Abstract
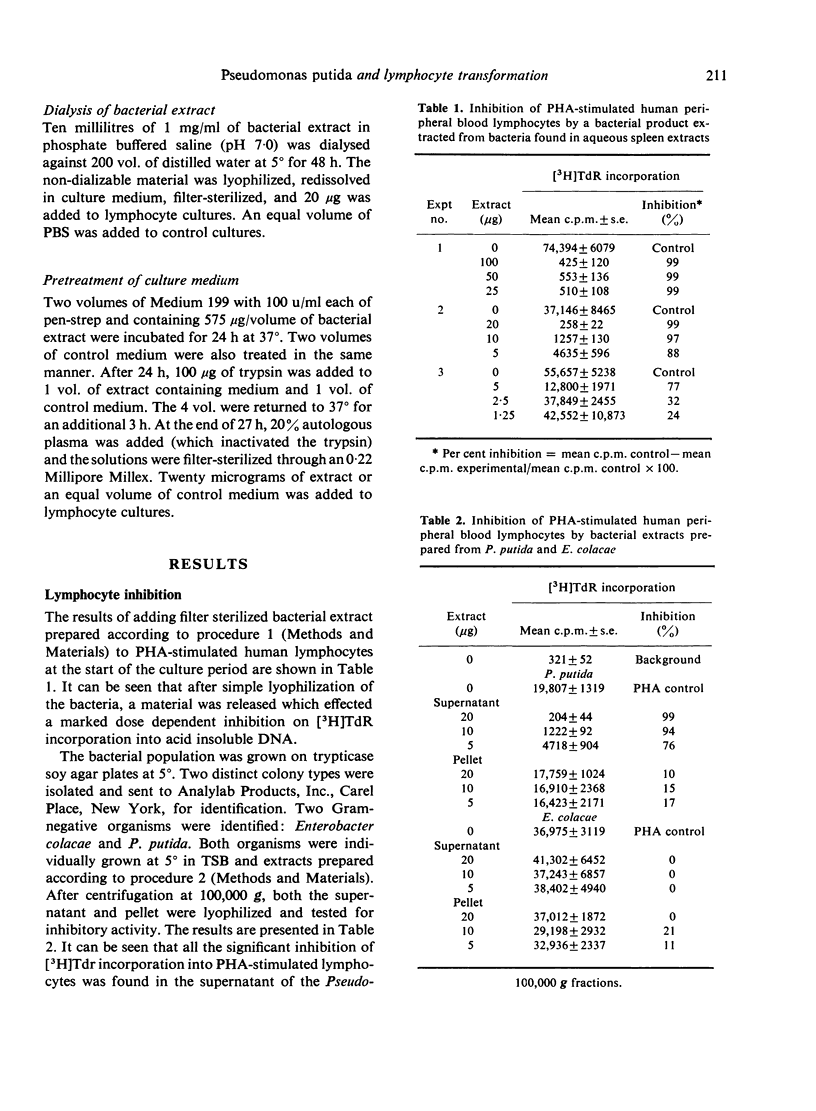
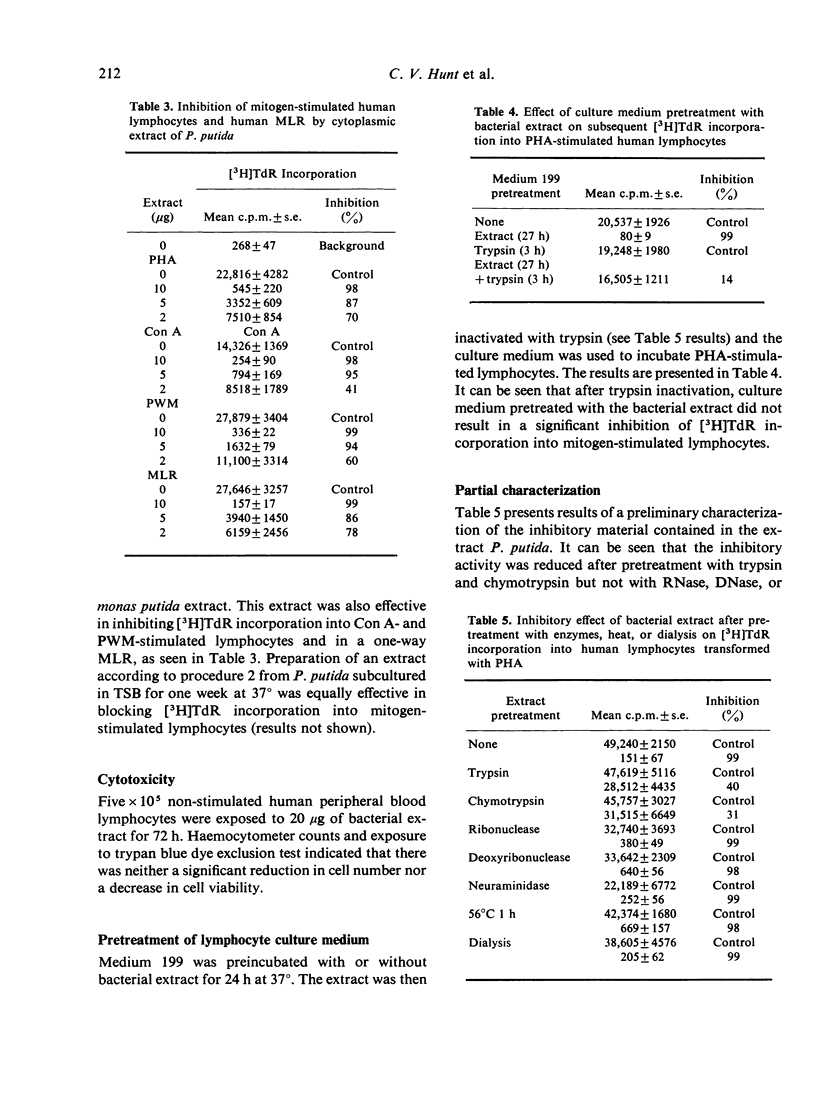
An extract prepared from a psychrophilic strain of Pseudomonas putida was found to cause a dose-dependent inhibition of [H3]TdR incorporation into human peripheral blood lymphocytes stimulated with PHA, ConA, PWM, or in a mixed lymphocyte reaction. The inhibition was found not to be the result of cytotoxicity, culture medium depletion of a component necessary for lymphocyte transformation, or interference with label uptake by blast lymphocytes. The extract was most effective when added prior to 48 h of mitogen stimulation. The inhibitory material was photeolytic enzyme degradable, heat-stable and non-dialyzable.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astaldi G., Burgio G. R., Krc J., Genova R., Astaldi A. A., Jr L-asparaginase and blastogenesis. Lancet. 1969 Feb 22;1(7591):423–423. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Northrup R. S., Chen L. C. The modulating effect of cholera enterotoxin on the immune response. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):729–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Northrup R. S. Pathophysiologic effects of lethal and immunoregulatory doses of cholera enterotoxin in the mouse. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):740–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. A., Finkelstein R. A. Inhibition of mitogen stimulation of human peripheral blood leukocytes by Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):476–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham J. L., Stokes J. L. PSYCHROPHILIC BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):97–108. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.97-108.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kateley J. R., Kasarov L., Friedman H. Modulation of in vivo antibody responses by cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpatovski I. D., Stanislavski E. S. Immunosuppressive effect of cell-free extracts from Escherichia coli. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):831–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malakian A. H., Kaloustian S. A potent antimitogenic factor from group A streptococci. Immunology. 1975 Jan;28(1):103–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malakian A., Schwab J. H. Immunosuppressant from group A streptococci. Science. 1968 Feb 23;159(3817):880–881. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3817.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seravalli E., Taranta A. Lymphocyte transformation and macrophage migration inhibition by electrofocused and gel-filtered fractions of group A streptococcal filtrate. Cell Immunol. 1974 Dec;14(3):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simberkoff M. S., Thorbecke G. J., Thomas L. Studies of PPLO infection. V. Inhibition of lymphocyte mitosis and antibody formation by mycoplasmal extracts. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1163–1181. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. H., Given K. S., Martin J. D., Jr Delayed rejection of skin homografts in Pseudomonas sepsis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967 May;124(5):1067–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sörén L. Variability of the time at which PHA-stimulated lymphocytes initiate DNA synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 30;78(1):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer T. L., LoSpalluto J. J. The differential effect of cholera toxin on the lymphocyte stimulation induced by various mitogens. Immunology. 1975 Aug;29(2):275–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang H. Y., Neter E. Immunosuppression by endotoxin and its lipoid A component. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Mar;124(3):919–924. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


