Abstract
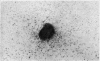
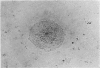
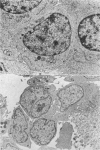
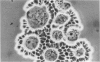
The purpose of this investigation was the induction of clonal proliferation of PHA-stimulated normal human lymphocytes using a two-layer soft agar technique. Essential conditions for colony formation include preceding sensitization of lymphocytes with PHA, and continuous presence of PHA in the soft agar culture. Two types of colonies developed: large colonies which appeared 3-4 days after seeding and comprised, after 5-6 days, 200-500 cells, and small colonies which were seen after 6-7 days of culture, resulting in production of 50-150 cells. Morphological study showed that all cells were blast-like and the mitotic index exceeded that in liquid medium by a factor of 50. Comparison between the number of colonies developing from cultured bone marrow and spleen cells with those from peripheral blood showed that, in proportion to the number of lymphocytes seeded, a larger number of colonies developed from bone marrow cells and a lower number of colonies developed from spleen cells. The time required for sensitization of lymphocytes in liquid medium with PHA was found to be no less than 12 hours. The greatest number of colonies appeared when the optimal concentration of PHA was placed in the lower agar layer. A linear relation between the number of cells seeded and the number of resulting colonies was found. One out of 2 X 10(3) or 3 X 10(3) lymphocytes in peripheral blood has the potential to develop as colony. The rosette-forming ability and morphological identification of the cells suggest that the colonies are composed of T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF







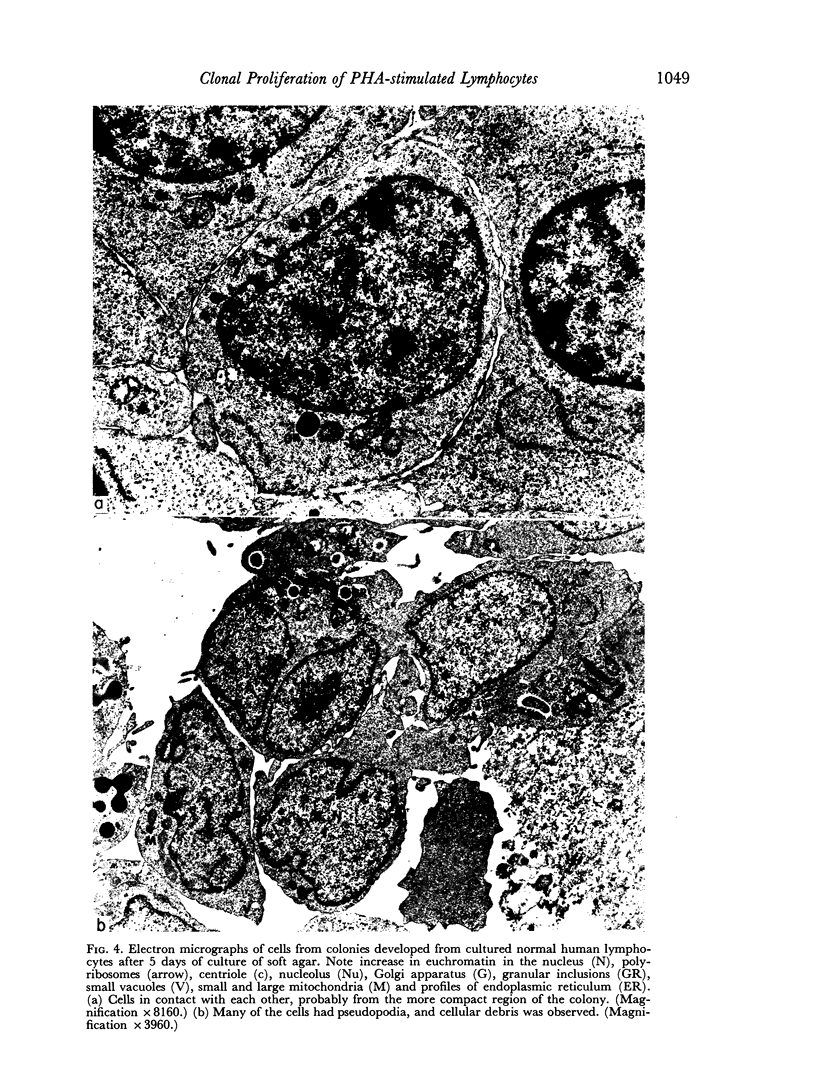
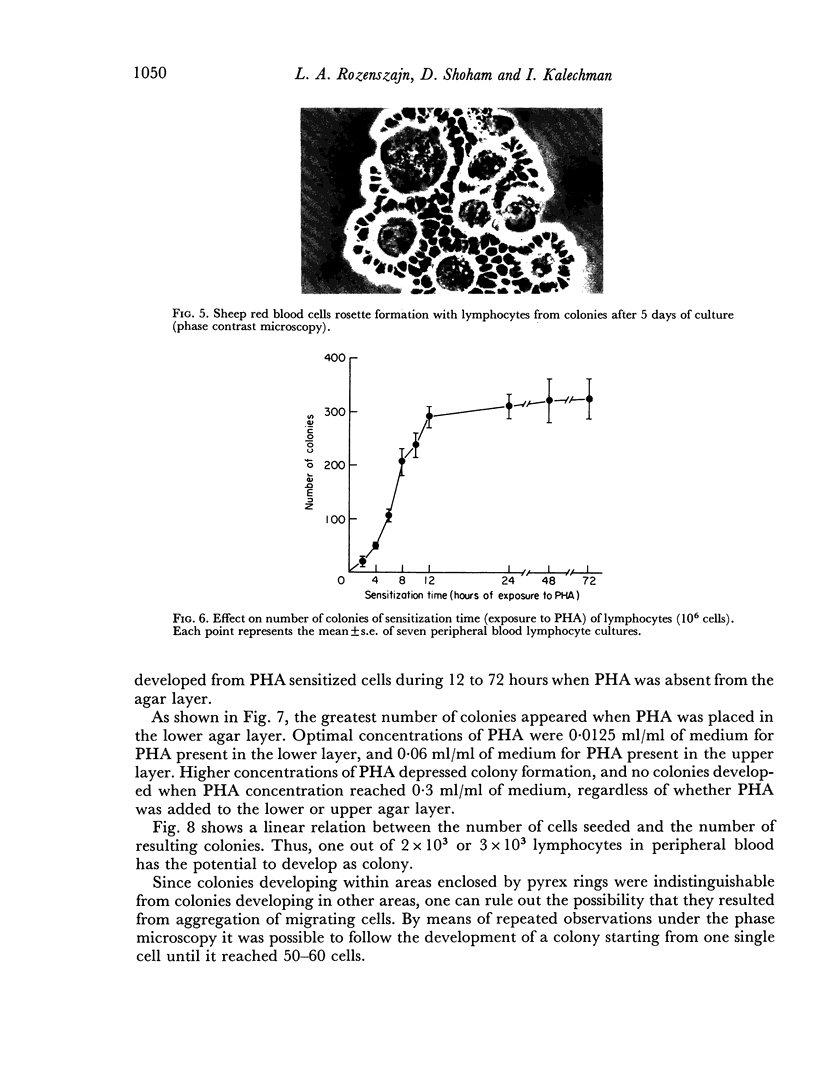
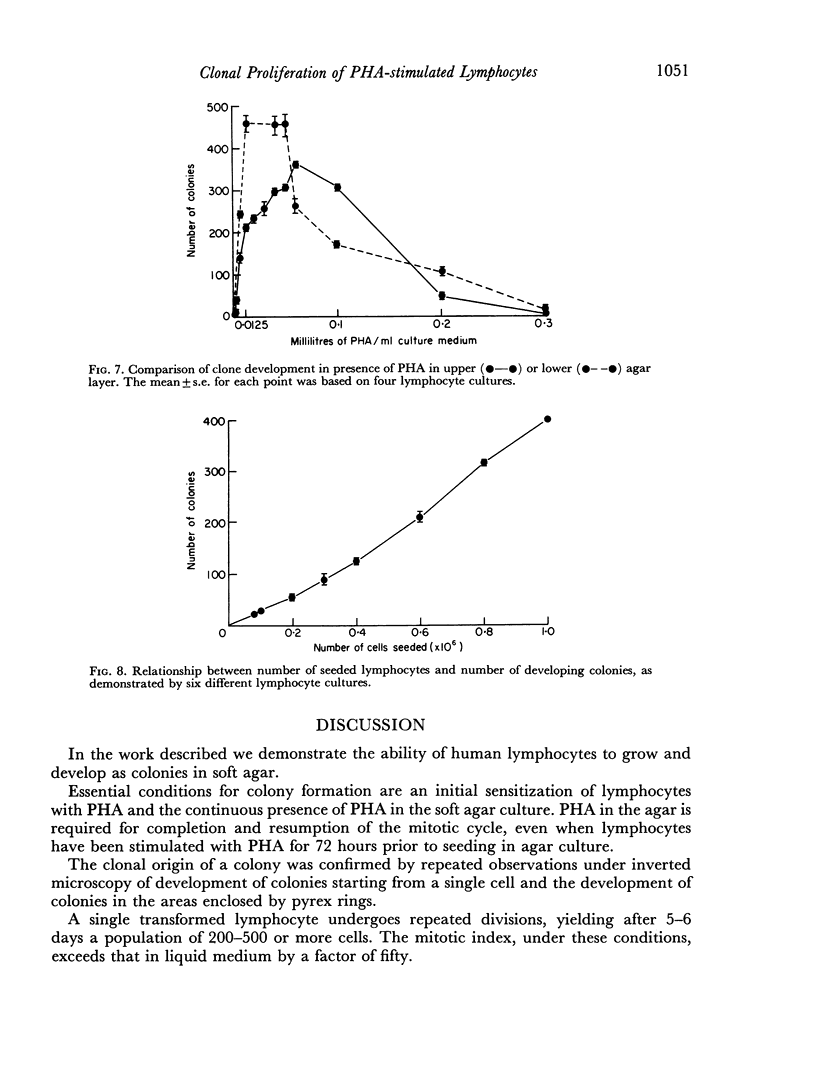




