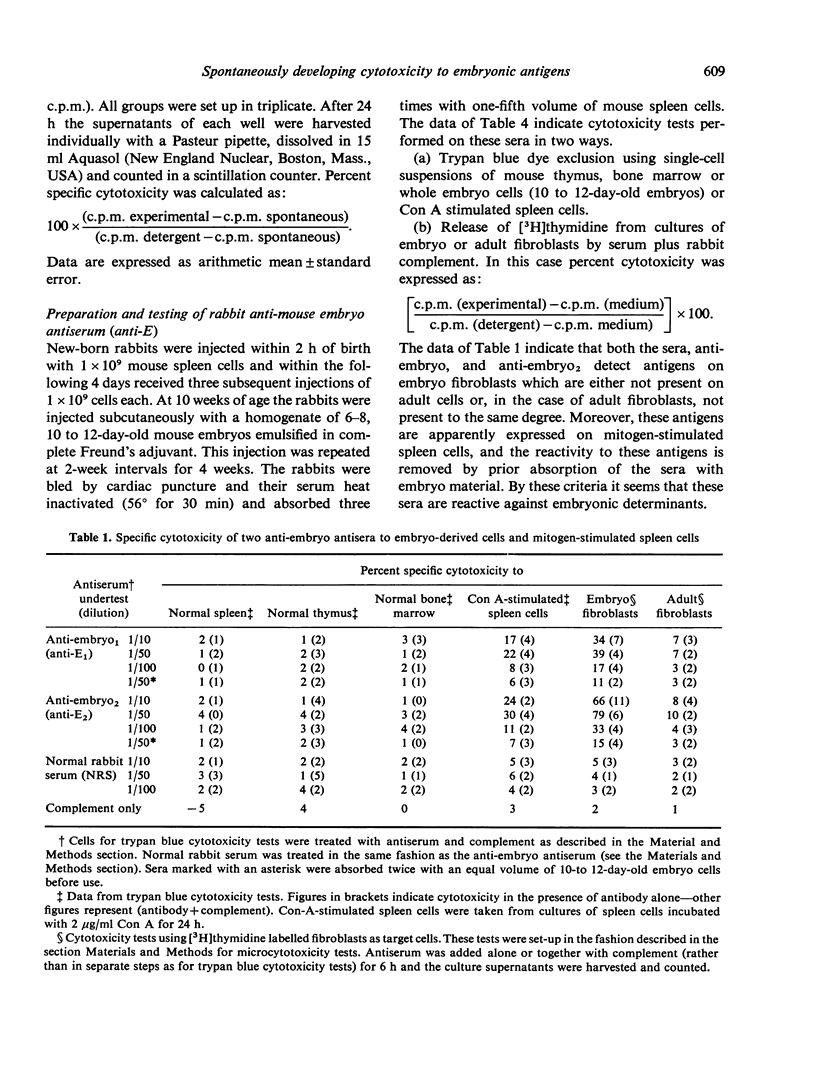
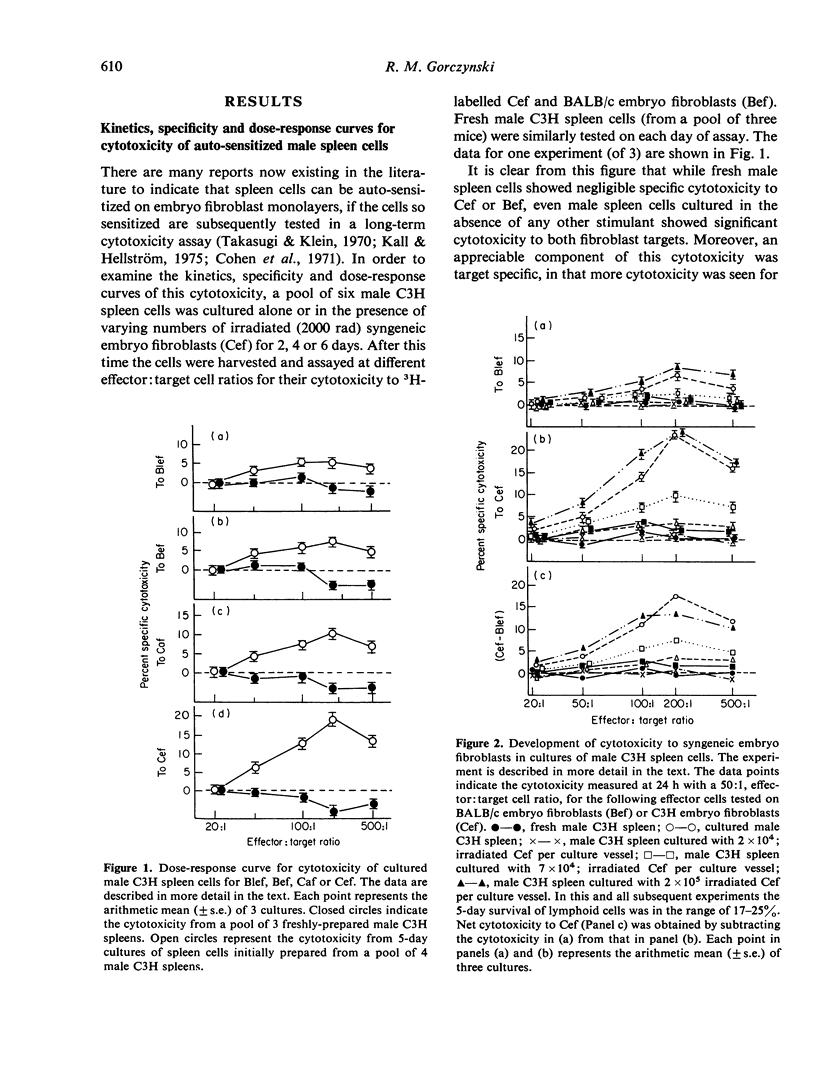
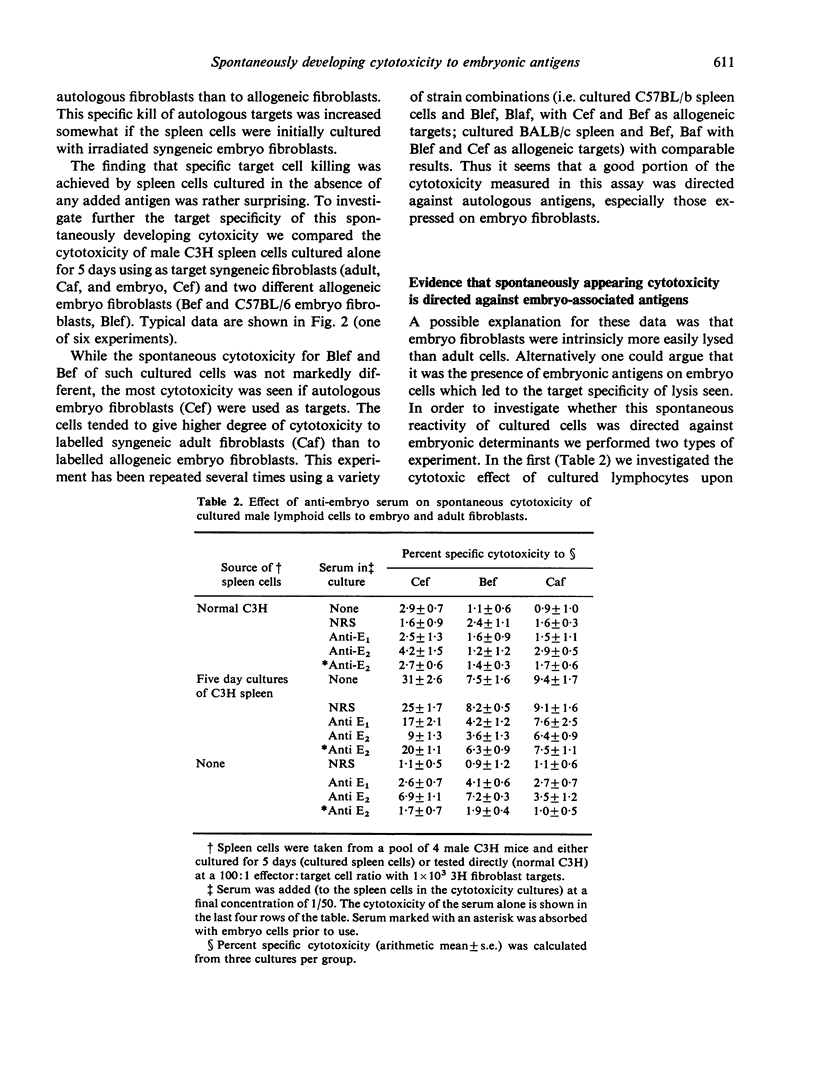
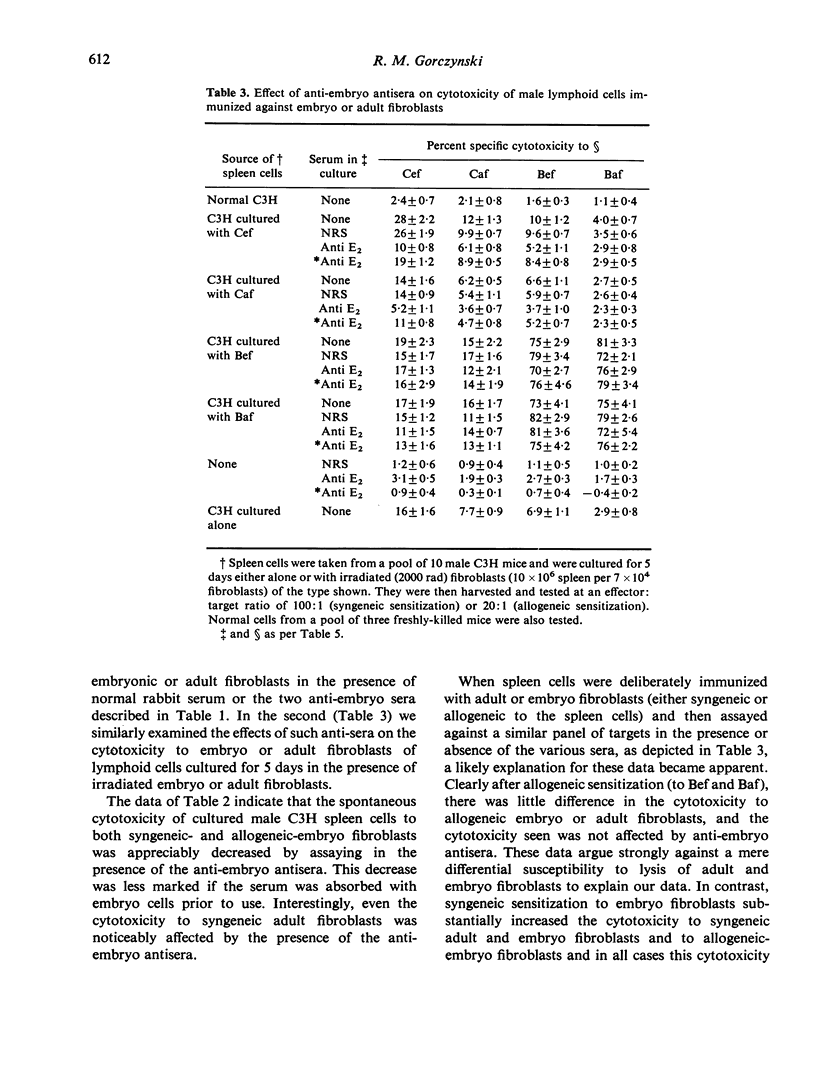
Abstract
We have investigated the ability of male-mouse spleen cells before and after culture in the absence of deliberate antigenic stimulation to show specific cytotoxicity to syngeneic embryo-fibroblast cells. The data suggest that cytotoxicity which develops spontaneously in such spleen cell cultures is directed primarily against embryo-associated antigens. Syngeneic Con-A-stimulated spleen cells, which, unlike fresh normal spleen cells, are also lysed by rabbit anti-mouse embryo antisera, are also a suitable target to demonstrate spontaneously developing cytotoxicity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin R. W., Embleton M. J., Price M. R., Vose B. M. Embryonic antigen expression on experimental rat tumours. Transplant Rev. 1974;20(0):77–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. An extension of the 51Cr-release assay for the estimation of mouse cytotoxins. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):761–764. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner K. T., Mauel J., Rudolf H., Chapuis B. Studies of allograft immunity in mice. I. Induction, development and in vitro assay of cellular immunity. Immunology. 