Abstract
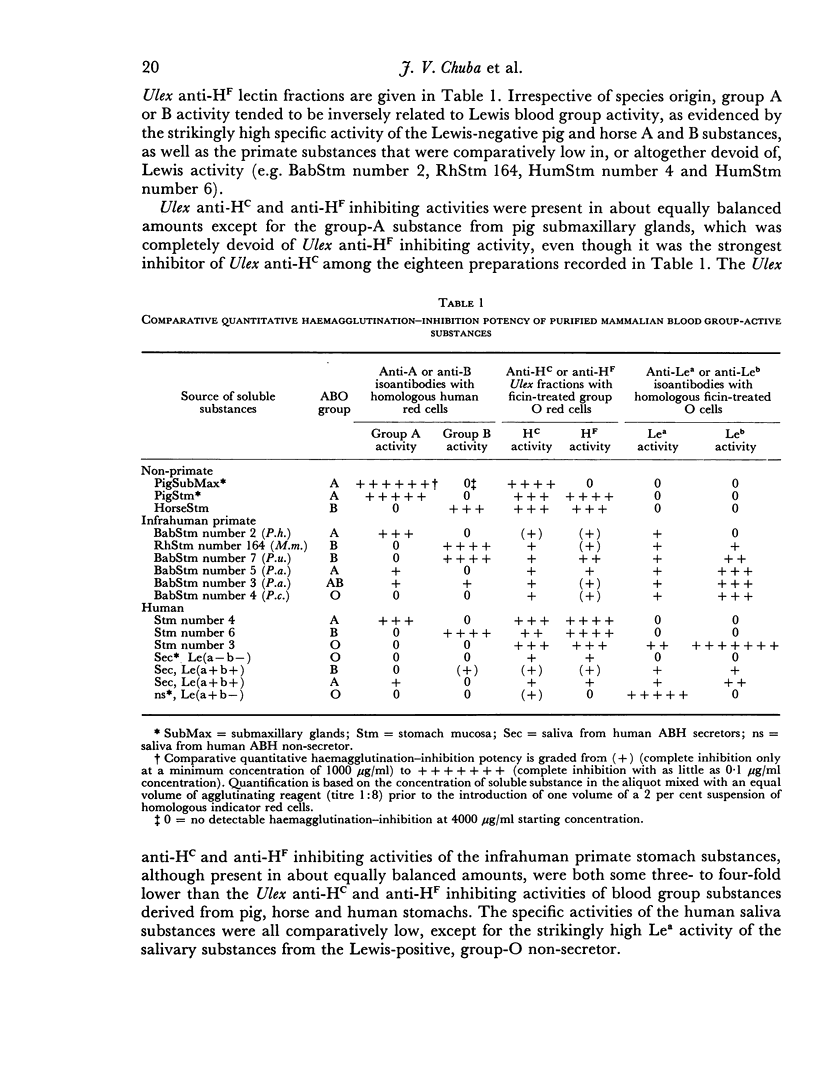
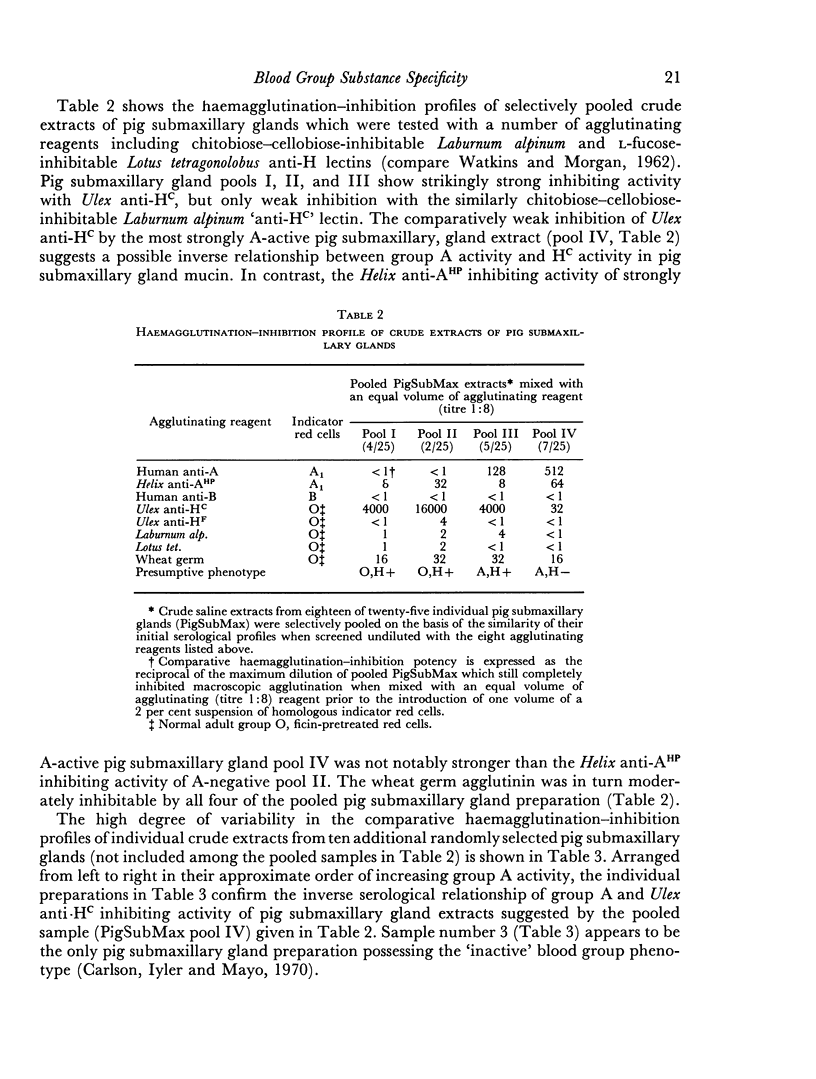
Purified blood group-active substances derived from different pig, horse, baboon, Rhesus monkey and human tissues were quantitatively studied for their haemagglutination inhibiting potency with: (1) human IgM anti-A and anti-B; (2) human anti-Lea and anti-Leb; (3) Ulex europaeus extracts separated into lectin fractions with respective L-fucose-inhibitable ('anti-HF') and chitobiose-cellobiose-inhibitable ('anti-HC') combining sites. Irrespective of species origin, A and B blood group activity per milligram of purified material tended to be strikingly higher in substances low in, or devoid of, Lewis blood group activity. Most of the blood group substances displayed variable but about equally balanced amounts of Ulex anti-HF and anti-HC inhibiting activity. In contrast, pig submaxillary gland mucins displayed strikingly high levels of Ulex anti-HC inihibiting activity, even in the complete absence of Ulex anti-HF inhibiting activity. These serological findings are consistent with current biochemical concepts regarding the heterosaccharide microheterogeneity of blood group-active glycoproteins.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aminoff D., Morrow M. P. Effect of sialidase on blood group specificity of hog submaxillary glycoproteins. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jul 3;8(6):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN P. C., GLYNN L. E., HOLBOROW E. J. Lewisa substance in saliva; a qualitative difference between secretors and non-secretors. Vox Sang. 1959 Feb;4(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1959.tb04306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester M. A., Watkins W. M. Alpha-L-fucosyltransferases in human submaxillary gland and stomach tissues associated with the H, Lea and Leb blood-group characters and ABH secretor status. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 31;34(6):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuba J. V., Kuhns W. J., Nigrelli R. F. The use of catfish, Ictalurus nebulosus (Le Sueur), as experimental animals for immunization with human secretor saliva and other antigenic materials. J Immunol. 1968 Jul;101(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuba J. V., Kuhns W. J., Nigrelli R. F., Vandenheede J. R., Osuga D. T., Feeney R. E. Inhibition of lectins by antifreeze glycoproteins from an Antarctic fish. Nature. 