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisenberg A. C., Bloch K. J. Immunoglobulins on the surface of neoplastic lymphocytes. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 10;287(6):272–276. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208102870603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENDER M. A., PRESCOTT D. M. DNA synthesis and mitosis in cultures of human peripheral leukocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Aug;27:221–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. R., Metcalf D. The growth of mouse bone marrow cells in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Jun;44(3):287–299. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER E. H., BARKHAN P., HALE A. J. Observations on the proliferation of human leucocytes cultured with phytohaemagglutinin. Br J Haematol. 1963 Jan;9:101–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1963.tb05446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervenick P. A., Boggs D. R. In vitro growth of granulocytic and mononuclear cell colonies from blood of normal individuals. Blood. 1971 Feb;37(2):131–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. W., Bloom A. D. Cloning human lymphocytes in vitro. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):171–173. doi: 10.1038/227171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Golde D. W. Production of colony-stimulating activity by human lymphocytes. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):703–704. doi: 10.1038/248703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A. S., Turk A., Glade P. R., Chessin L. N. Lymphocyte culture in agar. Lancet. 1968 Jan 13;1(7533):89–90. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARNES P., BARKER B. E., BROWNHILL L. E., FANGER H. MITOGENIC ACTIVITY IN PHYTOLACCA AMERICANA (POKEWEED). Lancet. 1964 Nov 21;2(7369):1100–1101. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYHOE F. G., QUAGLIONO D., FLEMANS R. J. Consecutive use of Romanowsky and periodic-acid-Schiff techniques in the study of blood and bone-marrow cells. Br J Haematol. 1960 Jan;6:23–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1960.tb06212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Senn J. S., Till J. E., McCulloch E. A. Colony formation by normal and leukemic human marrow cells in culture: effect of conditioned medium from human leukocytes. Blood. 