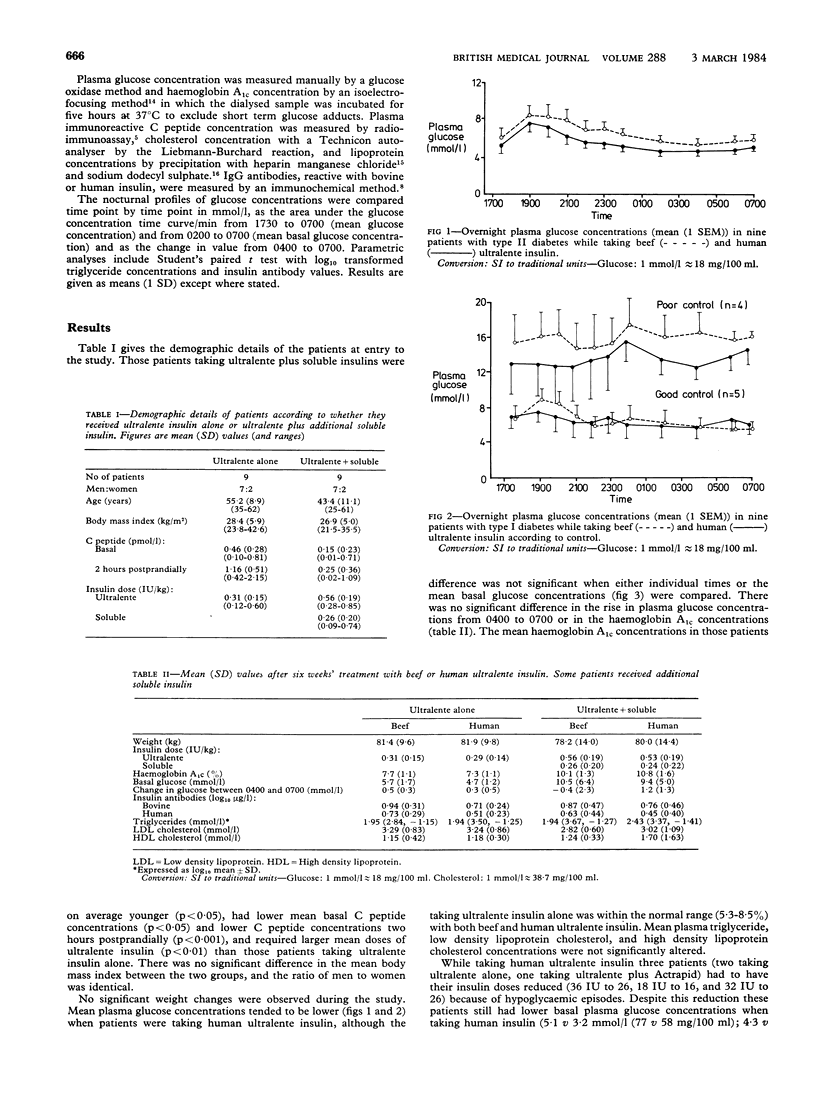
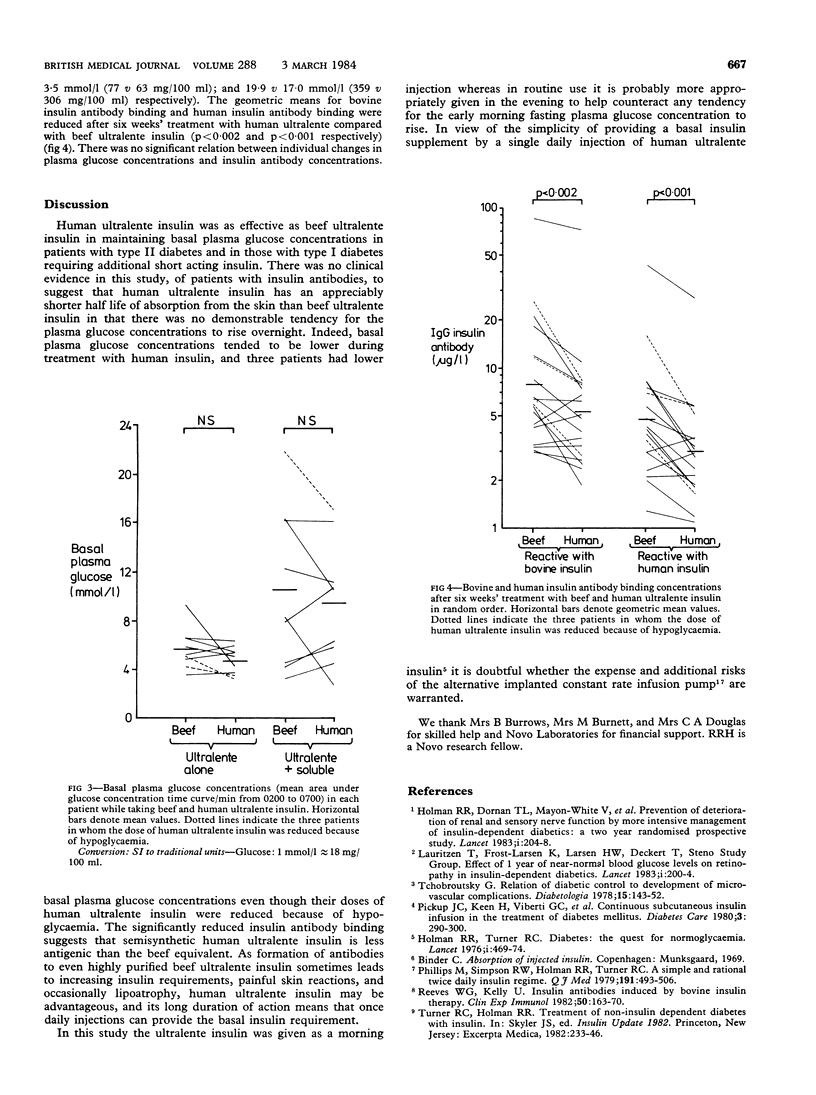

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burstein M., Scholnick H. R., Morfin R. Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):583–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Adeniyi-Jones R. O., Knight G., Leiper J. M., Wiles P. G., Jones R. H., Keen H., MacCuish A. C., Ward J. D., Watkins P. J. Biosynthetic human insulin in the treatment of diabetes. A double-blind crossover trial in established diabetic patients. Lancet. 1982 Aug 14;2(8294):354–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90548-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman R. R., Dornan T. L., Mayon-White V., Howard-Williams J., Orde-Peckar C., Jenkins L., Steemson J., Rolfe R., Smith B., Barbour D. Prevention of deterioration of renal and sensory-nerve function by more intensive management of insulin-dependent diabetic patients. A two-year randomised prospective study. Lancet. 1983 Jan 29;1(8318):204–208. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92586-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman R. R., Turner R. C. The basal plasma glucose: a simple relevant index of maturity-onset diabetes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1981 Mar;14(3):279–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1981.tb00196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritzen T., Frost-Larsen K., Larsen H. W., Deckert T. Effect of 1 year of near-normal blood glucose levels on retinopathy in insulin-dependent diabetics. Lancet. 1983 Jan 29;1(8318):200–204. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92585-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onongbu I. C., Lewis B. Lipoprotein fractionation by a precipitation method. A simple quantitative procedure. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Sep 20;71(3):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M., Simpson R. W., Holman R. R., Turner R. C. A simple and rational twice daily insulin regime. Distinction between basal and meal insulin requirements. Q J Med. 1979 Jul;48(191):493–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup J. C., Keen H., Viberti G. C., White M. C., Kohner E. M., Parsons J. A., Alberti K. G. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1980 Mar-Apr;3(2):290–300. doi: 10.2337/diacare.3.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. G., Kelly U. Insulin antibodies induced by bovine insulin therapy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):163–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. M., Barbosa J. J., Blackshear P. J., McCarthy H. B., Rohde T. D., Goldenberg F. J., Rublein T. G., Dorman F. D., Buchwald H. The use of an implantable insulin pump in the treatment of type II diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 29;307(5):265–270. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207293070501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchobroutsky G. Relation of diabetic control to development of microvascular complications. Diabetologia. 1978 Sep;15(3):143–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00421230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tietze C. Abortion deaths and social class. Lancet. 1976 Aug 28;2(7983):469–469. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92555-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]