Abstract
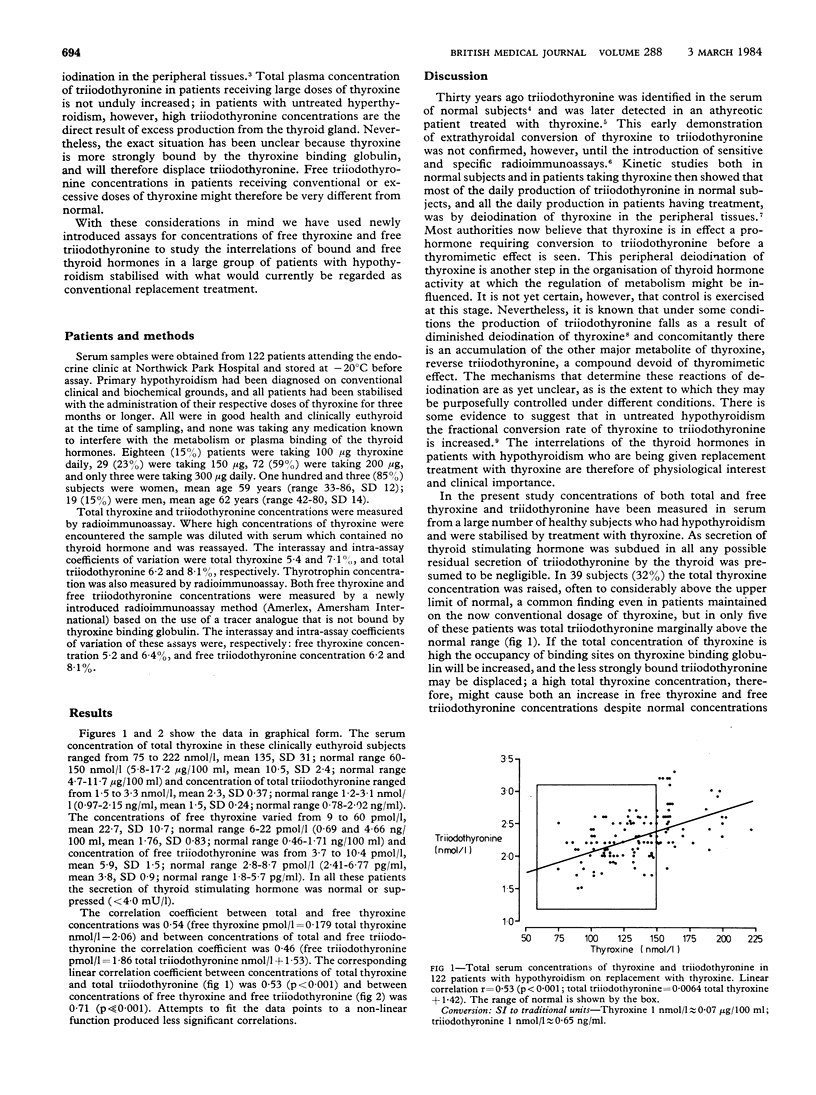
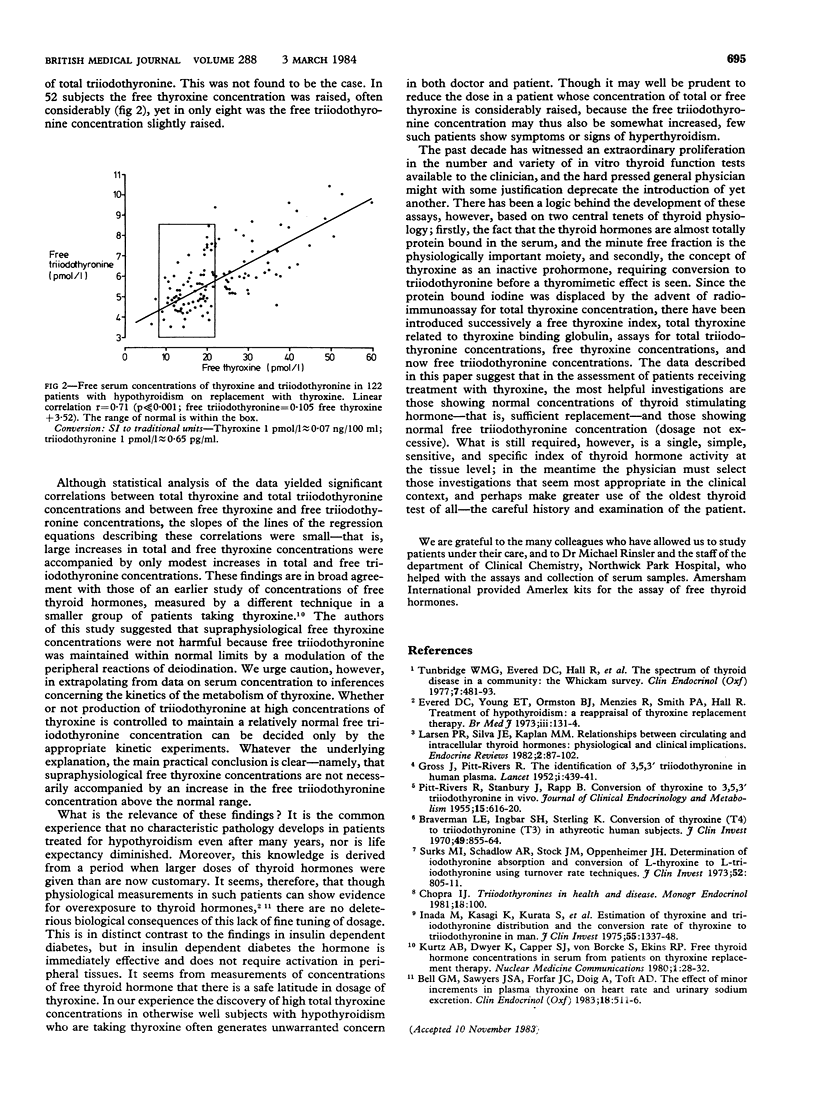
Total and free serum concentrations of thyroxine and triiodothyronine were measured in 122 subjects with hypothyroidism who were clinically well while receiving conventional replacement treatment with thyroxine. In a third of patients concentrations of total and free thyroxine were raised, often considerably; nevertheless concentrations of total and free triiodothyronine were usually normal. Though significant correlations were obtained between total triiodothyronine concentrations and total thyroxine concentrations (p less than 0.001) and between the triiodothyronine concentrations and free thyroxine concentrations (p less than 0.001) the slope of the line of the regression equation describing these correlations was small, hence large increases in both total and free thyroxine concentrations were accompanied by only modest increases in total and free triiodothyronine concentrations. The presence of total or free thyroxine concentrations above normal in patients taking thyroxine therefore are not necessarily of clinical consequence. In the assessment of adequacy of replacement treatment with thyroxine the most logical combination of in vitro thyroid function test results may be a normal thyrotrophin concentration and normal free triiodothyronine concentration.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. M., Sawers J. S., Forfar J. C., Doig A., Toft A. D. The effect of minor increments in plasma thyroxine on heart rate and urinary sodium excretion. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1983 May;18(5):511–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1983.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) in athyreotic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):855–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI106304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evered D., Young E. T., Ormston B. J., Menzies R., Smith P. A., Hall R. Treatment of hypothyroidism: a reappraisal of thyroxine therapy. Br Med J. 1973 Jul 21;3(5872):131–134. