Abstract
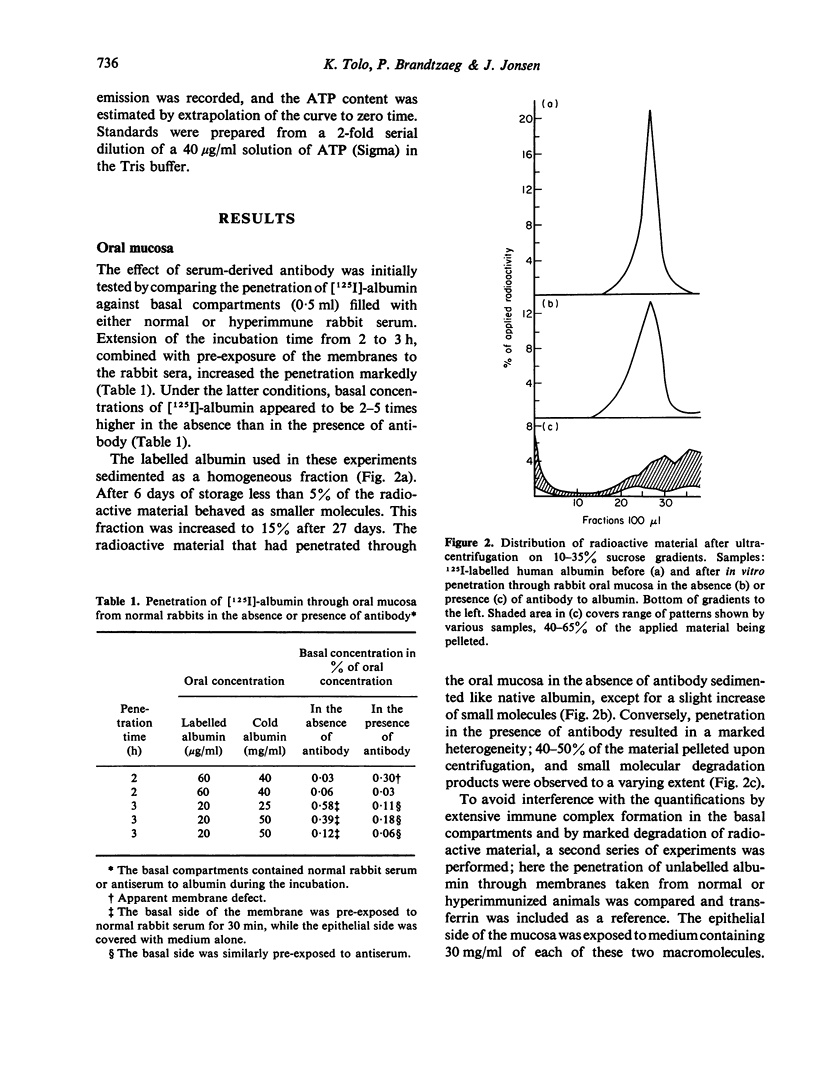
Rabbit mucous membranes were mounted in diffusion chambers within 30 min after excision. The epithelial side was exposed to cell culture medium containing `cold' and 125I-labelled human albumin. The basal side was exposed to normal rabbit serum (control chambers) or to rabbit anti-serum against human albumin. The chambers were incubated in a humidified atmosphere of CO2 in air for 2–3 h at 37°. The radioactive material recovered on the basal side of the sublingual control membranes sedimented virtually like native albumin on ultracentrifugation. The amount of radioactive material recovered after penetration through anti-serum-exposed sublingual mucosa was reduced by 50–80% and showed a very heterogeneous sedimentation pattern including aggregates, presumably immune complexes, as well as a considerable amount of degradation products.
