Abstract
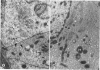
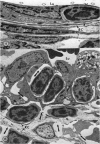
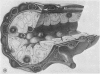
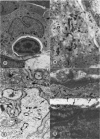
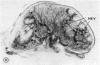
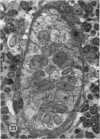
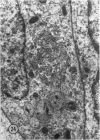
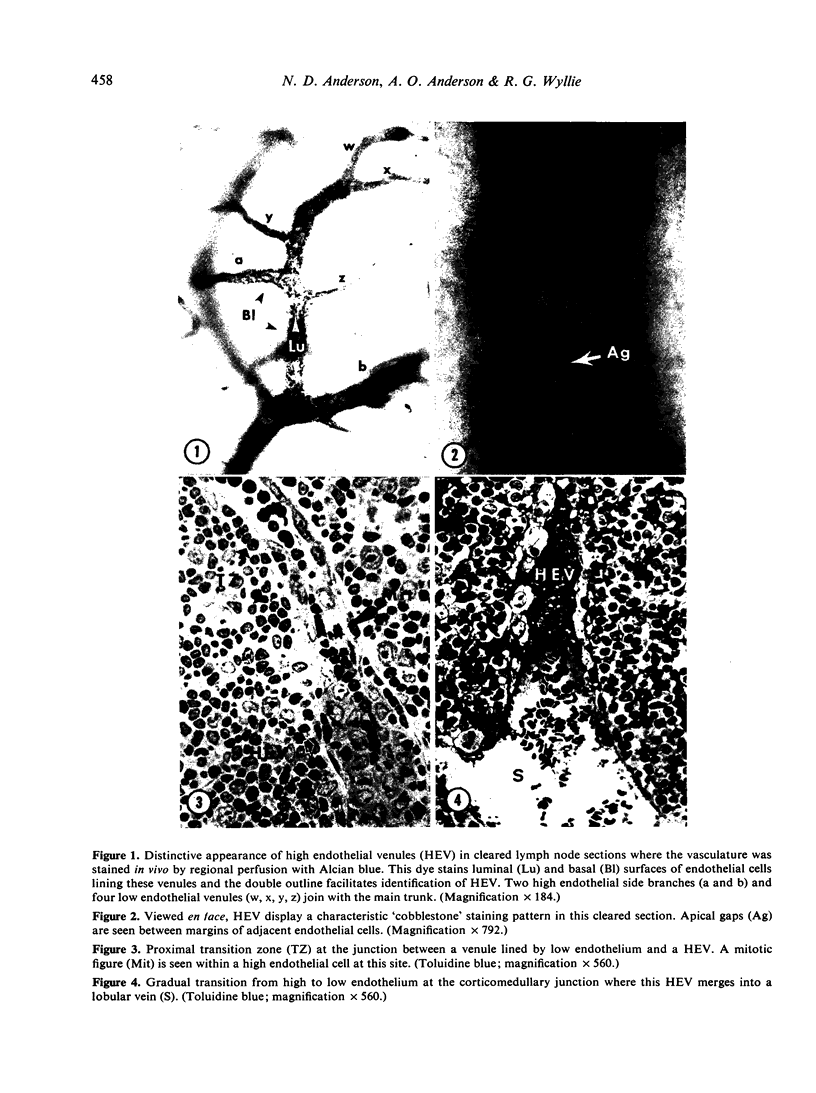
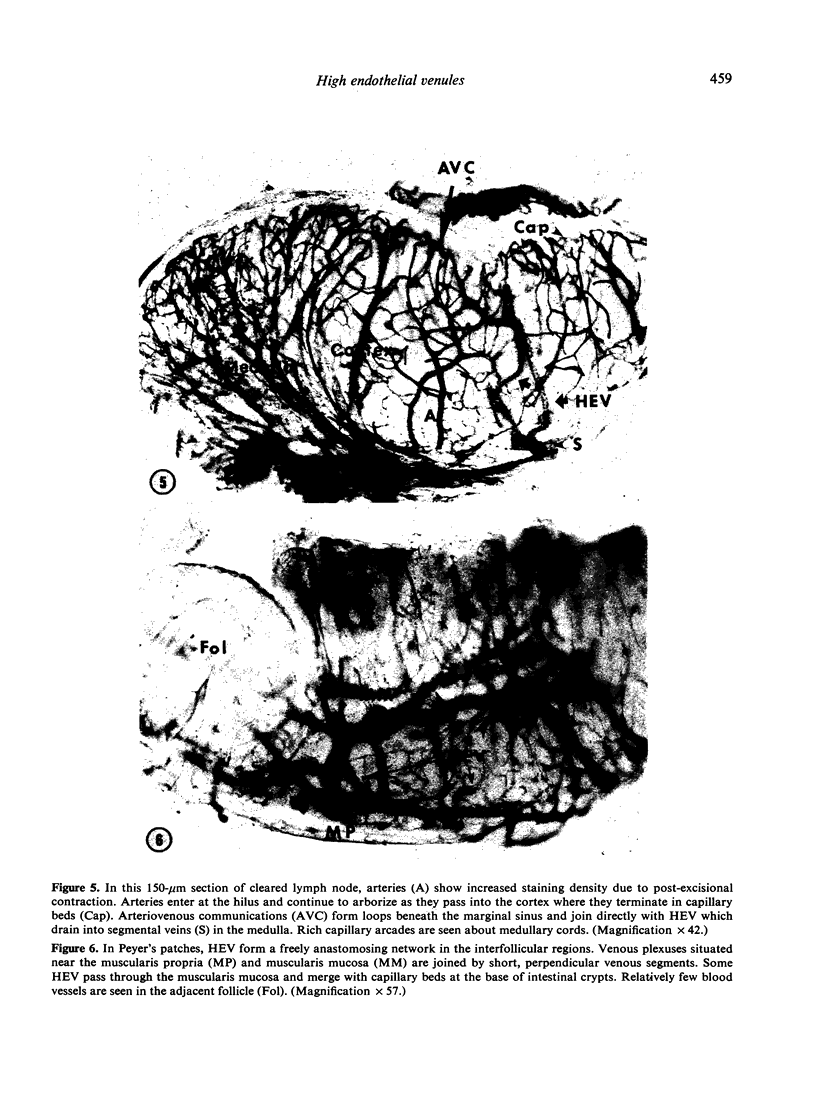
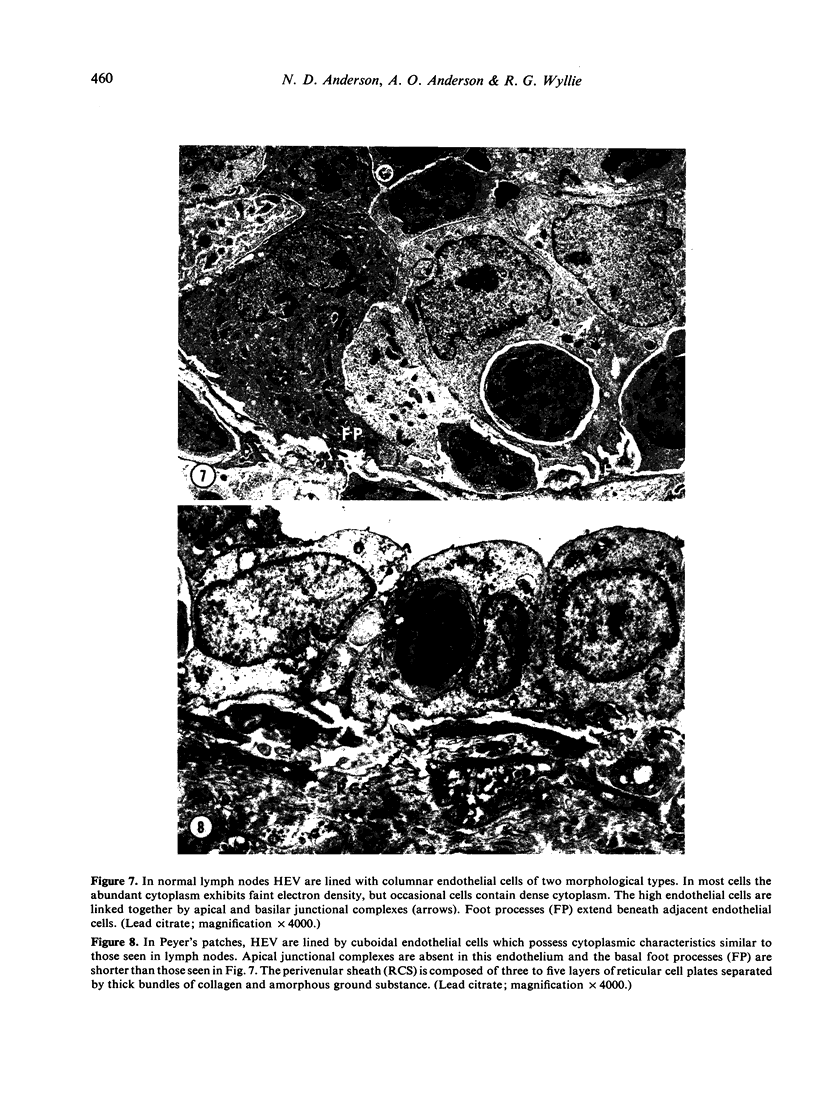
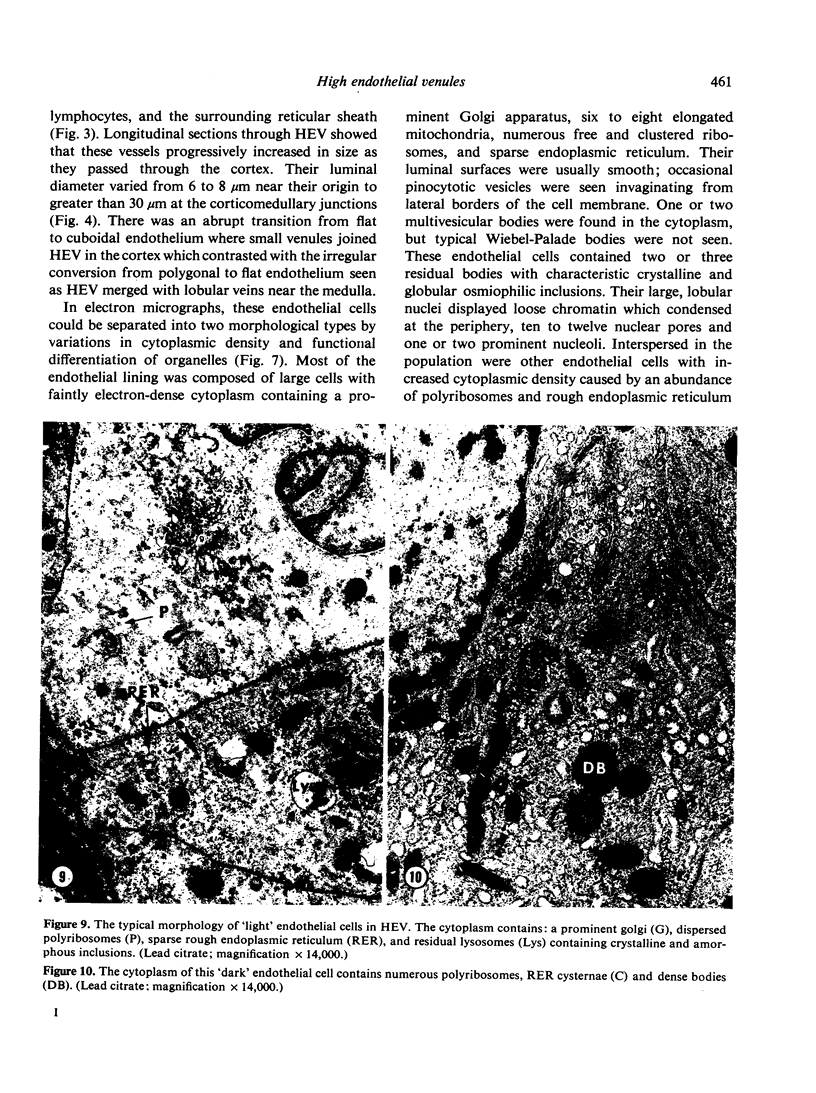
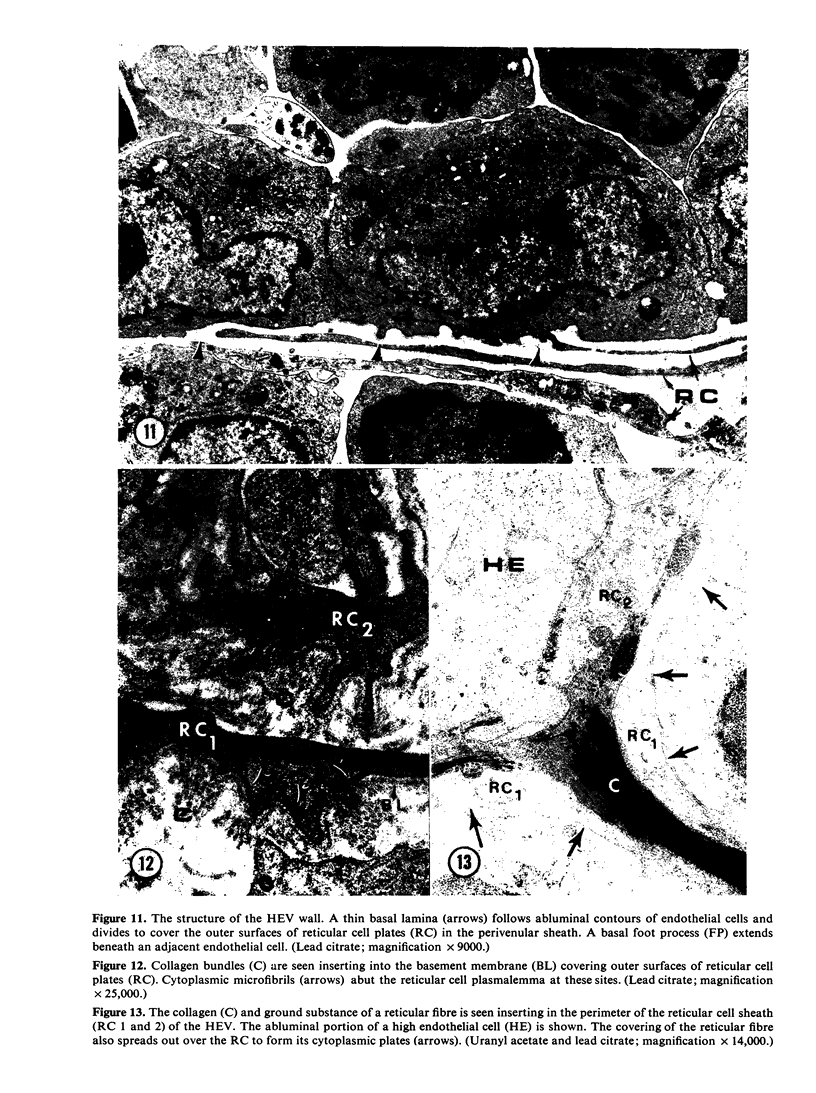
Microscopic, histochemical and ultrastructural techniques were used to define characteristics of high endothelial venules (HEV) in rat lymphatic tissues. This endothelium contained acetyl esterase and acid hydrolase activities which were not altered by lymphocyte depletion. No immunoglobulins were detected on luminal surfaces of HEV by fluorescent antibody staining. Only minor structural differences were seen between HEV within lymph nodes and Peyer's patches. At both sites, high endothelial cells were linked together by macular junctional complexes and interlocking basal foot processes. Endothelial cell cytoplasm moulded about surfaces of lymphocytes migrating through the venular wall, and flocculant deposits of basement membrane formed over lymphocytes penetrating the basal lamina. The endothelium was ensheathed by three to five layers of overlapping reticular cell plates and connective tissue. Each plate was linked to the reticular meshwork of the node by collagen bundles and anchoring filaments which inserted into the plate's external limiting membrane. This permitted individual paltes to separate or approximate each other as tissue and intravascular pressure varied, and lymphocytes moved across the sheath by insinuating themselves into gaps between overlapping plates. This composite structure of the HEV wall appeared to facilitate lymphocyte entry into the node and minimized vascular leakge.