Abstract
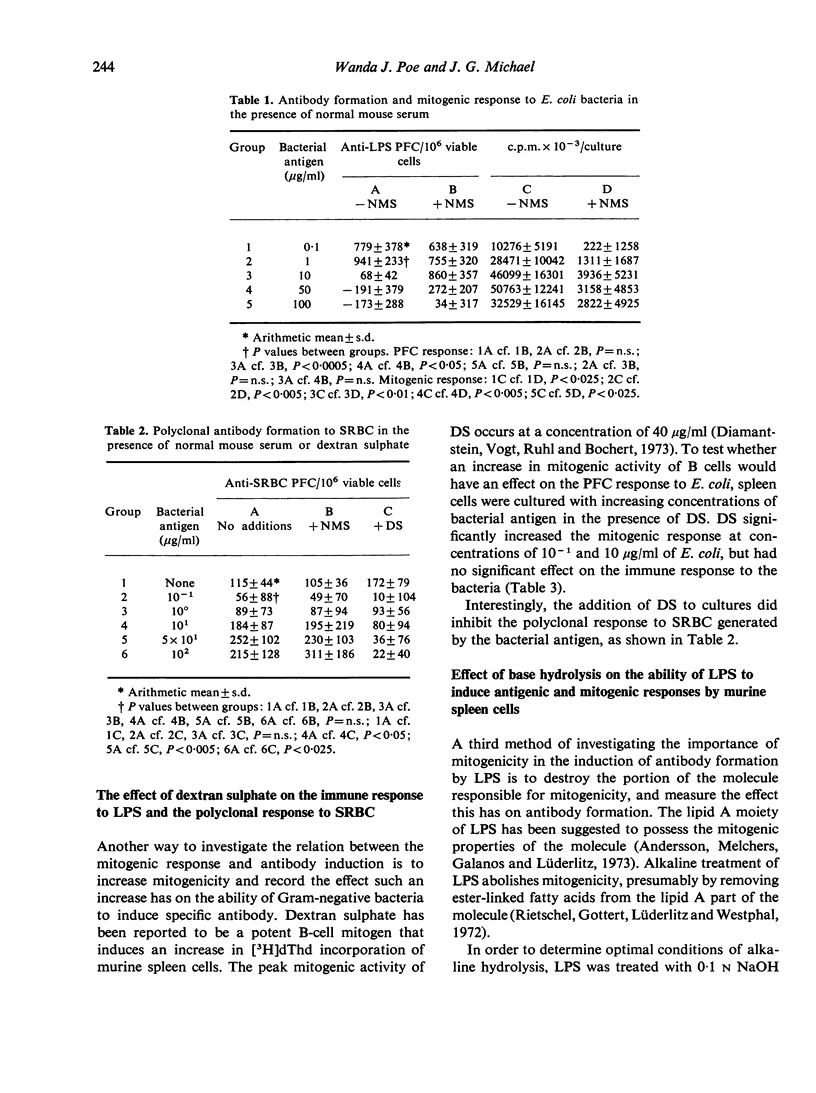
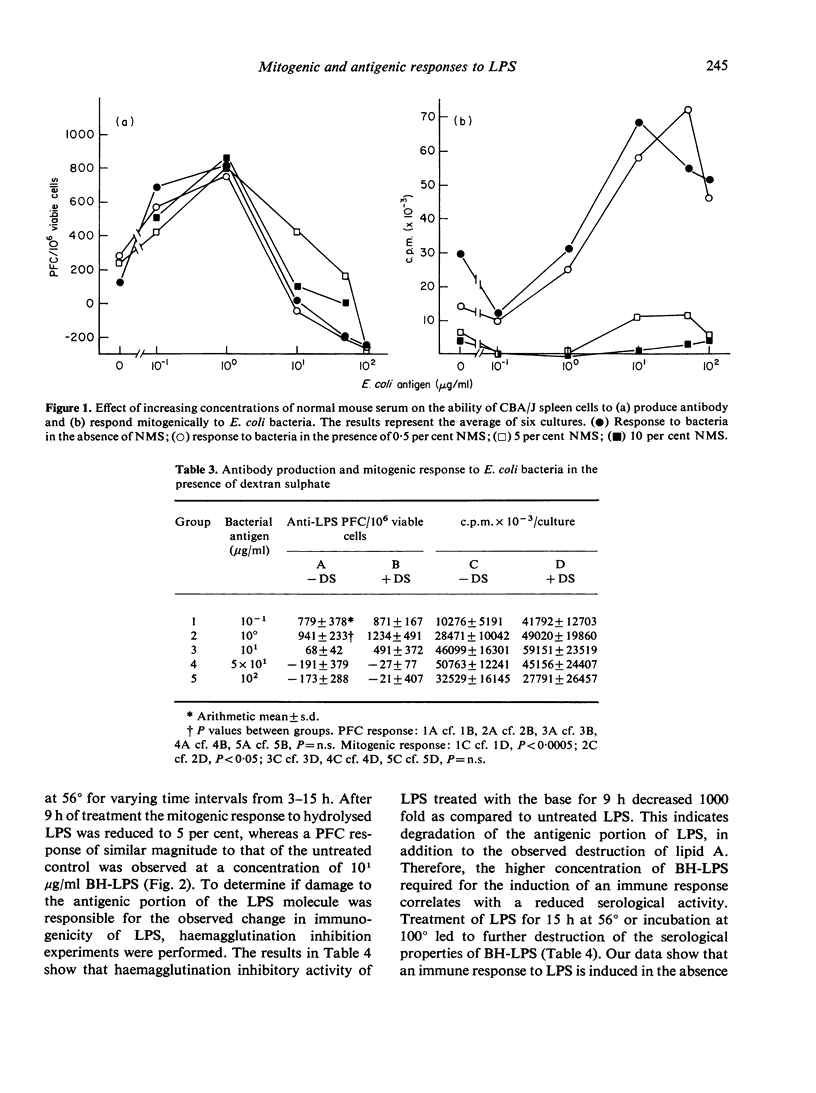
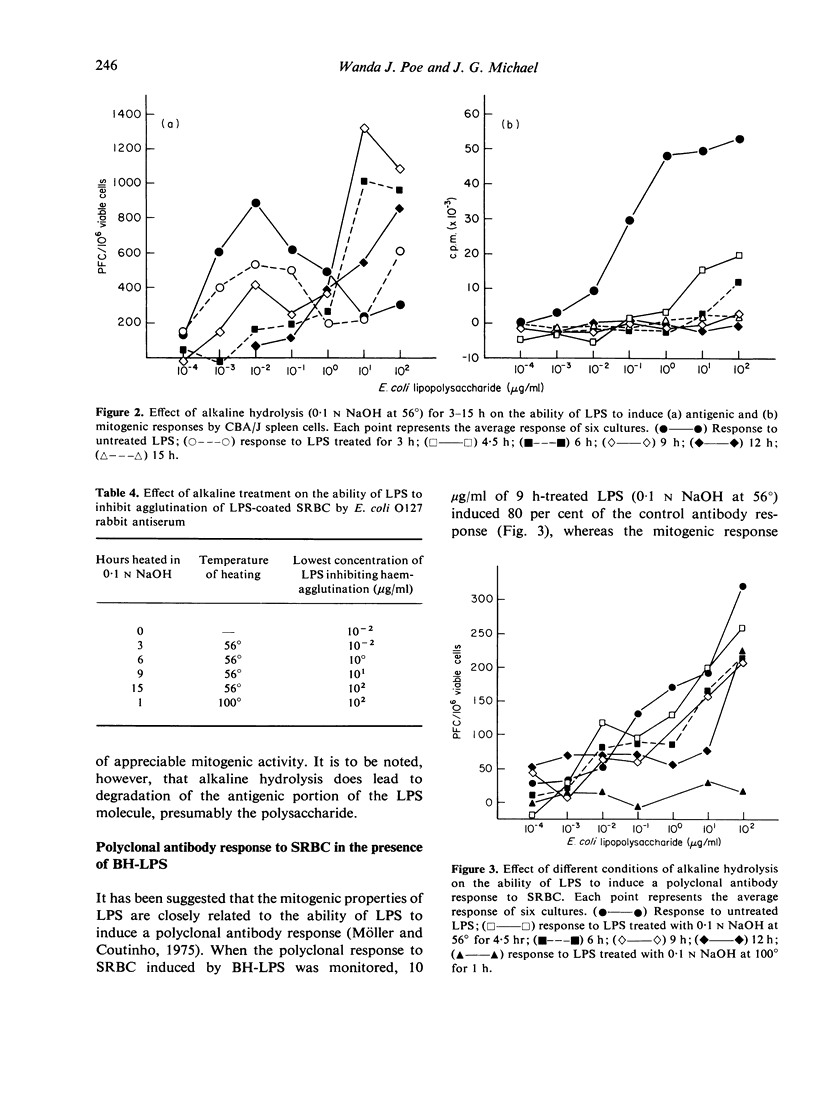
An attempt was made to separate the antigenic and mitogenic properties of E. coli bacteria and bacterial lipopolysaccharide antigen inhibited the mitogenic response by the cultures but did not inhibit the induction of anti-LPS antibody or polyclonal antibody synthesis to SRBC. Dextran sulphate, acting as a B-cell mitogen, increased the mitogenic response in spleen cell cultures incubated with bacteria, but did not affect the production of anti-LPS antibody. Mild alkaline hydrolysis (0-1 N NaOH at 56 degrees) of LPS destroyed the mitogenic properties of the molecule, leaving the antigenic properties qualitatively intact. Harsher conditions of base hydrolysis destroyed both the mitogenic and antigenic properties of LPS, as determined by antigenicity in murine spleen cell cultures and haemagglutination inhibition tests.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Melchers F., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. The mitogenic effect of lipopolysaccharide on bone marrow-derived mouse lymphocytes. Lipid A as the mitogenic part of the molecule. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):943–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Melchers F. Maturation of mitogen-activated bone marrow-derived lymphocytes in the absence of proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Aug;4(8):533–539. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Sjöberg O., Möller G. Induction of immunoglobulin and antibody synthesis in vitro by lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Aug;2(4):349–353. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Gronowicz E., Bullock W. W., Möller G. Mechanism of thymus-independent immunocyte triggering. Mitogenic activation of B cells results in specific immune responses. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):74–92. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Guercio P., Leuchars E. The immune response in mice to the haptenic determinant DNP coupled to a thymus-independent carrier (levan). J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):951–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamantstein T., Vogt W., Rühl H., Bochert G. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in mouse lymphoid cells by polyanions in vitro. I. Target cells and possible mode of action. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Aug;3(8):488–493. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Easten A. The relationship between antigenic structure and the requirement for thymus-derived cells in the immune response. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):103–119. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Nossal G. J. Tolerance, enhancement and the regulation of interactions between T cells, B cells and macrophages. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:3–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. THE NATURAL-SELECTION THEORY OF ANTIBODY FORMATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Nov 15;41(11):849–857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.11.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of normal mouse spleen cell suspensions in vitro. Science. 1966 Aug 26;153(3739):1004–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3739.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Coutinho A. Role of C'3 and Fc receptors in B-lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):647–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Michael G. Frequency of antigen-sensitive cells to thymus-independent antigens. Cell Immunol. 1971 Aug;2(4):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poe W. J., Michael J. B. Effect of allogeneic cell interaction and graft-versus-host reaction on the antibody response to Escherichia coli 0127 antigen. Cell Immunol. 1975 Feb;15(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poe W. J., Michael J. G. The lack of cellular cooperation in the immune response to E. coli 0127. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):1033–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Gottert H., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Nature and linkages of the fatty acids present in the lipid-A component of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):166–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela M., Mozes E., Shearer G. M. Thymus-independence of slowly metabolized immunogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veit B. C., Michael J. G. Immune response suppression by an inhibitor in normal and immune mouse serum. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 23;235(60):238–240. doi: 10.1038/newbio235238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veit B. C., Michael J. G. The lack of thymic influence in regulating the immune response to Escherichia coli 0127 endotoxin. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):547–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Trenkner E., Cohn M. The use of bacterial lipopolysaccharides to show that two signals are required for the induction of antibody synthesis. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):699–714. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


