Abstract
NZB/NZW F1 (B/W) mice were subjected to sham surgery or neonatal thymectomy and/or splenectomy and studied for immunoglobulin class of antibodies to double stranded DNA and polyadenylic acid (Poly A) at 1 and 2 months of age. These antibodies occur spontaneously during the course of autoimmune disease in B/W mice.
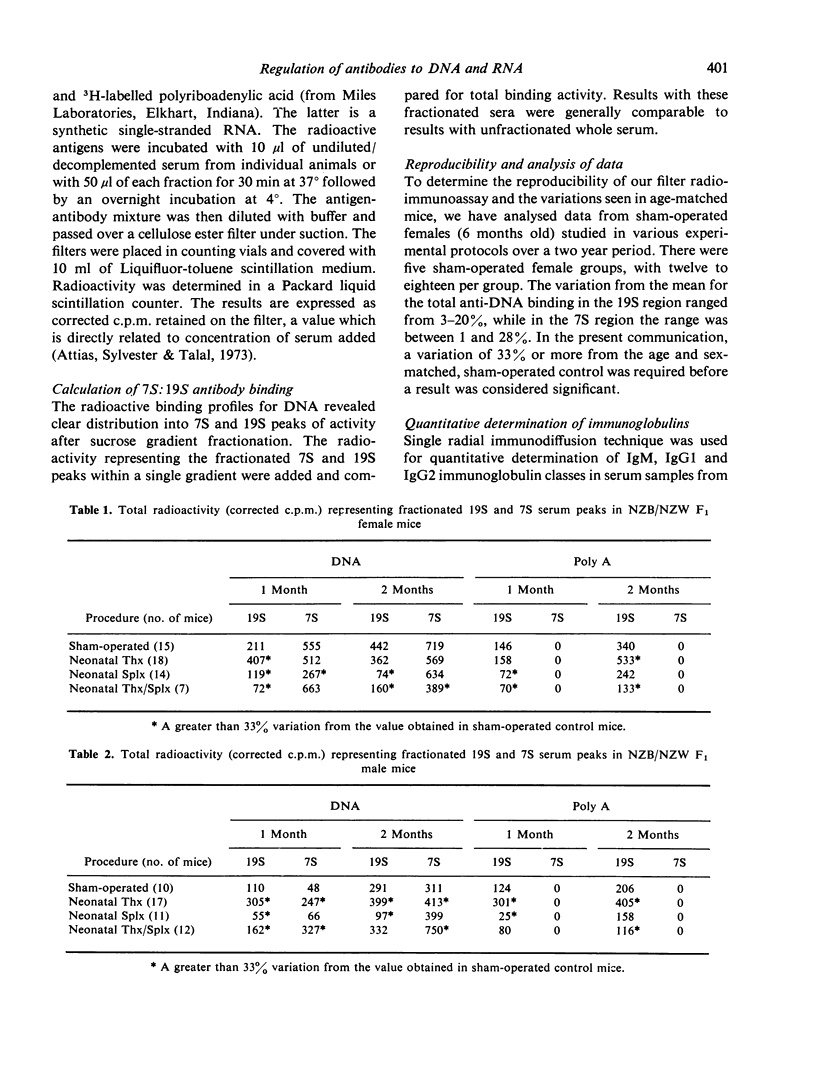
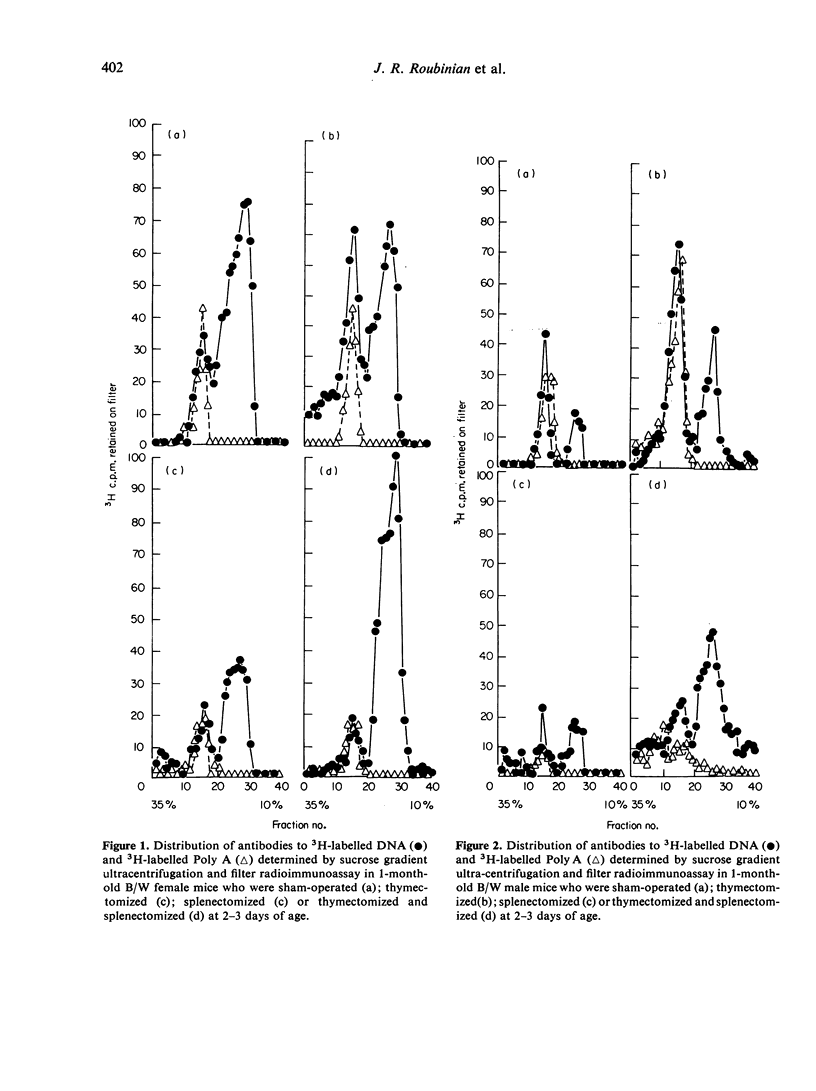
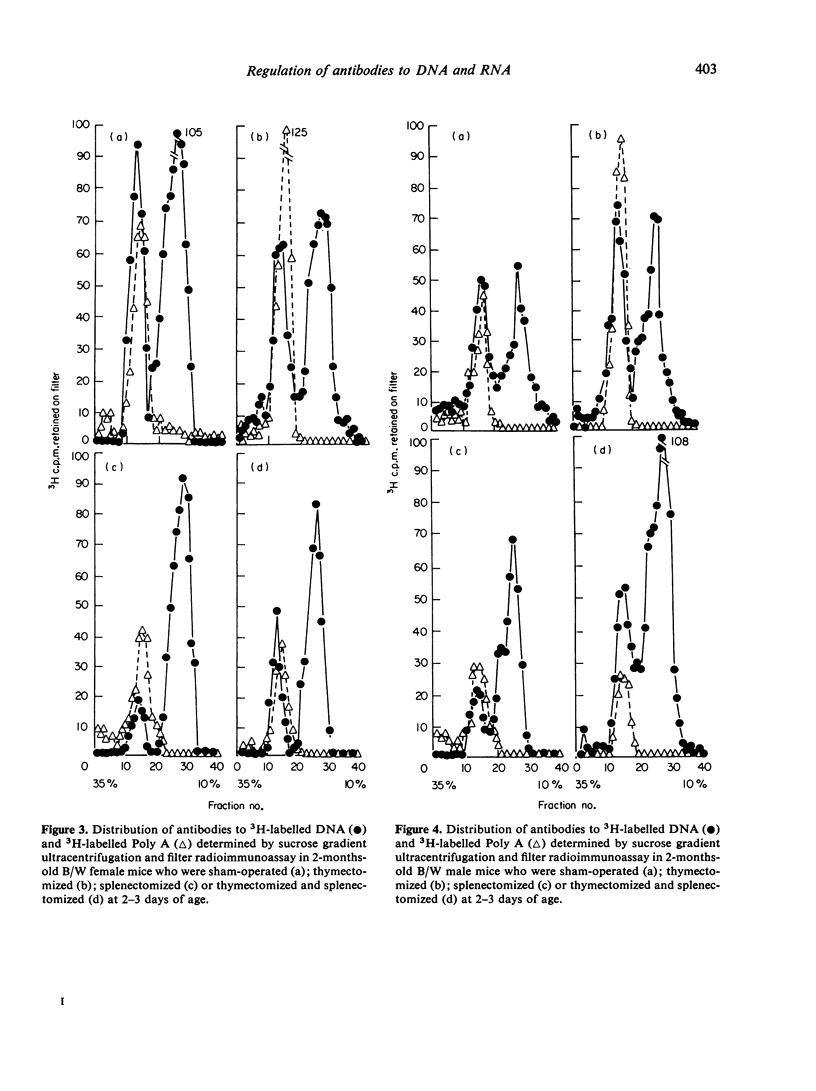
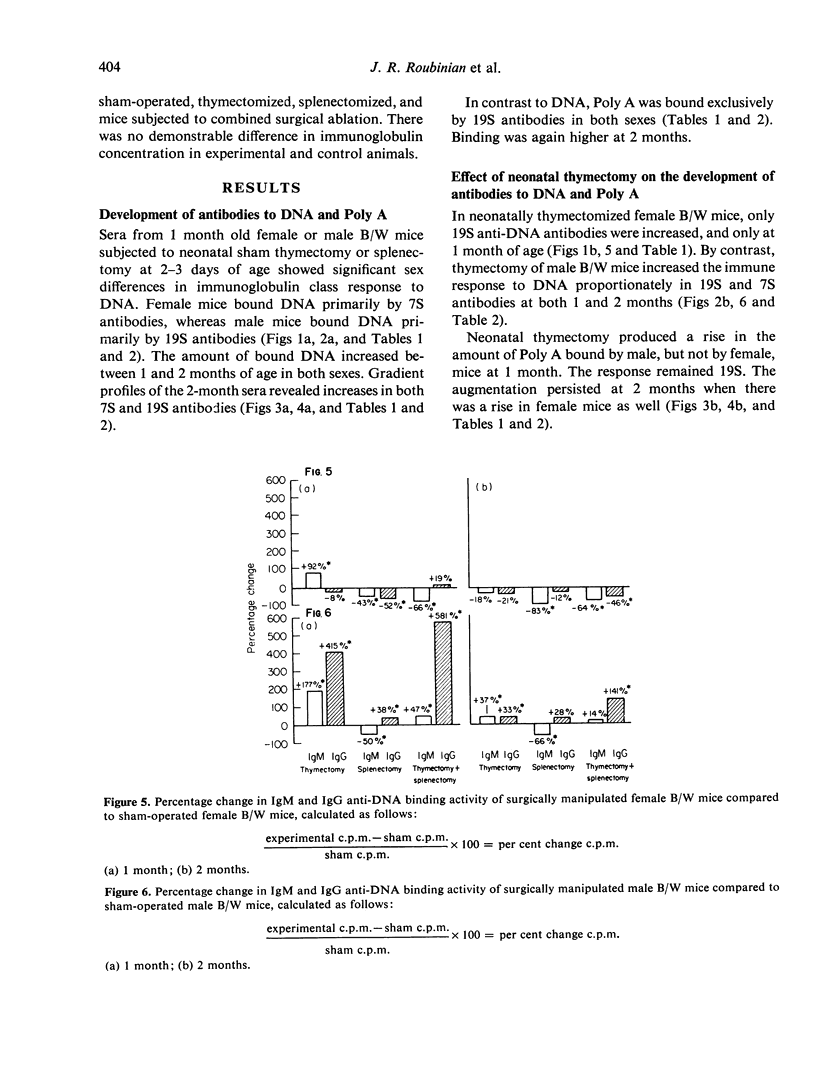
The serum from sham-operated female mice bound DNA predominantly in the 7S fraction, whereas serum from sham-operated male mice bound DNA primarily in the 19S fraction. Antibodies to Poly A were exclusively 19S in both sexes. Thymectomy of male B/W mice caused an increase in 7S and 19S antibodies to DNA at the ages studied, while it increased 19S antibodies to DNA in female mice only at 1 month of age. Thymectomy increased the 19S antibodies to Poly A in both sexes. Splenectomy had similar effects in males and females. It reduced both the 19S and 7S responses to DNA and the 19S response to Poly A at 1 month. By the second post-operative month, both 7S anti-DNA and 19S anti-Poly A antibody responses had recovered. Combined thymectomy and splenectomy of male B/W mice produced a disproportionate increase in 7S antibodies to DNA, while the procedures resulted in a decline in 7S and 19S antibodies to DNA in female B/W mice.