1971 Jan;37(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Mendes N. F., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Binding of sheep red blood cells to a large population of human lymphocytes. Nature. 1971 Apr 23;230(5295):531–532. doi: 10.1038/230531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORHEAD P. S., NOWELL P. C., MELLMAN W. J., BATTIPS D. M., HUNGERFORD D. A. Chromosome preparations of leukocytes cultured from human peripheral blood. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Sep;20:613–616. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall W. H., Valentine F. T., Lawrence H. S. Cellular immunity in vitro. Clonal proliferation of antigen-stimulated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):327–343. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOWELL P. C. Phytohemagglutinin: an initiator of mitosis in cultures of normal human leukocytes. Cancer Res. 1960 May;20:462–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paran M., Sachs L., Barak Y., Resnitzky P. In vitro induction of granulocyte differentiation in hematopoietic cells from leukemic and non-leukemic patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1542–1549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike B. L., Robinson W. A. Human bone marrow colony growth in agar-gel. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Aug;76(1):77–84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040760111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The cloning of normal "mast" cells in tissue culture. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):319–324. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ Y. SEPARATION OF LYMPHOCYTES, POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES AND MONOCYTES ON GLASS COLUMNS, INCLUDING TISSUE CULTURE OBSERVATIONS. Blood. 1964 Jun;23:811–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabellino E., Colon S., Grey H. M., Unanue E. R. Immunoglobulins on the surface of lymphocytes. I. Distribution and quantitation. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):156–167. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. T and B lymphocytes and immune responses. Nature. 1973 Mar 2;242(5392):19–23. doi: 10.1038/242019a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Two distinct populations of peripheral lymphocytes in mice distinguishable by immunofluorescence. Immunology. 