Abstract
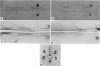
Rabbit antisera were produced against purified calf dermatosparatic procollagen and against the purified procollagens obtained from the culture medium of calf dermatosparatic cells. These antisera and their derived gamma-globulins were characterized by immunoprecipitation, double immunodiffusion and immunoelectrophoresis. Antiserum directed against dermatosparatic procollagen cross-reacted with the two different forms of procollagen obtained from the culture medium of dermatosparatic calf cells. Antiserum directed against onw of these procollagens, namely (pro alpha1)2 pro alpha2, cross reacted with dermatosparatic procollagen and also cross-reacted with the other procollagen,(pro alpha1)3. Antiserum directed against procollagen (pro alpha1)3 cross-reacted with dermatosparatic procollagen and with the procollagen (pro alpha1)2 pro alpha2. None of the antisera reacted with authentic calf skin collagen, or with the collagen extracted from the cell layer of the dermatosparatic calf cells in culture. Reduction andalkylation of the procollagens abolished the antigen-antibody reactions, while prior digestion of the antigens with bacterial collagenase did not eliminate the immunological reaction. Antigenic determinants in the cell culture procollagens were found at the COOH-terminal non-collagen peptide as well as at the NH2-terminal non-collagen peptide.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker U., Timpl R., Kühn K. Carboxyterminal antigenic determinants of collagen from calf skin. Localization within discrete regions of the nonhelical sequence. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):221–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church R. L., Tanzer M. L., Lapiere C. M. Identification of two distinct species of procollagen synthesized by a clonal line of calf dermatosparactic cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 8;244(136):188–190. doi: 10.1038/newbio244188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church R. L., Yaeger J. A., Tanzer M. L. Isolation and partial characterization of procollagen fractions produced by a clonal strain of calf dermatosparactic cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):785–799. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn L. D., Isersky C., Zupnik J., Lenaers A., Lee G., Lapiére C. M. Calf tendon procollagen peptidase: its purification and endopeptidase mode of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):40–44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapière C. M., Lenaers A., Kohn L. D. Procollagen peptidase: an enzyme excising the coordination peptides of procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3054–3058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCroskery P. A., Wood S., Jr, Harris E. D., Jr Gelatin: a poor substrate for a mammalian collegenase. Science. 1973 Oct 5;182(4107):70–71. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4107.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer M. L., Church R. L., Yaeger J. A., Wampler D. E., Park E. Procollagen: intermediate forms containing several types of peptide chains and non-collagen peptide extensions at NH2 and COOH ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Wick G., Furthmayr H., Lapiére C. M., Kühn K. Immunochemical properties of procollagen from dermatosparactic calves. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 1;32(3):584–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]