These results suggest that the newborn (B/W) thymus and spleen contain regulatory cells exerting different controlling influences on spontaneous antibodies to DNA and Poly A. Moreover, they suggest that the male thymus exerts a suppressor influence while the female thymus exerts primarily a helper effect.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attias M. R., Sylvester R. A., Talal N. Filter radioimmunoassay for antibodies to reovirus RNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Nov-Dec;16(6):719–725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. M., Williamson W. G., Irvine W. J. The appearance of immunological competence at an early age in New Zealand black mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Jun;3(5):375–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K. A disquisition on suppressor T cells. Transplant Rev. 1975;26:170–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie J. B., Helyer B. J. The immunology and pathology of NZB mice. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:215–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. The regulatory influence of activated T cells on B cell responses to antigen. Adv Immunol. 1972;15:1–94. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60683-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors R. C., Huang C. Y. Immunopathology of NZB/BL mice. V. Viruslike (filtrable) agent separable from lymphoma cells and identifiable by electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1031–1038. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples P. J., Talal N. Relative inability to induce tolerance in adult NZB and NZB-NZW F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):123–139. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Disordered immunologic regulation and autoimmunity. Transplant Rev. 1976;31:240–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb01456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Immunologic and viral factors in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):887–894. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Pillarisetty R. IgM and IgG antibodies to DNA, RNA, and DNA:RNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):24–31. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