1970 Oct;19(4):637–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenszajn L. A., Fischer D. Enzymatic and chemical changes in human lymphocyte cultures. Acta Haematol. 1969;42(3):138–147. doi: 10.1159/000208773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenszajn L., Leibovich M., Shoham D., Epstein J. The esterase activity in megaloblasts, leukaemic and normal haemopoietic cells. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jun;14(6):605–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb00366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoham D., David E. B., Rozenszajn L. A. Cytochemical and morphologic identification of macrophages and eosinophils in tissue cultures of normal human bone marrow. Blood. 1974 Aug;44(2):221–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulos G., Elliott E. V. Formation of mouse or sheep red-blood-cell rosettes by lymphocytes from normal and leukaemic individuals. Lancet. 1974 Apr 6;1(7858):600–601. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92655-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA Y., EPSTEIN L. B., BRECHER G., STOHLMAN F., Jr TRANSFORMATION OF LYMPHOCYTES IN CULTURES OF HUMAN PERIPHERAL BLOOD. Blood. 1963 Nov;22:614–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Grey H. M., Rabellino E., Campbell P., Schmidtke J. Immunoglobulins on the surface of lymphocytes. II. The bone marrow as the main source of lymphocytes with detectable surface-bound immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1188–1198. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Carr M. C., Fudenberg H. H. The human rosette-forming cell as a marker of a population of thymus-derived cells. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2537–2543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Chantler S., Fudenberg H. H. Isolation of normal T cells in chronic lymphatic leukaemia. Lancet. 1973 Jan 20;1(7795):126–129. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. The ultrastructure of lymphocytes. Semin Hematol. 1969 Jan;6(1):4–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]