Abstract
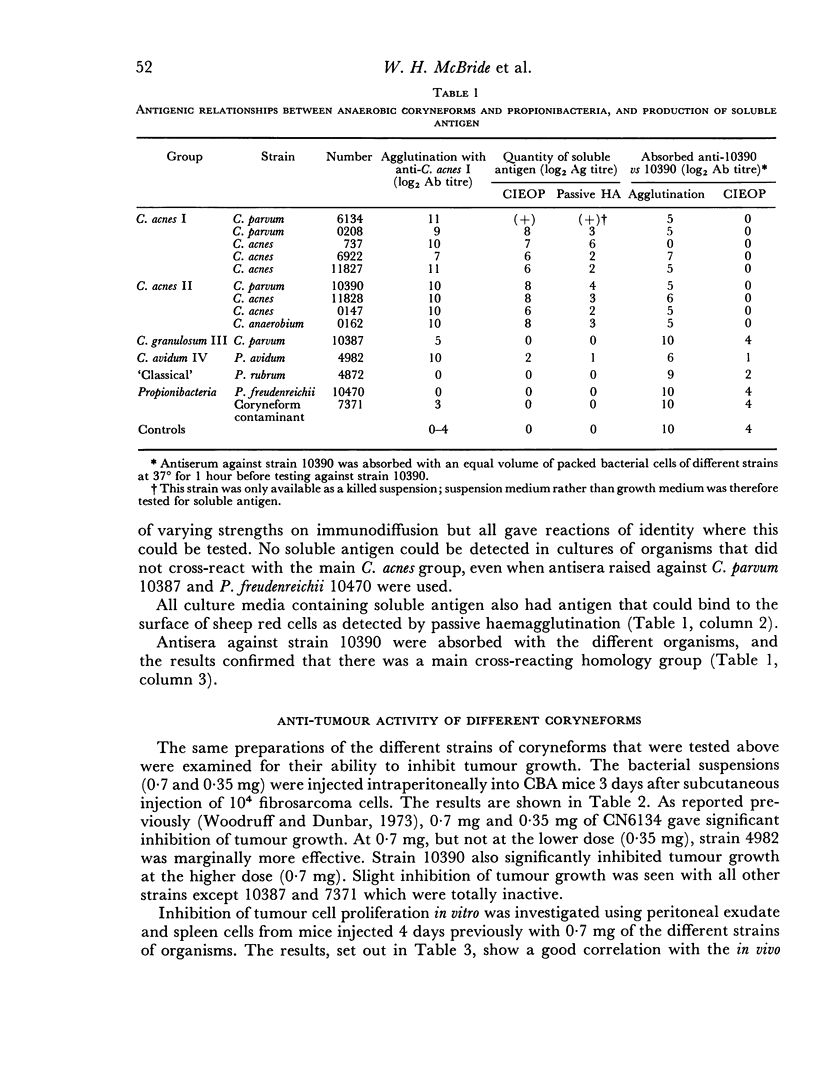
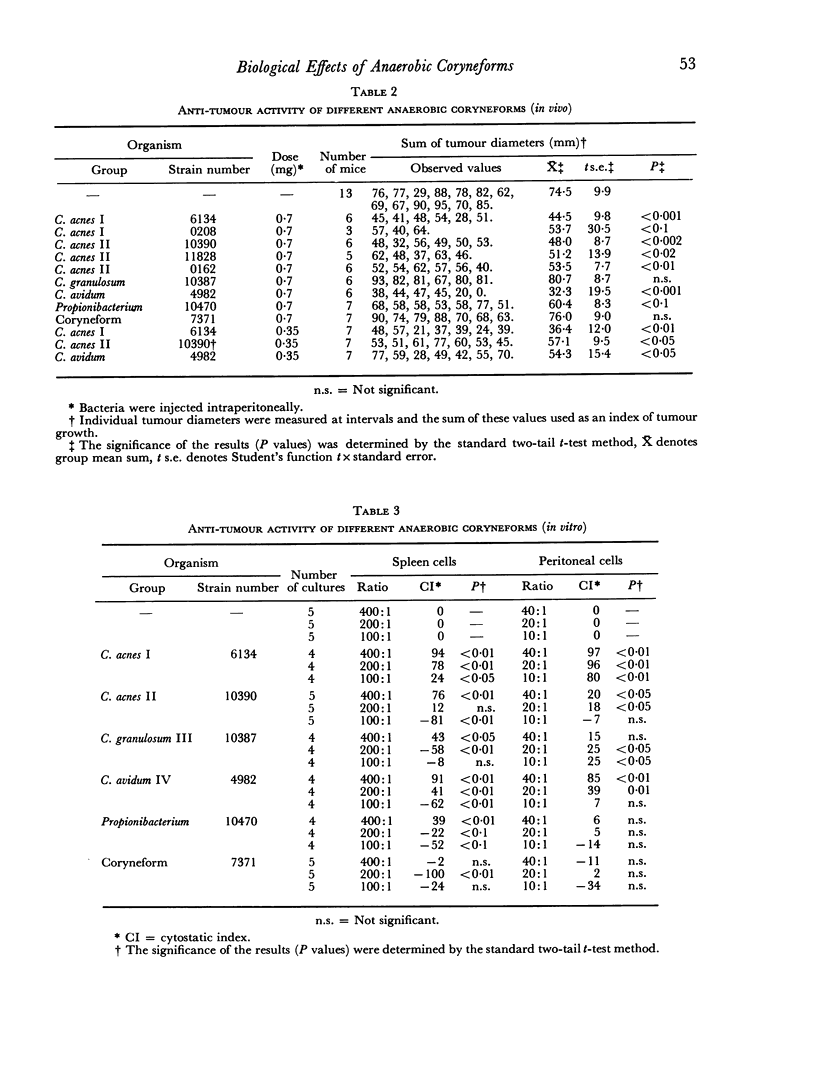
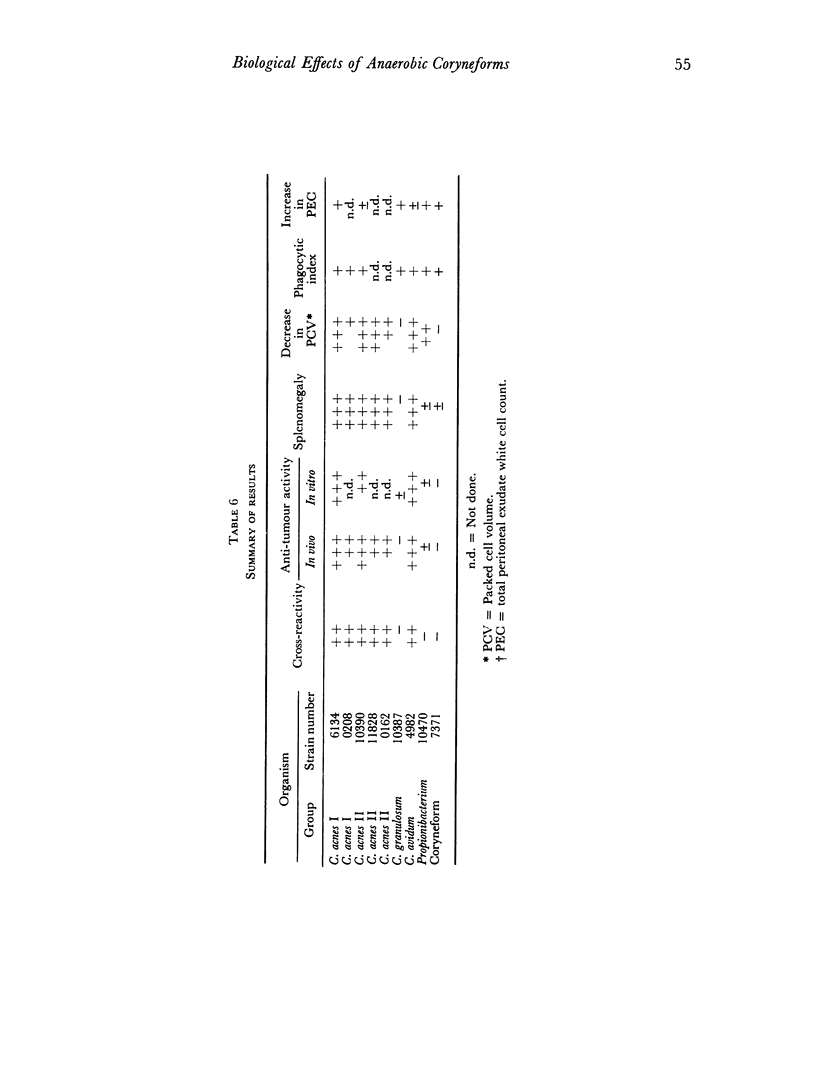
Various strains of anaerobic coryneforms and the closely related Propionibacteria have been compared in vivo with respect to their anti-tumour activity. Their effectiveness has been correlated with their serological relationship and to some extent with their ability to stimulate the lymphoreticular system. Organisms belonging to Corynebacterium acnes groups I and II and C. avidum group IV were active anti-tumour agents, although of varying effectiveness. These strains are serologically closely related and all produce a soluble cross-reacting antigen. The single C. granulosum group III strain which we tested, an unclassified coryneform, and the classical Propionibacteria did not cross-react with the main group and had little or no anti-tumour activity. At the high dose (0.7 mg) we used, all strains, whether they inhibited tumour development or not, enhanced clearance of colloidal carbon and stimulated production of an inflammatory peritoneal exudate; at lower dosage the results were too variable to permit valid comparison. At the higher dose anti-tumour activity of a strain appeared to correlate best with ability to produce splenomegally and decrease red cell volume in the blood.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIOZZI G., BENACERRAF B., STIFFEL C., HALPERN B. N. Etude quantitative de l'activité granulopexique du système réticuloendothéliai chez la souris. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1954 Mar;148(5-6):431–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas H. C., Gunter S. E. The Taxonomic Position of Corynebacterium acnes. J Bacteriol. 1946 Jul;52(1):15–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Immunostimulation-inhibition of tumor cell growth in vitro utilizing tumor target cells labeled with 125I-iodo-deoxyuridine. Immunol Commun. 1973;2(5):483–493. doi: 10.3109/08820137309022820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN B. N., PREVOT A. R., BIOZZI G., STIFFEL C., MOUTON D., MORARD J. C., BOUTHILLIER Y., DECREUSEFOND C. STIMULATION DE L'ACTIVIT'E PHAGOCYTAIRE DU SYST'EME R'ETICULOENDOTH'ELIAL PROVOQU'EE PAR CORYNEBACTERIUM PARVUM. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1964 Jan;1:77–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Cummins C. S. Cell wall composition and deoxyribonucleic acid similarities among the anaerobic coryneforms, classical propionibacteria, and strains of Arachnia propionica. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1047–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1047-1066.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride W. H., Jones J. T., Weir D. M. Increased phagocytic cell activity and anaemia in Corynebacterium parvum treated mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Feb;55(1):38–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Henderson D. C., White R. G. The role of anaerobic coryneforms on specific and non-specific immunological reactions. I. Effect on particle clearance and humoral and cell-mediated immunological responses. Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):977–995. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr I., Wheeler E., Alexander P. Similarities of the anti-tumour actions of endotoxin, lipid A and double-stranded RNA. Br J Cancer. 1973 May;27(5):370–389. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1973.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Burke K. Serum hepatitis antigen (SH): rapid detection by high voltage immunoelectroosmophoresis. Science. 1970 Aug 7;169(3945):593–595. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3945.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., O'Neill G. J., Wapshaw K. G. Role of anaerobic coryneforms in specific and non-specific immunological reactions. II. Production of a chemotactic factor specific for macrophages. Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):997–1006. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., Boak J. L. Inhibitory effect of injection of Corynebacterium parvum on the growth of tumour transplants in isogenic hosts. Br J Cancer. 1966 Jun;20(2):345–355. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1966.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., McBride W. H., Dunbar N. Tumour growth, phagocytic activity and antibody response in Corynebacterium parvum-treated mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jul;17(3):509–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M., Dunbar N., Ghaffar A. The growth of tumours in T-cell deprived mice and their response to treatment with Corynebacterium parvum. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Aug 31;184(1074):97–102. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