1973 Mar 30;242(5396):342–343. doi: 10.1038/242342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Salegui M., Plonska H. Preparation and properties of porcine submaxillary mucins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jan;129(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing H. J., Moores P. P., Bolstridge M. C., Schleyer M. E., Klomfass H. J., Davidson G. R. The secretion of A,B,H and Lewis blood group substances in the gastric juice and saliva of chacma baboons (Papio ursinus, Kerr) and vervet monkeys (Cercopithecus pygerythrus, Cuvier. J Med Primatol. 1974;3(3):185–194. doi: 10.1159/000460002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory L. L. Comparison of lectin anti-H reagents. Vox Sang. 1967 Oct;13(4):357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1967.tb03120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory L. L. Differences in the H antigen on human buccal cells from secretor and non-secretor individuals. Vox Sang. 1966 Mar-Apr;11(2):137–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1966.tb04217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman E. F., Kobata A., Ginsburg V. An enzymatic basis for Lewis blood types in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1489–1494. doi: 10.1172/JCI106115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO Y., TSUIKI S., NISIZAWA K., PIGMAN W. Action of proteolytic enzymes on purified bovine submaxillary mucin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 30;106:233–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb16641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Kabat E. A. Studies on specificity and binding properties of the blood group A reactive hemagglutinin from Helix pomatia. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1684–1692. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearn V. M., Smith Z. G., Watkins W. M. An a-N-acetyl-D-galactosaminyltransferase associated with the human blood-group A character. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(2):315–317. doi: 10.1042/bj1090315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Kahane I., Marchesi V. T. Studies on the major sialoglycoprotein of the human red cell membrane. Isolation and characterization of tryptic glycopeptides. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3131–3138. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobata A., Grollman E. F., Ginsburg V. An enzymic basis for blood type A in humans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 20;124(1):609–612. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. O., Kabat E. A., Beychok S. Immunochemical studies on blood groups. 43. The interaction of blood group substances from various sources with a plant lectin, concanavalin A. J Immunol. 1969 Jun;102(6):1354–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Tillack T. W., Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Scott R. E. Chemical characterization and surface orientation of the major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1445–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus D. M., Cass L. E. Studies of blood group substances. 