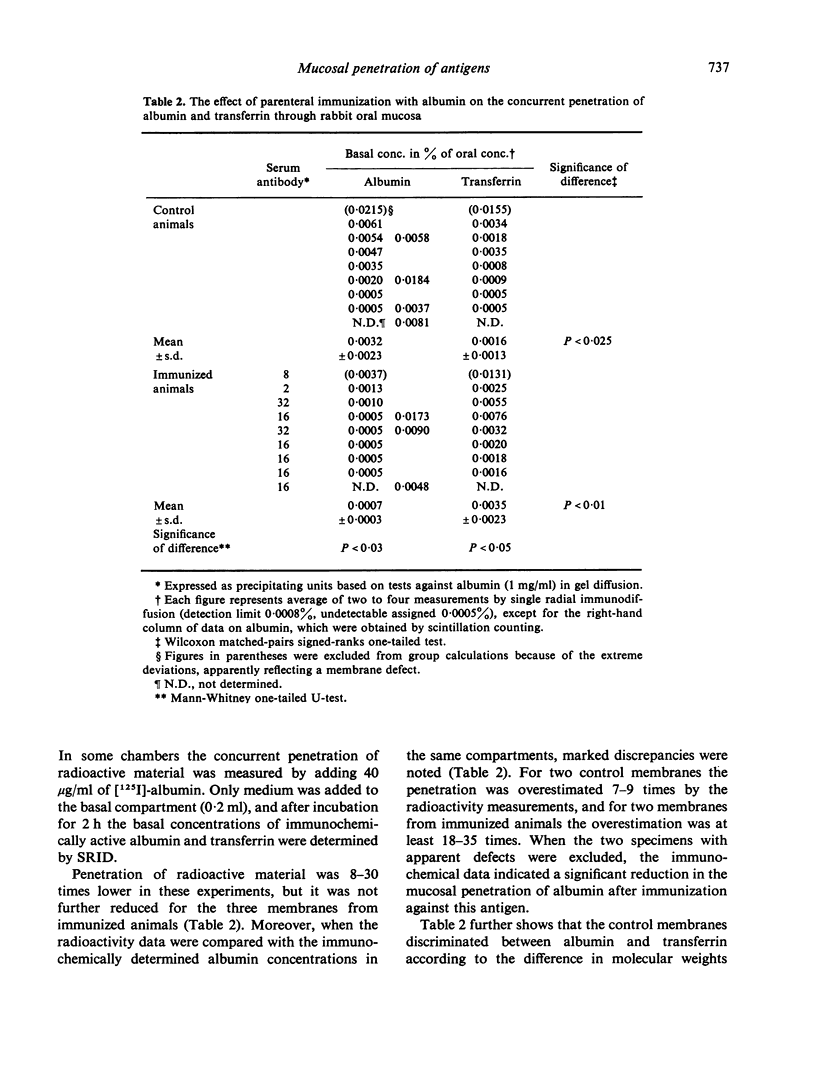
In a second series of experiments the concurrent penetration of human albumin and transferrin through the sublingual mucosa of rabbits immunized parenterally with albumin was compared with that occurring through control membranes. With reference to immunochemical quantification, scintillation counting was found to overestimate the penetration of intact albumin considerably, and jeopardized evaluation of the influence of serum-derived antibody. Radial immunodiffusion showed that in controls the basal antigen concentration, expressed in percentage of the oral (30 mg/ml for both molecules), was after 2 h 0.0032±0.0023 for albumin and 0.0016±0013 for transferrin. Penetration of immunoreactive albumin through mucosa from immunized animals was clearly reduced (0.0007±0.0003), whereas there was a significant tendency toward increased penetration of transferrin (0.0035±0.0023). These results suggest that antibody within the mucosa retards the penetration of intact homologous antigen, while immune reactions may enhance the penetration of unrelated macromolecules.
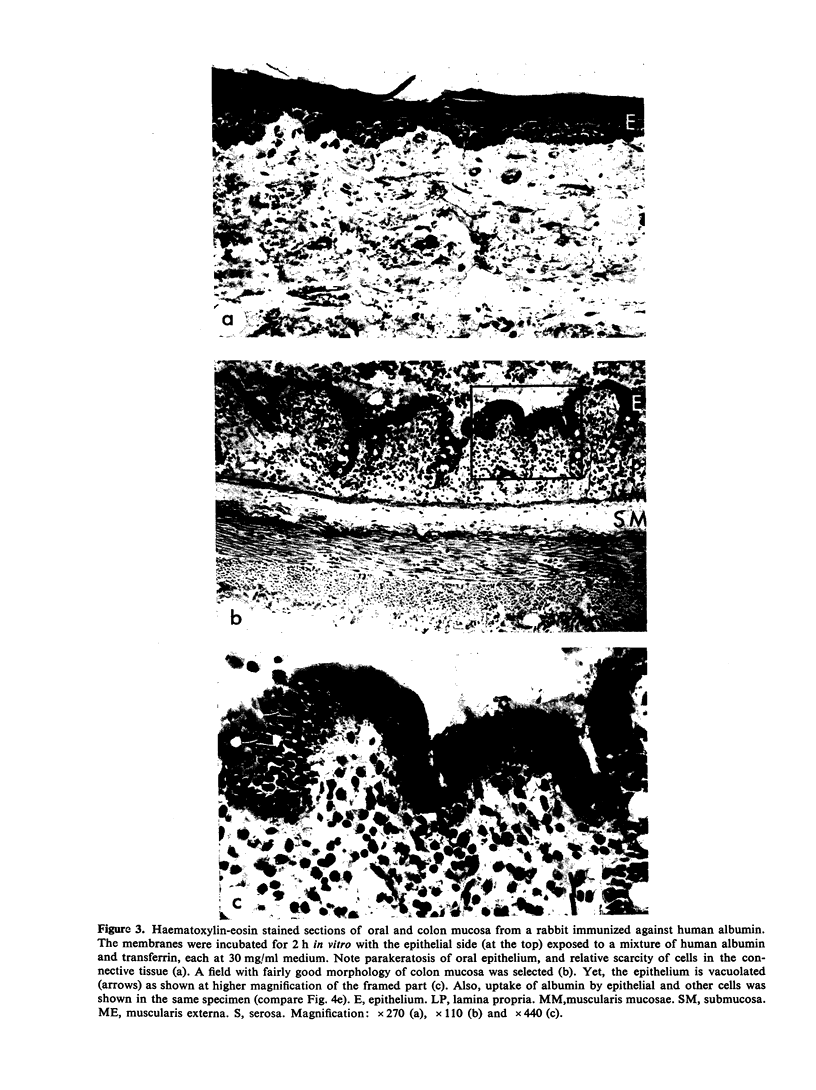
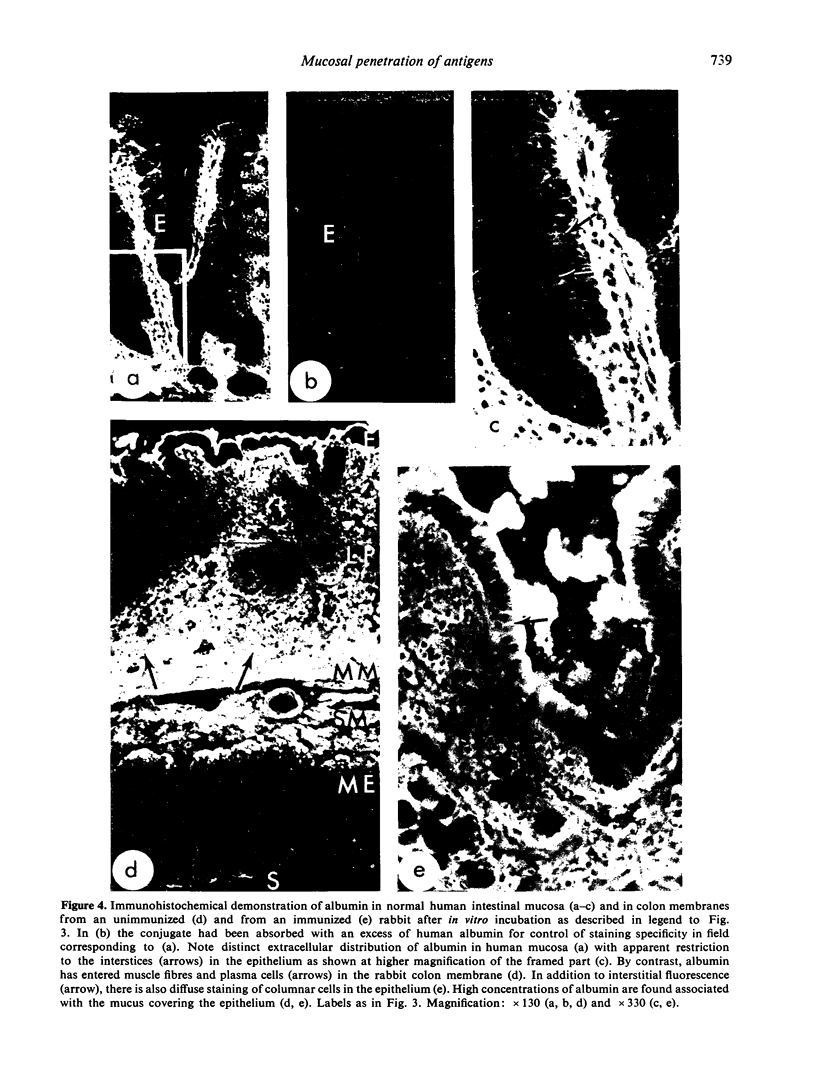
In similar experiments with colon mucosa penetration was 50–100 times increased, but the membranes did not discriminate between albumin and transferrin and there was no effect of immunization. Histological and immunohistochemical studies of the latter membranes indicated marked defects in cell viability after 2 h in vitro.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André C., Lambert R., Bazin H., Heremans J. F. Interference of oral immunization with the intestinal absorption of heterologous albumin. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Oct;4(10):701–704. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830041013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy J. E., Nielsen N. O. Immune-mediated emigration of neutrophils into the lumen of the small intestine. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):615–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.615-619.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Baklien K. Immunohistochemical studies of the formation and epithelial transport of immunoglobulins in normal and diseased human intestinal mucosa. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1976;36:1–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Conjugates of immunoglobulin G with different fluorochromes. I. Characterization by anionic-exchange chromatography. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(3):273–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Fjellanger I., Gjeruldsen S. T. Human secretory immunoglobulins. I. Salivary secretions from individuals with normal or low levels of serum immunoglobulins. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1970;12:3–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Human secretory component. II. Physicochemical characterization of free secretory component purified from colostrum. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):707–716. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Mucosal and glandular distribution of immunoglobulin components. Immunohistochemistry with a cold ethanol-fixation technique. Immunology. 1974 Jun;26(6):1101–1114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Tolo K. Mucosal penetrability enhanced by serum-derived antibodies. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):262–263. doi: 10.1038/266262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronk J. R., Leese H. J. Changes in the adenine nucleotide content of preparations of the rat small intestine in vitro. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):183–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Dees S. C. Correlation of milk precipitins with IgA deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1969 Aug 28;281(9):465–469. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196908282810903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceska M., Berglund A., Lundkvist U., Grossmüller F. Influence of the degree of iodination and storage time on the immunological activity of 125 I-IgE. Immunochemistry. 1972 May;9(5):565–575. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E. Report of a workshop: disease accentuation after immunization with inactivated microbial vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):749–754. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammar H. ATP and ADP levels and epidermal replacement rate in the normal human skin and in some papulosquamous diseases of the skin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1973;53(4):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huntley C. C., Robbins J. B., Lyerly A. D., Buckley R. H. Characterization of precipitating antibodies to ruminant serum and milk proteins in humans with selective IgA deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jan 7;284(1):7–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197101072840102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingham J. G., Whorwell P. J., Loehry C. A. Small intestinal permeability. 1. Effects of ischaemia and exposure to acetyl salicylate. Gut. 1976 May;17(5):354–361. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.5.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall W. A. The effect of topical antigen on the gingiva of sensitized rabbits. J Periodontal Res. 1974;9(3):153–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1974.tb00667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nencioni T., Brambati B., Crosignani P. G. Concentration d'albumine, de transferrine, IgA, IgG, IgM et bêta-lipoprotéines dans le sérum maternel, le liquide amniotique et le sérum funiculaire dans la grossesse normale près du terme. Gynecol Obstet (Paris) 1970 May-Jul;69(3):219–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKINS R. A., DIMITRIADOU A., BOOTH C. C. The rates and sites of absorption of 131 I-labelled albumin and sodium 131 I in the rat. Clin Sci. 1960 Nov;19:595–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen H. L. Interstitial fluid concentrations of albumin and immunoglobulin G in normal men. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 Oct;34(2):119–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. S., Karnovsky M. J. Loss of macromolecular barrier function associated with surgical trauma to the intestine. Lab Invest. 1971 Sep;25(3):220–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieber A., Becker W. Quantitative determination of IgE by single radial immunodiffusion. A comparison of three different methods for intensification of precipitates. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Jan 19;50(1):153–155. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolo K., Jonsen J. In vitro penetration of tritiated dextrans through rabbit oral mucosa. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Jul;20(7):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Abel S. N., Wu M., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. V. Comparison of the in vitro uptake by rat small intestine of antigen-antibody complexes prepared in antibody or antigen excess. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):1028–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A. Antigen absorption from the small intestine and gastrointestinal disease. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1975 Nov;22(4):731–746. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)33204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Cornell R., Davenport L. M., Isselbacher K. J. Macromolecular absorption. Mechanism of horseradish peroxidase uptake and transport in adult and neonatal rat intestine. J Cell Biol. 1972 Aug;54(2):195–205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. II. Effect of parenteral immunization. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules: effect of oral immunization. Science. 1972 Aug 18;177(4049):608–610. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4049.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Wu M., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. III. Studies on the mechanism by which immunization interferes with antigen uptake. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):854–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Wu M., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. IV.--The effect of pancreatic duct ligation on the breakdown of antigen and antigen-antibody complexes on the intestinal surface. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1223–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]