Abstract
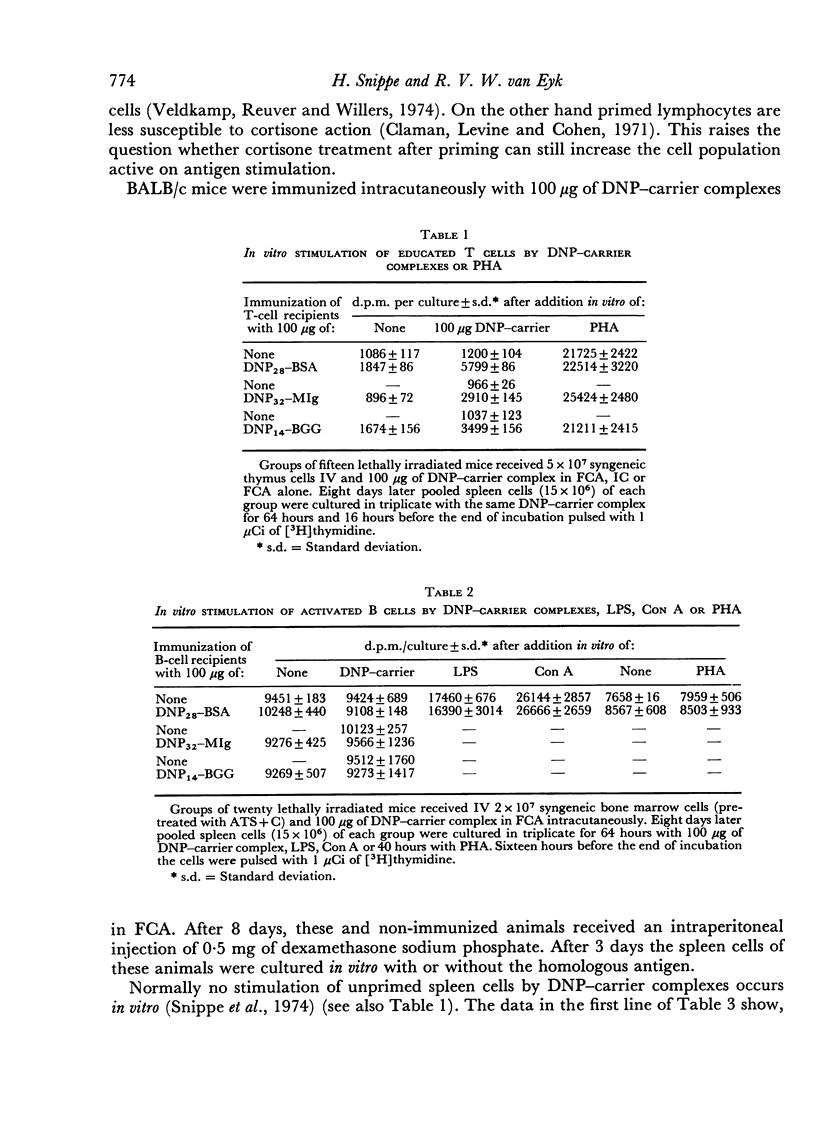
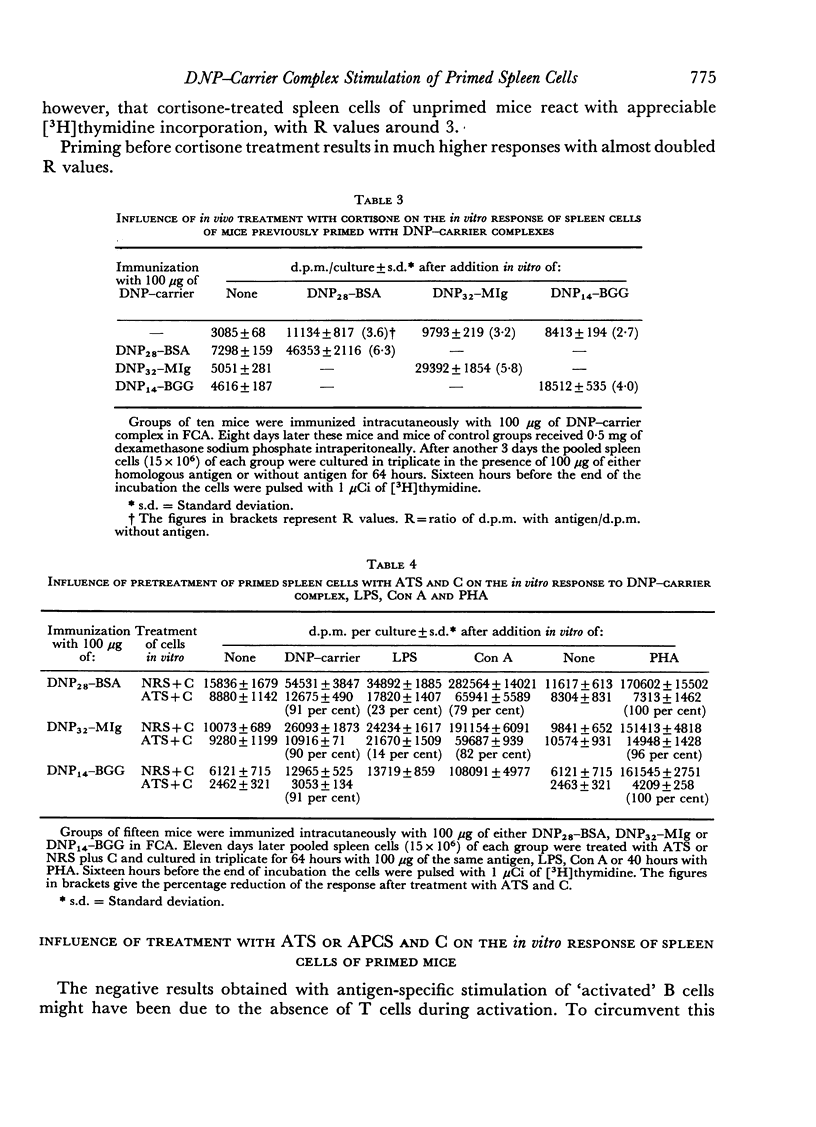
The target cell of in vitro stimulation of primed spleen cells by hapten—carrier complexes was studied. The antigens DNP28—bovine serum albumin (DNP28—BSA), which gives only 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) specific responses and DNP14—mouse immunoglobulin (DNP14—MIg), which probably reveals DNP as well as carrier specificity (new antigenic determinant) were used. Educated T cells could be stimulated with the antigens used for activation. A similar experiment with educated B cells, however, gave no indication that these B cells could be stimulated with antigen in the absence of T cells. Cortisone treatment of primed mice yielded spleen cells which had a higher activity than spleen cells from unprimed, cortisone-treated mice. This also points to stimulation of T cells by antigen. Treatment of primed spleen cells with anti-thymocyte serum (ATS) and complement (C) abolished stimulation by phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) completely, by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) slightly, while the antigen-specific activity was 90 per cent reduced. This indicates a mainly T cell-specific stimulation by the antigen. A corresponding experiment with anti-plasma cell serum (APCS) and C revealed a complete reduction of LPS activity and a small impairment of the PHA and conavalin A (Con A) activity. However, the antigen-specific activity was reduced by one-third to a half for the different antigens. This is an indication for a specific B-cell stimulation by the antigen, although it is on a lower level than the T-cell stimulation. The role of the hapten in the T-cell stimulation is discussed.
Full text
PDF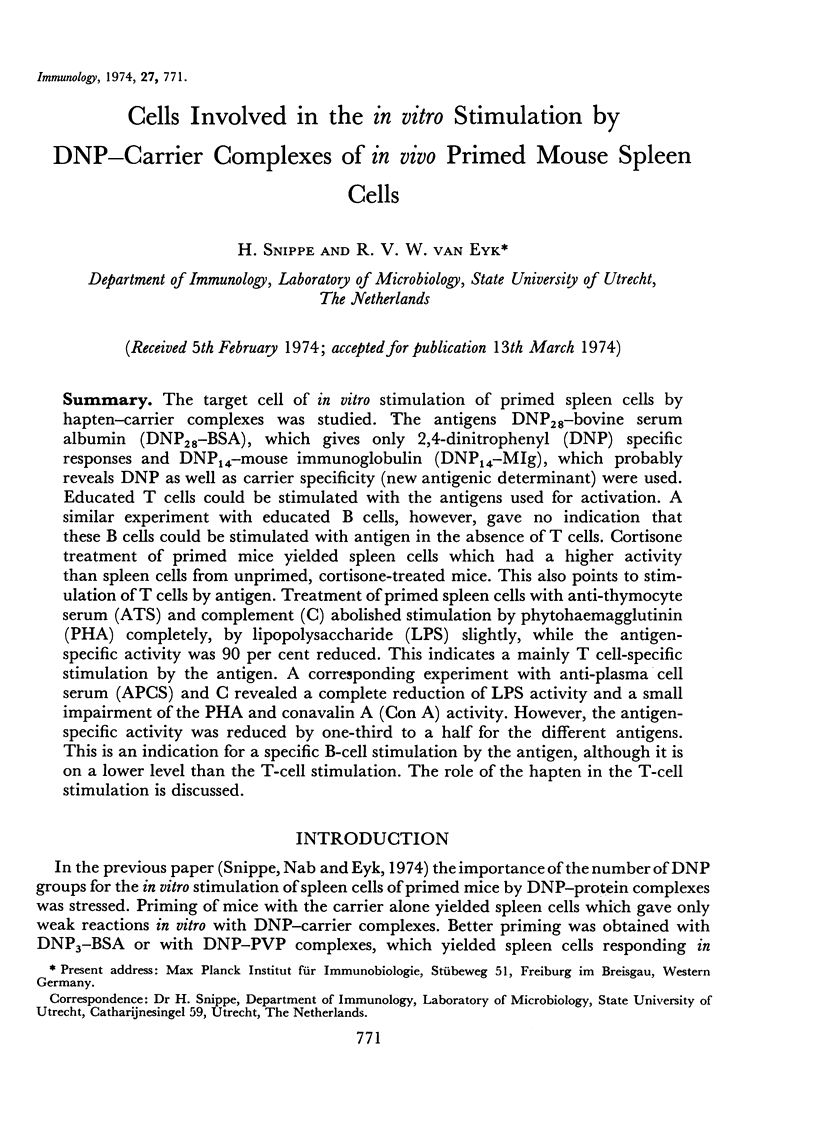