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5872.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., PITT-RIVERS R. The identification of 3:5:3'-L-triiodothyronine in human plasma. Lancet. 1952 Mar 1;1(6705):439–441. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)91952-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada M., Kasagi K., Kurata S., Kazama Y., Takayama H., Torizuka K., Fukase M., Soma T. Estimation of thyroxine and triiodothyronine distribution and of the conversion rate of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1337–1348. doi: 10.1172/JCI108053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R., Silva J. E., Kaplan M. M. Relationships between circulating and intracellular thyroid hormones: physiological and clinical implications. Endocr Rev. 1981 Winter;2(1):87–102. doi: 10.1210/edrv-2-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITT-RIVERS R., STANBURY J. B., RAPP B. Conversion of thyroxine to 3-5-3'-triiodothyronine in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1955 May;15(5):616–620. doi: 10.1210/jcem-15-5-616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Schadlow A. R., Stock J. M., Oppenheimer J. H. Determination of iodothyronine absorption and conversion of L-thyroxine (T 4 ) to L-triiodothyronine (T 3 ) using turnover rate techniques. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):805–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI107244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunbridge W. M., Evered D. C., Hall R., Appleton D., Brewis M., Clark F., Evans J. G., Young E., Bird T., Smith P. A. The spectrum of thyroid disease in a community: the Whickham survey. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1977 Dec;7(6):481–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1977.tb01340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


