Abstract
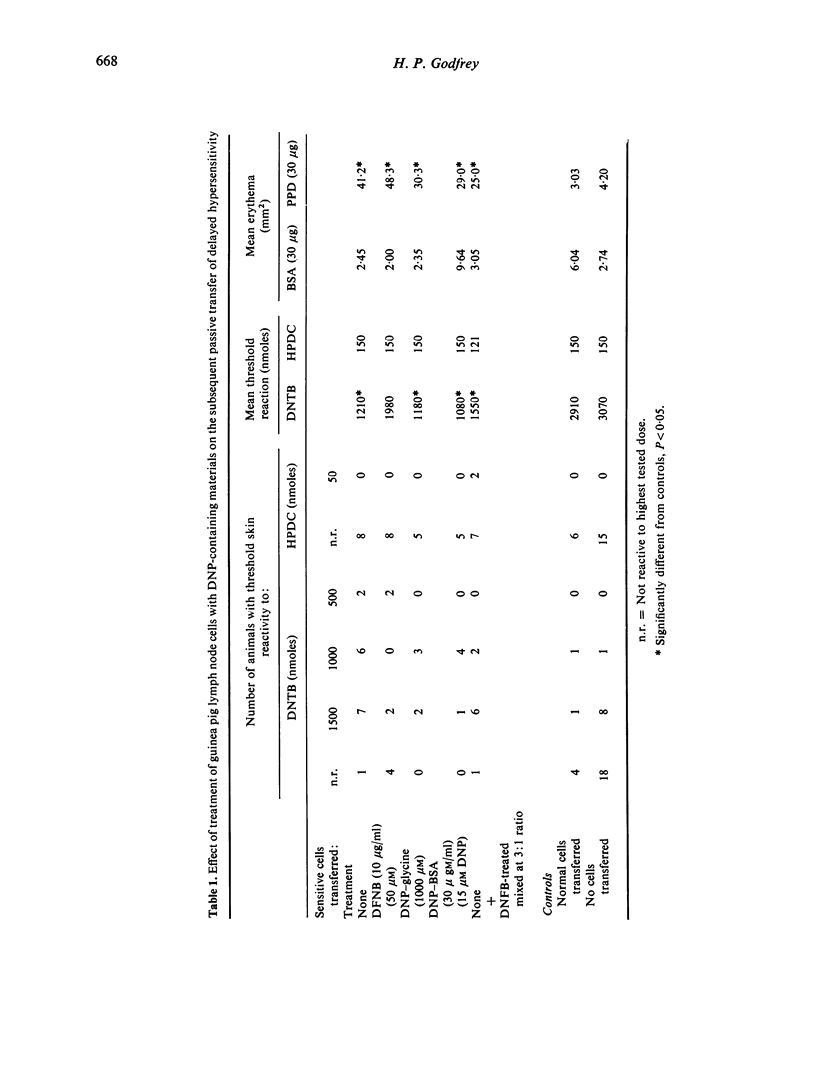
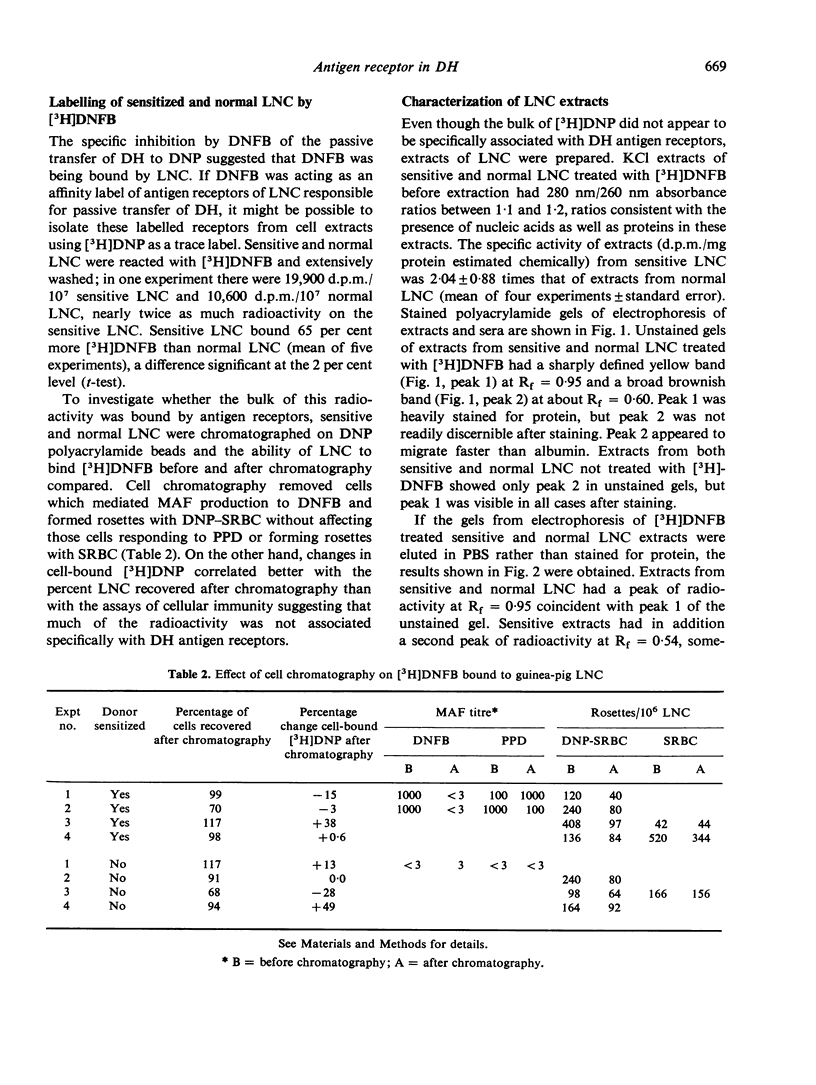
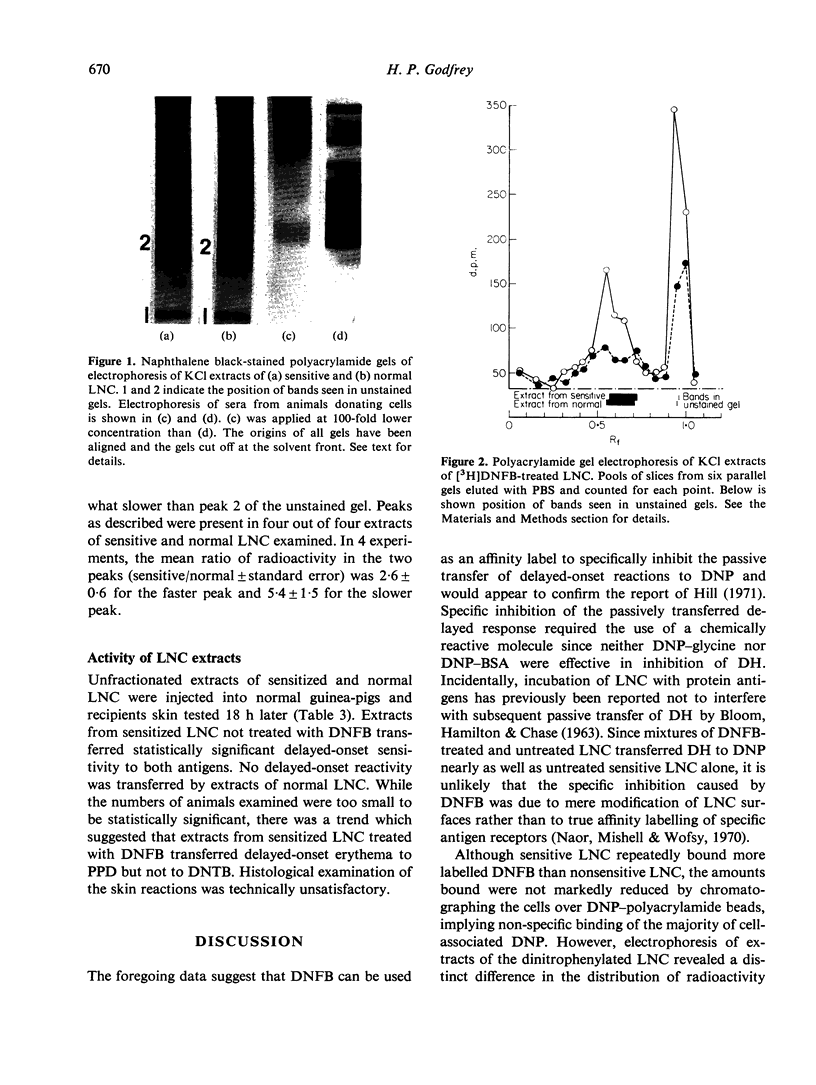
The passive transfer of delayed contact sensitivity to dinitrophenyl can be specifically inhibited by brief treatment of lymph node cells (LNC) from sensitized guinea-pigs with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (DNFB). Analysis of KC1 extracts of LNC previously treated with (3H)DNFB, using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, revealed a peak of radioactivity present in both sensitive and normal cell extracts as well as a peak found only in sensitive cell extracts. Cell-free extracts appeared capable of transmitting delayed-onset skin reactivity to non-sensitized recipients.