3. A caprine antiserum containing antibodies to two antigenic determinants on type H hog gastric mucin. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):987–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto I., Osawa T. On the specificity of various heterologous anti-H hemagglutinins. Vox Sang. 1971 Dec;21(6):548–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb04814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto I., Osawa T. Purification and characterization of a Cytisus-type Anti-H(O) phytohemagglutinin from Ulex europeus seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Oct;140(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90092-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto I., Osawa T. Purification and characterization of an anti-H(O) phytohemagglutinin of Ulex europeus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 11;194(1):180–189. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokop O., Uhlenbruck G., Köhler W. A new source of antibody-like substances having anti-blood group specificity. A discussion on the specificity of Helix agglutinins. Vox Sang. 1968;14(5):321–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1968.tb01722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race C., Ziderman D., Watkins W. M. An alpha-d-galactosyltransferase associated with the blood-group B character. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(5):733–735. doi: 10.1042/bj1070733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Grollman E. F., Ginsburg V. An enzymatic basis for secretor status and blood group substance specificity in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):224–230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbruck G., Reifenberg U., Heggen M. On the specificity of broad spectrum agglutinins. IV. Invertebrate agglutinins: current status, conceptions and further observations on the variation of the Hel receptor in pigs. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1970 Jun;139(5):486–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATKINS W. M., MORGAN W. T. Further observations on the inhibition of blood-group specific serological reactions by simple sugars of known structure. Vox Sang. 1962;7:129–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1962.tb03238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zschocke R. H., Grieble H. G., Bach G. L., Anderson T. O. Studies on IgA. I. Fractionation procedure for isolation of IgA from pooled normal human plasma. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):625–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]