Abstract
Prednisolone causes a dose-related inhibition of antigen-evoked histamine release from IgE-sensitized human skin in vitro. The effective concentrations are of the same order as are achieved in plasma therapeutically.
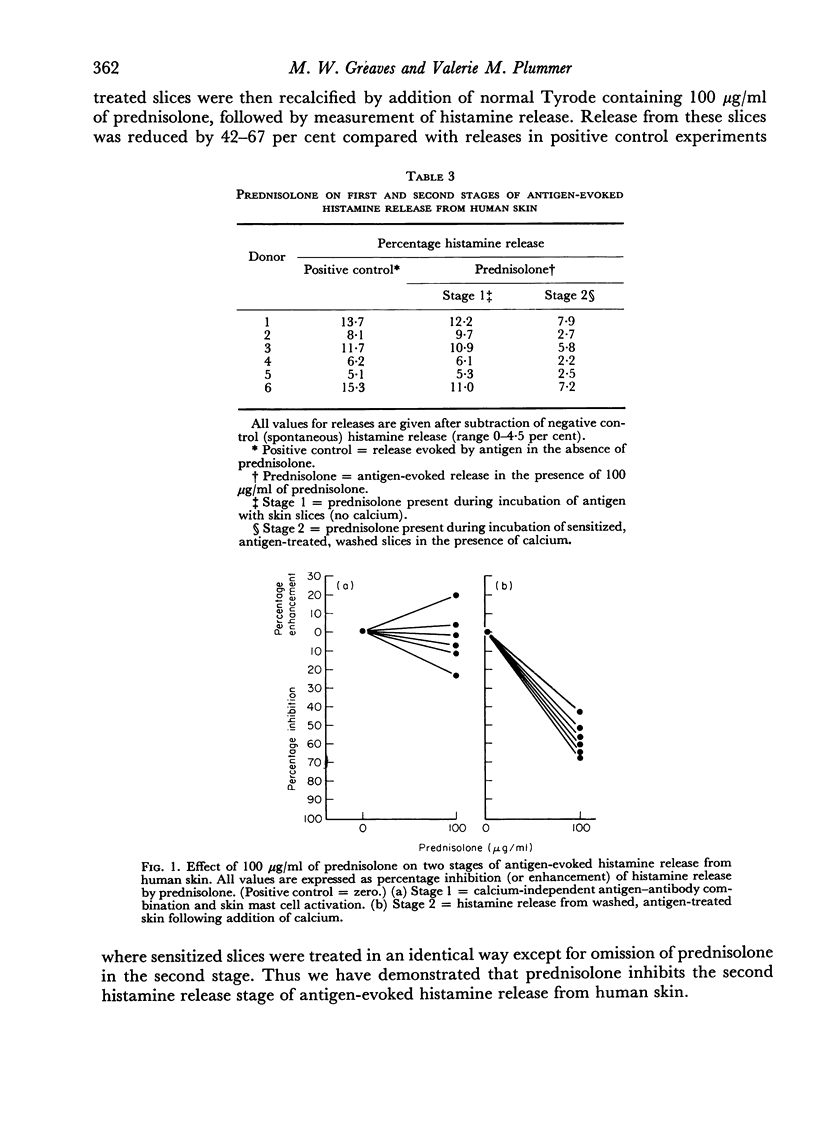
Analysis of prednisolone inhibition shows that it acts on the second histamine release stage, antigen—antibody combination being unaffected.
In contrast with the traditional view, our results show that, at least in human skin, glucocorticoids can inhibit antigen-evoked histamine release.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAREY R. A., HARVEY A. M., HOWARD J. E., WAGLEY P. F. The effect of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and cortisone on drug hypersensitivity reactions. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1950 Nov;87(5):354–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAREY R. A., HARVEY A. M., HOWARD J. E., WINKENWERDER W. L. The effect of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and cortisone on the course of chronic bronchial asthma. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1950 Nov;87(5):387–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARRYER H. M., CODE C. F. The effect of cortisone upon the release of histamine during in vitro hemolytic reactions in rabbit blood. J Allergy. 1950 Jul;21(4):310–313. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(50)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY W. D., PEDRICK L., WINNE R. Effect of cortisone on anaphylactic response of guinea pig ileum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Dec;78(3):679–683. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. W., Yamamoto S., Fairley V. M. IgE-mediated hypersensitivity in human skin studied using a new in vitro method. Immunology. 1972 Aug;23(2):239–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENCH P. S., KENDALL E. C., SLOCUMB C. H., POLLEY H. F. Effects of cortisone acetate and pituitary ACTH on rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatic fever and certain other conditions. Arch Intern Med (Chic) 1950 Apr;85(4):545–666. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1950.00230100002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H. The effect of cortisone upon some experimental hypersensitivity reactions. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Jun;32(3):274–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logsdon P. J., Middleton E., Jr, Coffey R. G. Stimulation of leukocyte adenyl cyclase by hydrocortisone and isoproterenol in asthmatic and nonasthmatic subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972 Jul;50(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONGAR J. L., SCHILD H. O. Cellular mechanisms in anaphylaxis. Physiol Rev. 1962 Apr;42:226–270. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1962.42.2.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON D. H. Relative merits of the adreno-cortical steroids. Annu Rev Med. 1962;13:241–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.13.020162.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte J. G., Feduska N. J., Carpenter E. W., McDonald F. D., Bacon G. E. Rejection crises in human renal transplant recipients: control with high dose methylprednisolone therapy. Arch Surg. 1972 Aug;105(2):230–236. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180080084014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., THOMAS L. THE EFFECTS OF CORTICOSTEROIDS UPON CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND LYSOSOMES. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1964;20:215–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Greaves M. W., Fairley V. M. Cyclic AMP-induced inhibition of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity in human skin. Immunology. 1973 Jan;24(1):77–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Greaves M. W., Plummer V. Inhibition of human cutaneous anaphylaxis by cytochalasin B. Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):1007–1012. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Greaves M. W. The role of calcium in human cutaneous anaphylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;44(6):797–803. doi: 10.1159/000230983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