Full text
PDF




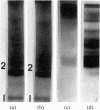
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asherson G. L., Zembala M. Contact sensitivity in the mouse. IV. The role of lymphocytes and macrophages in passive transfer and the mechanism of their interaction. J Exp Med. 1970 Jul 1;132(1):1–15. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askenase P. W. Cutaneous basophil hypersensitivity in contact-sensitized guinea pigs. I. Transfer with immune serum. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1144–1155. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM B. R., HAMILTON L. D., CHASE M. W. EFFECTS OF MITOMYCIN C ON THE CELLULAR TRANSFER OF DELAYED-TYPE HYPERSENSITIVITY IN THE GUINEA PIG. Nature. 1964 Feb 15;201:689–691. doi: 10.1038/201689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B., Katz D. H. Failure to induce tolerance to 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene contact sensitivity with a 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) conjugate of a copolymer of D-glutamic acid and D-lysine, a specific tolerogen for DNP B cells. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1158–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Chase M. W. Transfer of delayed-type hypersensitivity. A critical review and experimental study in the guinea pig. Prog Allergy. 1967;10:151–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone M., Koch C., Simonsen M. The elusive T cell receptor. Transplant Rev. 1972;10:36–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb01538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geczy C. L., Friedrich W., de Weck A. L. Production and in vivo effect of antibodies against guinea pig lymphokines. Cell Immunol. 1975 Sep;19(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey H. P., Baer H. The effect of physical and chemical properties of the sensitizing substance on the induction and elicitation of delayed contact sensitivity. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):431–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey H. P. Differences in sensitivity to a cytotoxic anti-thymus-derived lymphocyte serum of cells mediating delayed-onset reactions in guinea pigs to hapten-protein conjugates and contactants. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 1;22(1):28–42. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey H. P., Gell P. G. Separation by column chromatography of cells active in delayed-onset hypersensitivities. Immunology. 1976 May;30(5):695–703. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey H. P. Hapten-specific responses to contact sensitizers. Use of fluorodinitrobenzene to elicit migration inhibition and macrophage agglutination factors from lymph node cells of contact-sensitive guinea-pigs. Immunology. 1976 May;30(5):685–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F. Biological effects of anti-immunoglobulins: evidence for immunoglobulin receptors on 'T' and 'B' lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1970;5:45–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1970.tb00356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. C., Nissen B. The antigen receptor in delayed-type hypersensitivity. II. Passive sensitization of guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):421–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. C. The antigen receptor in delayed-type hypersensitivity. I. Isolation with an affinity label. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):414–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H. Cell-mediated immunity--general perspectives. Br Med Bull. 1967 Jan;23(1):93–97. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Nielsen H. E. Effect of anti light-chain antibodies on rat leukocytes in vitro. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason S., Warner N. L. The immunoglobulin nature of the antigen recognition site on cells mediating transplantation immunity and delayed hypersentivity. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):762–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naor D., Mishell R. I., Wofsy L. Specific inhibition of an anti-hapten immune response by chemical modifications of cells. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1322–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. K., Pellegrino M. A., Reisfeld R. A. Hypertonic salt extraction of HL-A antigens: assessment of protease activity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1272–1277. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajapakse D. A., Mapamichail M., Holborow E. J. Immunoglobulin nature of PPD receptors on human T lymphocytes. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 3;245(144):155–157. doi: 10.1038/newbio245155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld R. A., Pellegrino M. A., Kahan B. D. Salt extraction of soluble HL-A antigens. Science. 1971 Jun 11;172(3988):1134–1136. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3988.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlossman S. F. Antigen recognition: the specificity of T cells involved in the cellular immune response. Transplant Rev. 1972;10:97–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb01540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]