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. O., Anderson N. D. Studies on the structure and permeability of the microvasculature in normal rat lymph nodes. Am J Pathol. 1975 Sep;80(3):387–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. D., Anderson A. O., Wyllie R. G. Microvascular changes in lymph nodes draining skin allografts. Am J Pathol. 1975 Oct;81(1):131–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anton E., Brandes D., Barnard S. Lysosomes in uterine involution: distribution of acid hydrolases in luminal epithelium. Anat Rec. 1969 Jun;164(2):231–251. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091640209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKA T. A simple azo-dye method for histochemical demonstration of acid phosphatase. Nature. 1960 Jul 16;187:248–249. doi: 10.1038/187248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURWELL R. G. Studies of the primary and the secondary immune responses of lymph nodes draining homografts of fresh cancellous bone (with particular reference to mechanisms of lymph node reactivity). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Oct 24;99:821–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb45365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G., Nachman R. L. Contractile proteins of endothelial cells, platelets and smooth muscle. Am J Pathol. 1973 Apr;71(1):1–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK S. L., Jr The reticulum of lymph nodes in mice studied with the electron microscope. Am J Anat. 1962 May;110:217–257. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001100303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson M. H., Jorgensen O., Ropke C. Light and electron microscopic studies of the paracortical post-capillary high-endothelial venules. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;119(2):195–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00324521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., De Bruyn P. P. The mode of lymphocyte migration through postcapillary venule endothelium in lymph node. Am J Anat. 1975 May;143(1):59–92. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001430104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda J. Studies on the vascular architecture and the fluid exchange in the rabbit popliteal lymph node. Keio J Med. 1968 Mar;17(1):53–70. doi: 10.2302/kjm.17.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMORI G. Aldehyde-fuchsin: a new stain for elastic tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 1950 Jul;20(7):665–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS J. L., KNIGHT E. J. THE ROUTE OF RE-CIRCULATION OF LYMPHOCYTES IN THE RAT. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Jan 14;159:257–282. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS J. L. The recirculation of lymphocytes from blood to lymph in the rat. J Physiol. 1959 Apr 23;146(1):54–69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., McGregor D. D. Migration of lymphocytes and thymocytes in the rat. I. The route of migration from blood to spleen and lymph nodes. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):155–168. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Shannon S. L. Peroxidase arthritis. II. Lymphoid cell-endothelial interactions during a developing immunologic inflammatory response. Am J Pathol. 1972 Oct;69(1):7–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHI M., NAKAJIMA Y., FISHMAN W. H. THE CYTOLOGIC DEMONSTRATION OF BETA-GLUCURONIDASE EMPLOYING NAPHTHOL AS-BI GLUCURONIDE AND HEXAZONIUM PARAROSANILIN; A PRELIMINARY REPORT. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Apr;12:293–297. doi: 10.1177/12.4.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS R., STAEUBLI W. THE DEVELOPMENT OF AORTIC LIPIDOSIS IN THE RAT. A CORRELATIVE HISTOCHEMICAL AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY. Am J Pathol. 