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkan S. S., Nitecki D. E., Goodman J. W. Antigen recognition and the immune response: the capacity of L-tyrosine-azobenzenearsonate to serve as a carrier for a macromolecular hapten. J Immunol. 1971 Aug;107(2):353–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Möller G., Sjöberg O. Selective induction of DNA synthesis in T and B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Aug;4(4):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomgren H., Andersson B. Evidence for a small pool of immunocompetent cells in the mouse thymus. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Oct;57(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann K. U. Induction of a hemolysin response in vitro. Interaction of cells of bone marrow origin and thymic origin. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1267–1278. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson G. M. Ability of CBA mice to produce anti-idiotypic sera to 5563 myeloma protein. Nature. 1970 Jul 18;227(5255):273–274. doi: 10.1038/227273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Paul W. E. Hapten-specific augmentation of the anti-idiotype antibody response to hapten-myeloma protein conjugates in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Jun;3(6):340–347. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jooste S. V., Lance E. M., Levey R. H., Medawar P. B., Ruszkiewicz M., Sharman R., Taub R. N. Notes on the preparation and assay of anti-lymphocytic serum for use in mice. Immunology. 1968 Nov;15(5):697–705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison N. A. The carrier effect in the secondary response to hapten-protein conjugates. II. Cellular cooperation. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Jan;1(1):18–27. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead J. W., Walters C. S., Claman H. N. Immunologic reactions to haptens on autologous carriers. I. Participation of both thymus-derived and bone marrow-derived cells in the secondary in vitro response. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):411–423. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne D. P., Jr, Katz D. H. Antigen-induced deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in mouse lymphocytes. I. The nature and specificity of lymphocyte activation by hemocyanin and dinitrophenyl carrier conjugates. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1164–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne D. P., Jr, Katz D. H. Antigen-induced deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in mouse lymphocytes. II. Analysis of the cell populations required for and responding to antigen stimulation in vitro. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1176–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Adler W. H., Smith R. T. The mitogenic effects of endotoxin and staphylococcal enterotoxin B on mouse spleen cells and human peripheral lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1453–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S., Davie J. M., Rosenstreich D. L., Blake J. T. Depletion of antibody-forming cells and their precursors from complex lymphoid cell populations. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):279–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snippe H., Bruijnzeel P. L., Willers J. M. Effects of immunosuppressive treatment on the in vitro activity of mouse lymphoid cells after stimulation by PHA and allogeneic cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;45(5):731–743. doi: 10.1159/000231072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snippe H., Nab J., van Eyk R. V. In vitro stimulation of spleen cells of the mouse by DNP--carrier complexes. Immunology. 1974 Nov;27(5):761–770. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. B., Iverson G. M. Hapten competition and the nature of cell-cooperation in the antibody response. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Jan 12;176(1045):393–418. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldkamp J., De Reuver M. J., Willers J. M. Distribution of different cell types in the lymphoid organs of the mouse, as determined with sera against thymus and Peyer's patches. Immunology. 1974 Feb;26(2):359–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


