Abstract
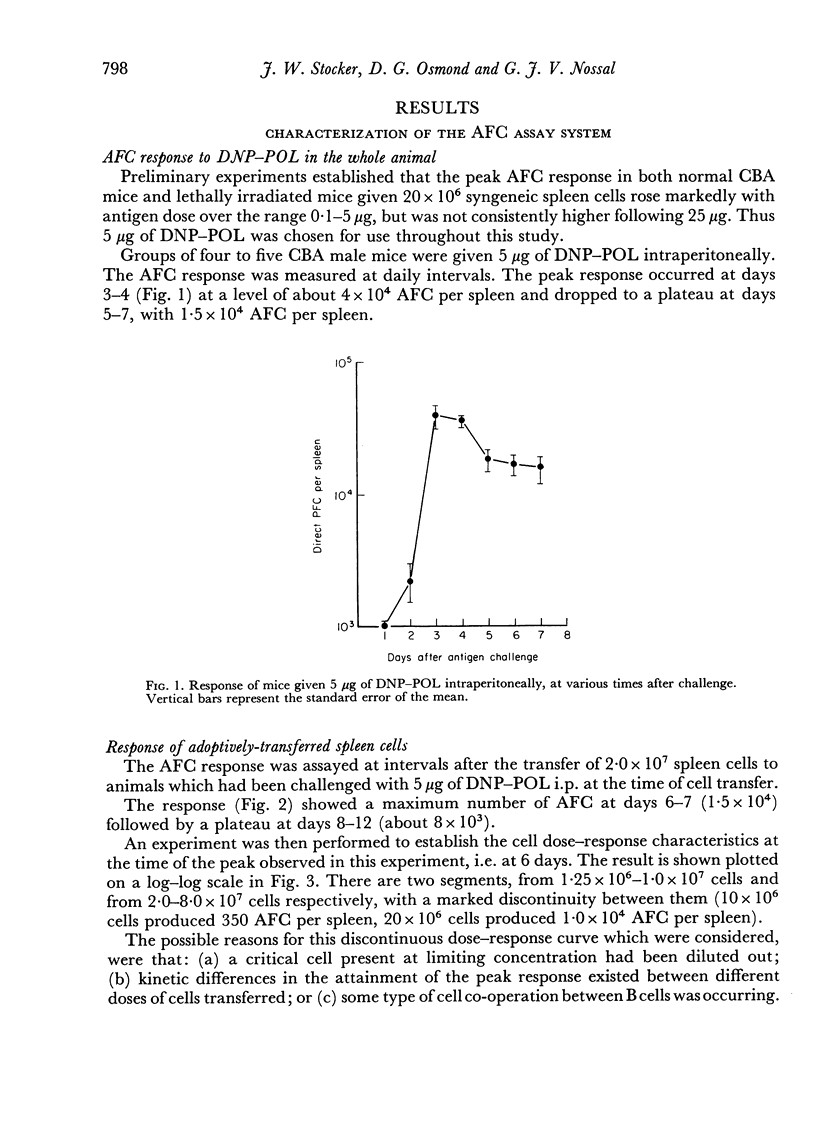
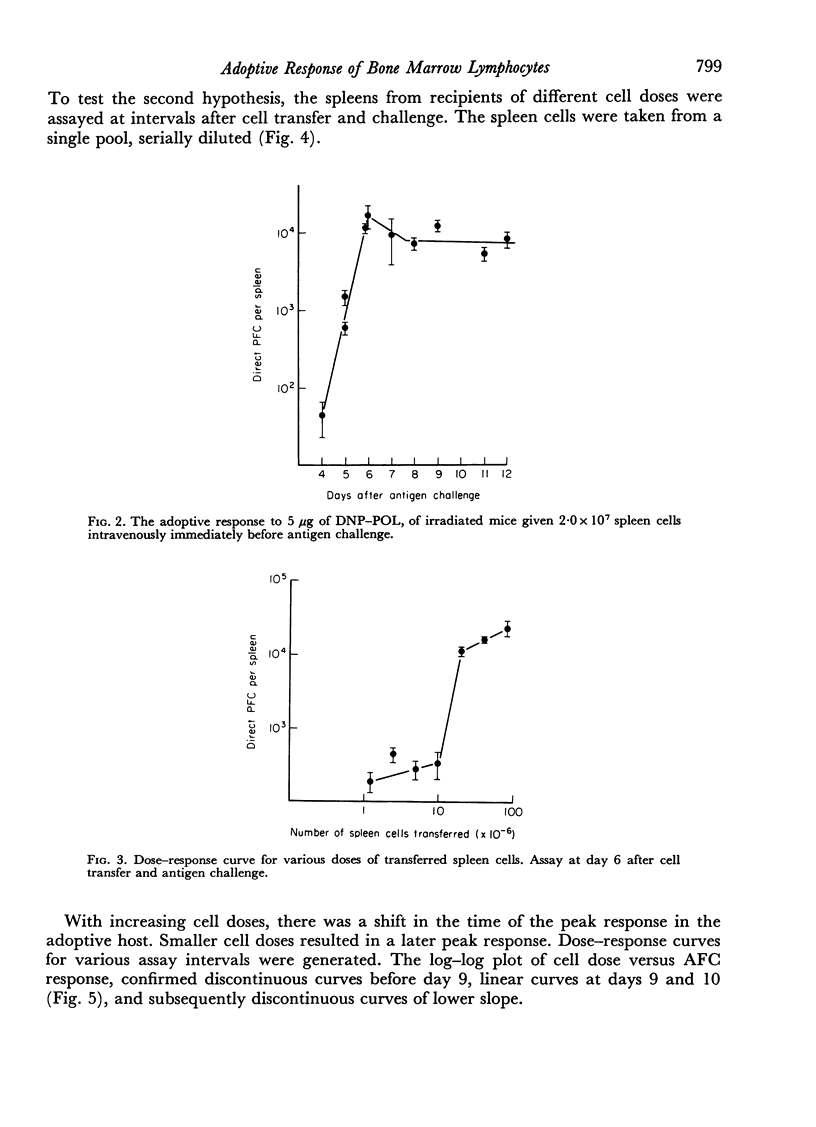
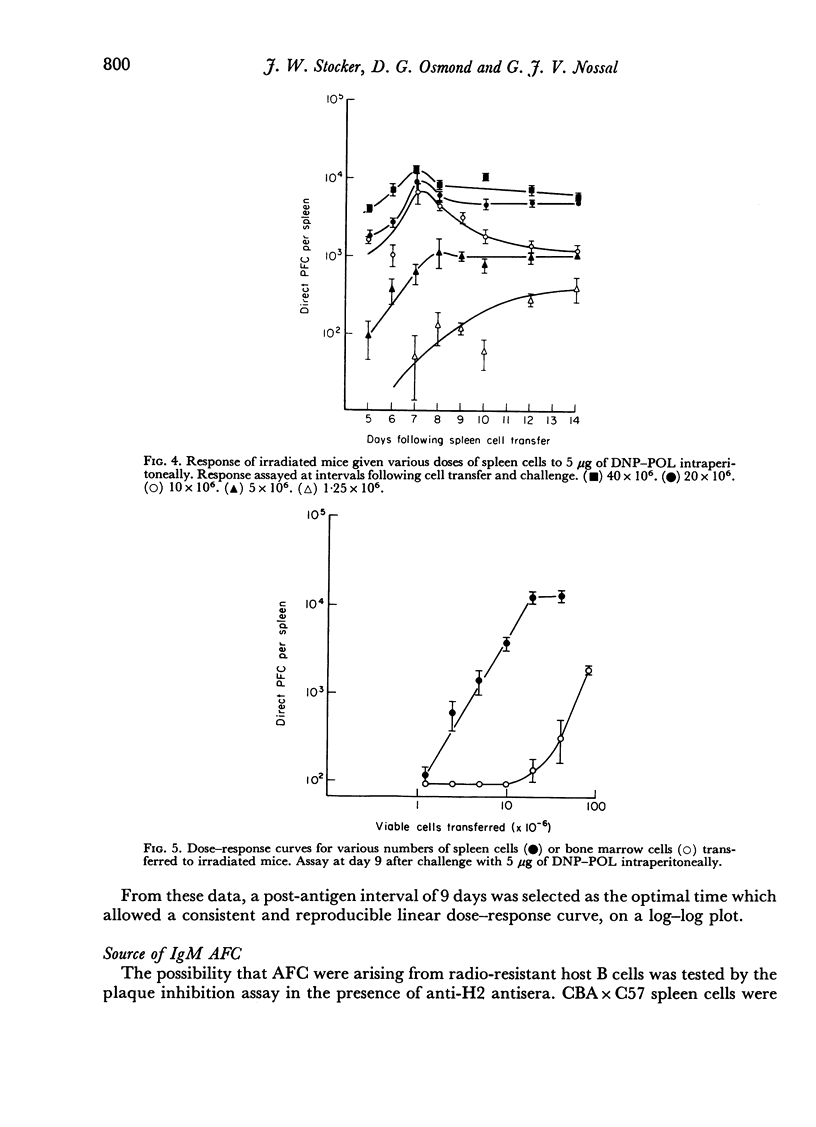
The response of mouse spleen cells to the T cell-independent antigen dinitrophenylated polymer of flagellin (DNP—POL), has been studied using an adoptive transfer system, and compared with the response of bone marrow cells. Spleen cells showed a complex cell dose—response relationship, with a markedly discontinuous curve, for assays performed before day 9 after transfer and antigen challenge. This discontinuity could be explained by a delay in attainment of the peak response for lower cell inocula. The curve became linear on a log—log scale when spleens were harvested on days 9 and 10 post-transfer.
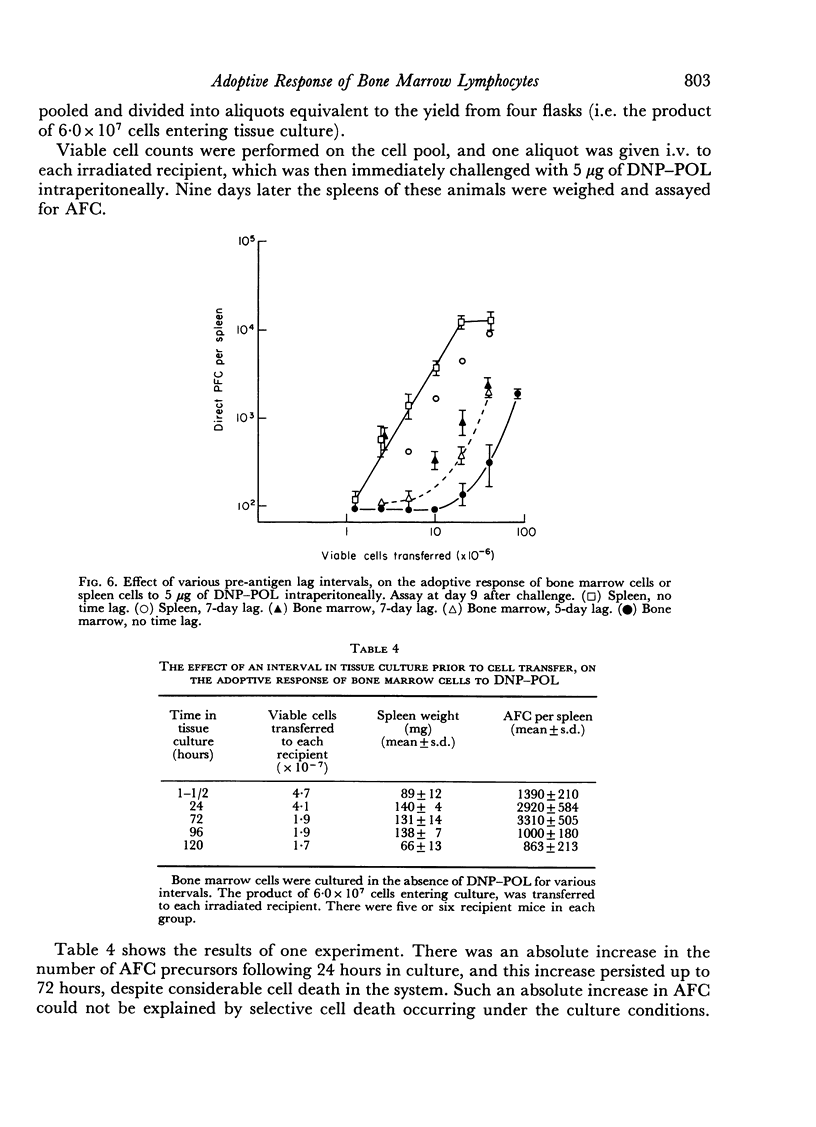
Bone marrow cells gave a lower response than would be expected from their lymphocyte content. This response increased progressively with a delay before antigen challenge in the irradiated recipient or in tissue culture prior to cell transfer, suggesting a functional maturation in this cell population, whereas the performance of spleen cells fell off under similar circumstances. The findings were consistent with, but could not prove, the hypothesis that the immediate precursors of anti-DNP antibody-forming cells in bone marrow were high surface immunoglobulin density small lymphocytes that had arisen locally from precursors lacking detectable surface immunoglobulin, by a non-mitotic maturation.