Abstract
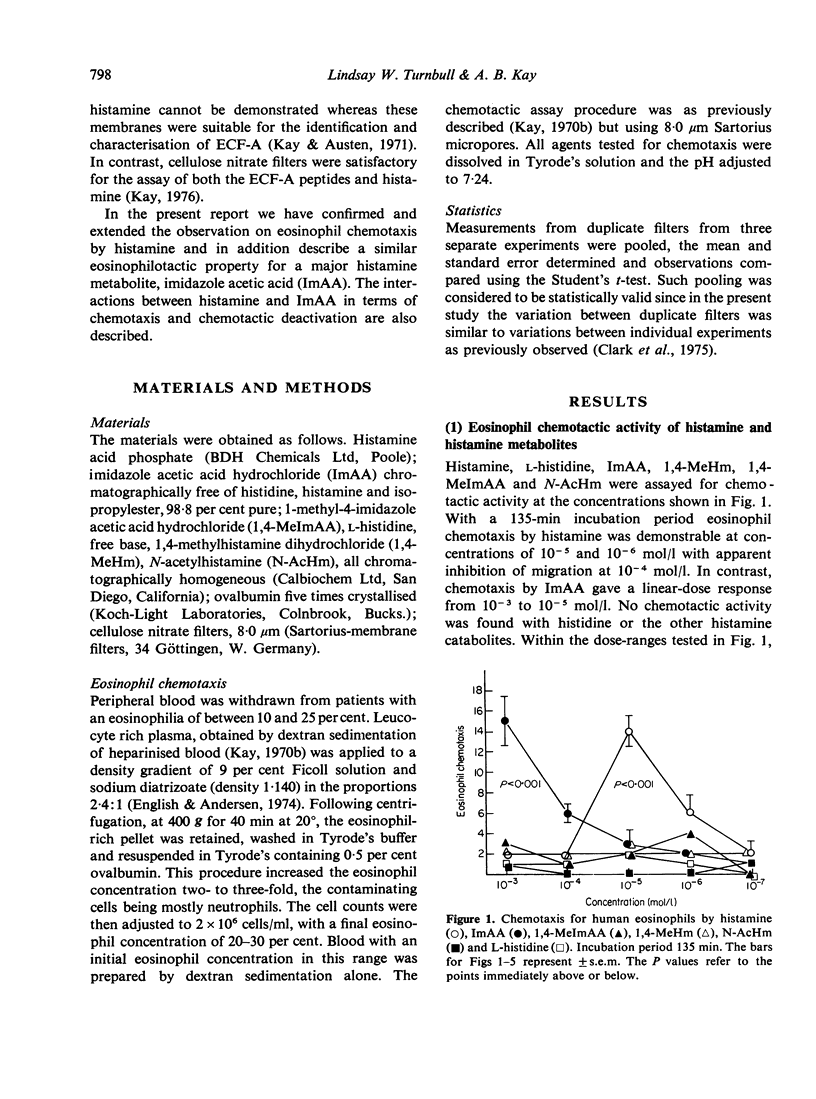
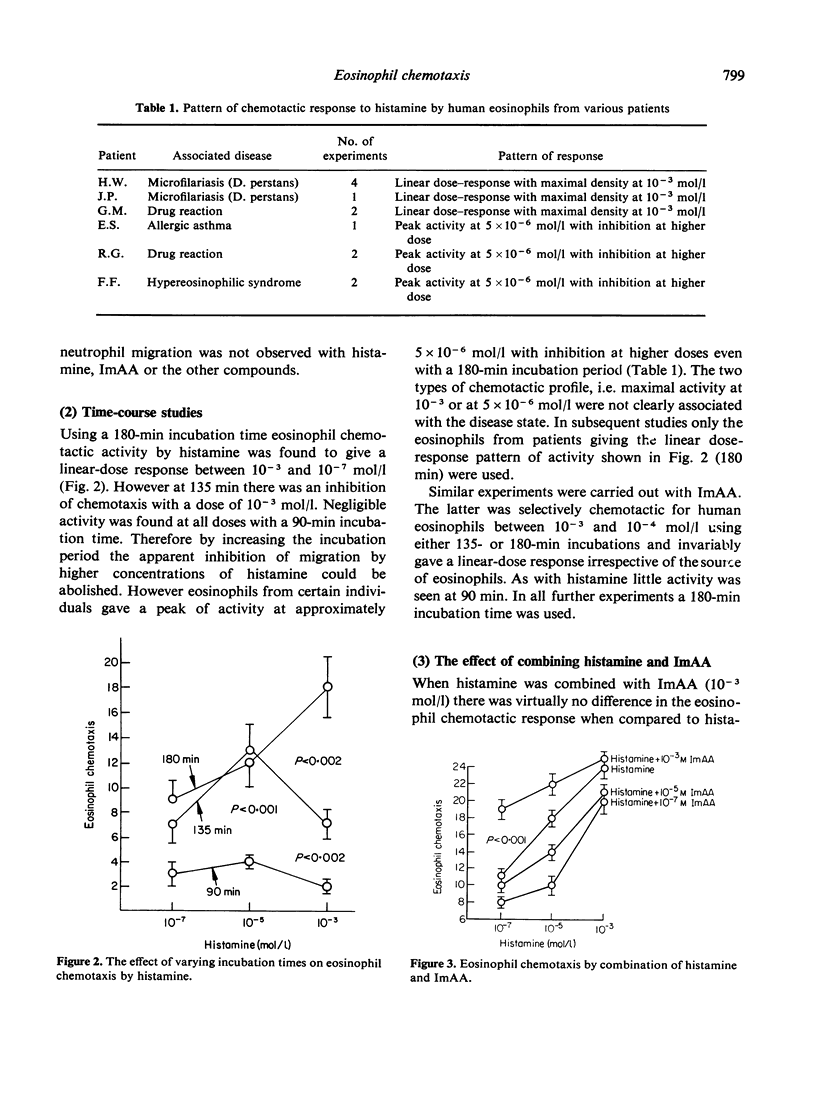
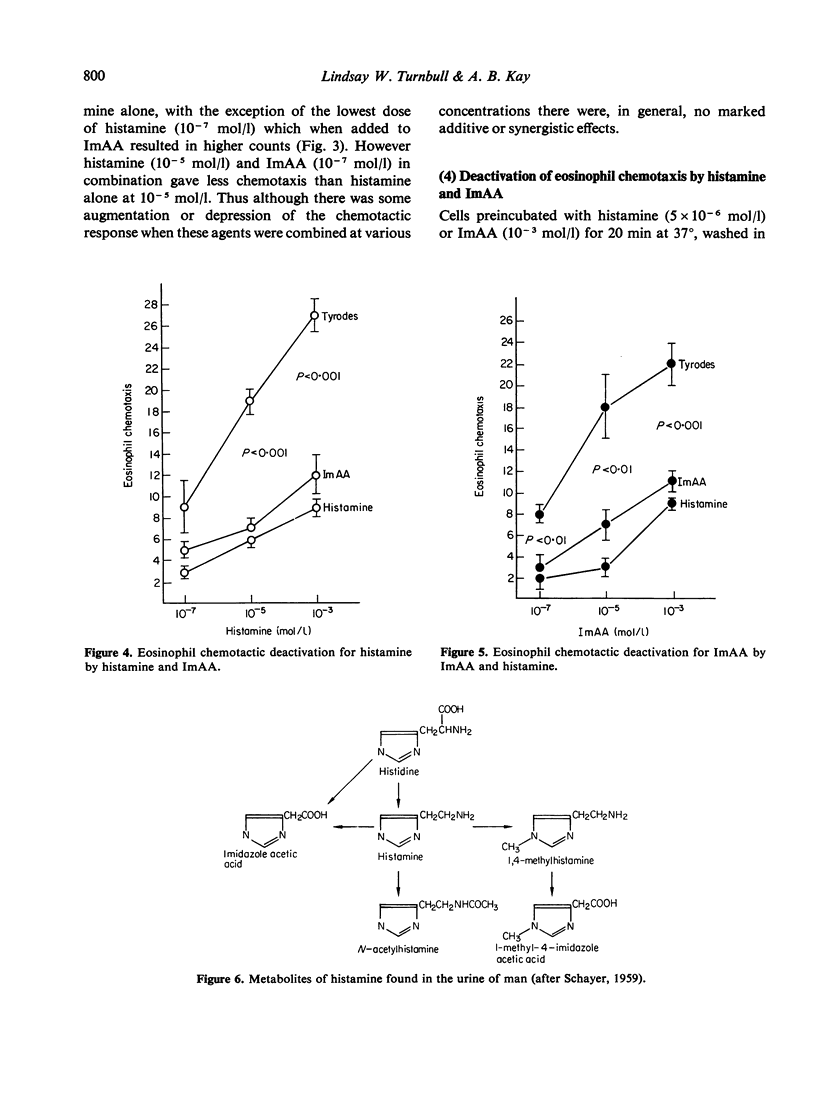
Histamine and one of its major catabolites, imidazole acetic acid (ImAA), were selectively chemotactic for human eosinophils, whereas L-histidine and other histamine catabolites including 1,4-methylhistamine, 1-methyl-4-imidazole acetic acid and N-acetylhistamine were inactive in eosinophilotaxis over a large dose range. The dose response for histamine was dependent on the chemotaxis incubation time and the source of eosinophils, although the latter was not clearly associated with particular disease states. When histamine and ImAA were combined the chemotactic response was similar to that obtained when one agent was assayed alone, no additive or synergistic effects being observed. There was cross-deactivation between histamine and ImAA. These experiments suggest that histamine and ImAA activate the same chemotactic recognition mechanism for eosinophils. Thus ImAA joins histamine and the tetrapeptides (ECF-A) as anaphylaxis-associated selective chemoattractants for human eosinophils
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHER R. K. The eosinophilic response in the horse to intramedullary and intradermal injections of histamine, ACTH, and cortisone. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):87–94. doi: 10.1002/path.1700720112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Gallin J. I., Kaplan A. P. The selective eosinophil chemotactic activity of histamine. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1462–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Andersen B. R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hösli L., Haas H. L. Effects of histamine, histidine and imidazole acetic acid on neurones of the medulla oblongata of the cat. Experientia. 1971;27(11):1311–1312. doi: 10.1007/BF02136707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Austen K. F. The IgE-mediated release of an eosinophil leukocyte chemotactic factor from human lung. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):899–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F. An eosinophil leukocyte chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):602–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B. Studies on eosinophil leucocyte migration. I. Eosinophil and neutrophil accumulation following antigen-antibody reactions in guinea-pig skin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jan;6(1):75–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B. Studies on eosinophil leucocyte migration. II. Factors specifically chemotactic for eosinophils and neutrophils generated from guinea-pig serum by antigen-antibody complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Nov;7(5):723–737. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON K., LINDELL S. E., SCHAYER R. W., WESTLING H. Metabolism of 14C-labelled histamine in pregnant and non-pregnant women. Clin Sci. 1959 May;18:313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAYER R. W. Catabolism of physiological quantities of histamine in vivo. Physiol Rev. 1959 Jan;39(1):116–126. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