1970 Apr;18(4):501–515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canty T. G., Wunderlich J. R., Fletcher F. Qualitative and quantitative studies of cytotoxic immune cells. J Immunol. 1971 Jan;106(1):200–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Globerson A., Feldman M. Rejection of tumor allografts by mouse spleen cells sensitized in vitro. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):821–833. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold P., Freedman S. O. Specific carcinoembryonic antigens of the human digestive system. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):467–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorczynski R. M., Knight R. A. Immunity to murine sarcoma virus induced tumours. IV. Direct cellular cytolysis of 51Cr labelled target cells in vitro and analysis of blocking factors which modulate cytotoxicity. Br J Cancer. 1975 Apr;31(4):387–404. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1975.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorczynski R. M., Miller R. G., Phillips R. A. Identification by density separation of antigen-specific surface receptors on the progenitors of antibody-producing cells. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):693–705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorczynski R. M., Tigelaar R. E. Cell-mediated immunity to Murine tumor allografts. Increase in the activities of activated thymus-derived cells following in vitro incubation. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jul;18(1):121–143. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinshead A., Glew D., Bunnag B., Gold P., Herberman R. Skin-reactive soluble antigen from intestinal cancer-cell-membranes and relationship to carcinoembryonic antigens. Lancet. 1970 Jun 6;1(7658):1191–1195. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91784-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kall M. A., Hellström I. Specific stimulatory and cytotoxic effects of lymphocytes sensitized in vitro to either alloantigens or tumor antigens. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1083–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Dunkley M. Quantitative analysis of the 51Cr release cytotoxicity assay for cytotoxic lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1974 Nov;14(2):284–302. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Klein E. A microassay for cell-mediated immunity. Transplantation. 1970 Mar;9(3):219–227. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197003000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