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Celada F. Quantitative studies of the adoptive immunological memory in mice. II. Linear transmission of cellular memory. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):199–211. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada F., Schmidt D., Strom R. Determination of avidity of anti-albumin antibodies in the mouse. Influence of the number of cells transferred on the quality of the secondary adoptive response. Immunology. 1969 Aug;17(2):189–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiller J. M., Habicht G. S., Weigle W. O. Kinetic differences in unresponsiveness of thymus and bone marrow cells. Science. 1971 Feb 26;171(3973):813–815. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3973.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N., Chaperon E. A., Triplett R. F. Thymus-marrow cell combinations. Synergism in antibody production. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Aug-Sep;122(4):1167–1171. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Guercio P., Leuchars E. The immune response in mice to the haptenic determinant DNP coupled to a thymus-independent carrier (levan). J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):951–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Diener E. Antibody-mediated suppression of the immune response in vitro. 3. Low zone tolerance in vitro. Immunology. 1971 Sep;21(3):387–404. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Easten A. The relationship between antigenic structure and the requirement for thymus-derived cells in the immune response. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):103–119. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. M., Cinader B. Cellular aspects of tolerance. II. Unresponsiveness of B cells. Cell Immunol. 1973 Mar;6(3):442–456. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontiainen S., Mäkelä O. Effect of the number of primed cells on the production of IgM and IgG antibodies in an adoptive secondary response. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(5):417–427. doi: 10.1159/000230136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafleur L., Miller R. G., Phillips R. A. A quantitative assay for the progenitors of bone marrow-associated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1363–1374. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. F., Miller J. F. Cell to cell interaction in the immune response. II. The source of hemolysin-forming cells in irradiated mice given bone marrow and thymus or thoracic duct lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Oct 1;128(4):821–837. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.4.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Pike B. L. Studies on the differentiation of B lymphocytes in the mouse. Immunology. 1973 Jul;25(1):33–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmond D. G., Nossal G. J. Differentiation of lymphocytes in mouse bone marrow. I. Quantitative radioautographic studies of antiglobulin binding by lymphocytes in bone marrow and lymphoid tissues. Cell Immunol. 1974 Jul;13(1):117–131. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmond D. G., Nossal G. J. Differentiation of lymphocytes in mouse bone marrow. II. Kinetics of maturation and renewal of antiglobulin-binding cells studied by double labeling. Cell Immunol. 1974 Jul;13(1):132–145. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif A. E., Allen J. M. Mouse thymic iso-antigens. Nature. 1966 Jan 29;209(5022):521–523. doi: 10.1038/209521b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausbauch P., Sulica A., Givol D. General method for the detection of cells producing antibodies against haptens and proteins. Nature. 1970 Jul 4;227(5253):68–69. doi: 10.1038/227068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