1963 Sep;43:301–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen O., Claësson M. H. Studies on the post-capillary high endothelial venules of neonatally thymectomized mice. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;132(3):347–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T., GOWANS J. L. THE MIGRATION OF LYMPHOCYTES THROUGH THE ENDOTHELIUM OF VENULES IN LYMPH NODES: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Jan 14;159:283–290. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T. SOME ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS ON INTERACTIONS BETWEEN LEUKOCYTES, PLATELETS, AND ENDOTHELIAL CELLS IN ACUTE INFLAMMATION. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 27;116:774–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb52545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. J., 3rd Studies of the phylogeny and ontogeny of the specialized lymphatic tissue venules. Lab Invest. 1969 Dec;21(6):484–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. V., De Sousa M. A., East J. Thymus-dependent areas in the lymphoid organs of neonatally thymectomized mice. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):191–204. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röpke C., Jorgensen O., Claësson M. H. Histochemical studies of high-endothelial venules of lymph nodes and Peyer's patches in the mouse. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;131(3):287–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00582852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C., HENON B. K. Histological and histochemical study of high endothelium of post-capillary veins of the lymph node. Anat Rec. 1959 Nov;135:207–213. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091350306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoefl G. I. The migration of lymphocytes across the vascular endothelium in lymphoid tissue. A reexamination. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):568–588. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., McIntosh G. H., Morris B. The migration of cells through chronically inflamed tissues. J Pathol. 1970 Jan;100(1):21–29. doi: 10.1002/path.1711000104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordat B., Hess M. W., Cottier H. IgG immunoglobulin in the wall of post-capillary venules: possible relationship to lymphocyte recirculation. Immunology. 1971 Jan;20(1):115–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderström N. Post-capillary venules as basic structural units in the development of lymphoglandular tissue. Scand J Haematol. 1967 Dec;4(6):411–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1967.tb01644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent P. C., Gunz F. W. Control of lymphocyte level in the blood. Lancet. 1970 Aug 15;2(7668):342–344. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92876-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WACHSTEIN M., MEISEL E. Histochemistry of hepatic phosphatases of a physiologic pH; with special reference to the demonstration of bile canaliculi. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Jan;27(1):13–23. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/27.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. H. The homing pattern of thymus-derived lymphocytes in calf and neonatal mouse Peyer's patches. J Immunol. 1973 Sep;111(3):878–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenk E. J., Orlic D., Reith E. J., Rhodin J. A. The ultrastructure of mouse lymph node venules and the passage of lymphocytes across their walls. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 May;47(2):214–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Röpke C. The postanatal development of high-endothelial venules in lymph nodes of mice. Anat Rec. 1975 Mar;181(3):659–677. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091810308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]