Abstract
Budding yeast securin/Pds1p, an inhibitor of the anaphase activator separase/Esp1p, is involved in several checkpoint pathways and in promoting Esp1p's nuclear localization. Using a modified synthetic genetic array (SGA) screen for genes that become essential in the absence of Pds1p, we uncovered roles for uncharacterized genes in cell cycle processes, including Esp1p activation.
THE fidelity of the cell division cycle is ensured, in part, by conserved regulatory mechanisms known as checkpoints that govern the timely execution of numerous cell cycle processes. Distinct checkpoints are activated in response to specific cellular defects, resulting in a cell cycle delay that persists until the defect is repaired. Thus, cells can compensate for certain intracellular deficiencies by activating a checkpoint response; conversely, in the absence of checkpoint pathways, innocuous mutations may become deleterious. This notion is the basis of the present study, in which we wished to identify novel genes involved in key cell cycle processes by sensitizing cells to internal damage through checkpoint inactivation.
The separation of sister chromatids at the metaphase-to-anaphase transition marks the commitment of cells to the completion of mitosis. As a result, cellular defects that could adversely affect chromosome segregation must be dealt with before anaphase takes place.
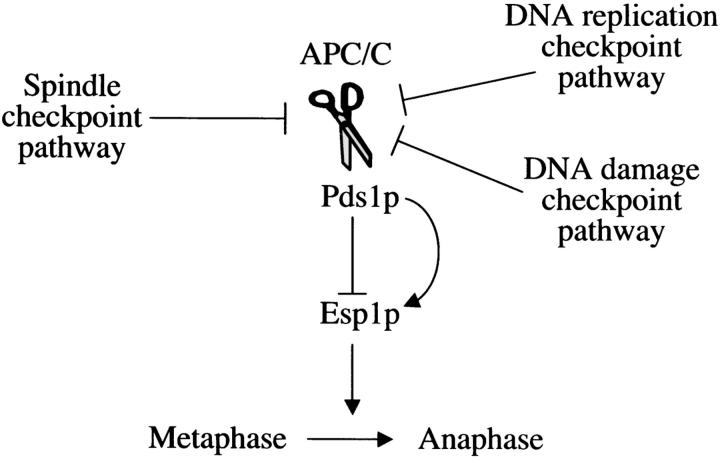
Anaphase initiation occurs when securin (Pds1p in budding yeast) is targeted for degradation by a ubiquitin ligase, the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) (Figure 1; for review see Peters 2002). Securin degradation leads to the activation of the protease separase (Esp1p in budding yeast), which is responsible for inducing sister chromatid separation (reviewed in Uhlmann 2003). Three checkpoint pathways are known to use the budding yeast Pds1p as a mediator of a mitotic cell cycle delay (Figure 1): the spindle checkpoint pathway, which is activated in the absence of proper kinetochore-spindle microtubule interactions (reviewed in Lew and Burke 2003); the DNA damage checkpoint pathway, which is activated in the presence of DNA damage (reviewed in Melo and Toczyski 2002); and the DNA replication checkpoint pathway, which is activated in response to stalled replication forks (reviewed in Longhese et al. 2003). The checkpoint-induced cell cycle delay is accomplished, at least in part, by the stabilization of Pds1p, either by affecting APC/C activity [in the case of the spindle checkpoint pathway (Yu 2002)] or by modifying Pds1p itself [in the case of the DNA damage checkpoint pathway (Wang et al. 2001; Agarwal et al. 2003)]. Deletion of the PDS1 gene results in the complete ablation of the spindle checkpoint pathway and the partial inactivation of the DNA damage and DNA replication checkpoint pathways, for which there are Pds1p-independent mechanisms for inducing a cell cycle delay (Melo and Toczyski 2002).
Figure 1.—
The role of Pds1p in mitotic regulation. Pds1p is an inhibitor of the protease Esp1p that activates anaphase by inducing sister chromatid separation. At the onset of anaphase, Pds1p is degraded in a process that involves the APC/C. At least three checkpoint pathways inhibit mitotic progression by affecting the degradation of Pds1p. Pds1p not only inhibits Esp1p but also serves as its activator by promoting the nuclear localization of Esp1p (indicated by the curved arrow). See text for more details.
Pds1p is also required for promoting the nuclear localization of Esp1p (Figure 1; Jensen et al. 2001; Agarwal and Cohen-Fix 2002) and, possibly, by analogy to higher eukaryotes, for Esp1p activation (Jager et al. 2001; Jallepalli et al. 2001; Mei et al. 2001). In the absence of Pds1p, cells fail to grow at elevated temperatures (>28°) due to a deficiency in Esp1p activity (Yamamoto et al. 1996; Jensen et al. 2001). However, unlike Esp1p, Pds1p is not essential for viability. Thus, under permissive conditions, the nuclear localization, and perhaps activation, of Esp1p in pds1Δ strains is carried out by Pds1p-independent mechanisms.
Given the involvement of Pds1p in several checkpoint pathways, we reasoned that by inactivating Pds1p we could uncover novel proteins involved in spindle function, DNA metabolism, or DNA replication. Mutations in genes coding for these proteins may be tolerated in an otherwise wild-type cell through the presence of one or more checkpoint pathways. However, in a pds1Δ background, where checkpoint responses are either abolished or compromised, these mutations could cause a severe growth inhibition or death. This type of genetic interaction, known as synthetic lethality, has been traditionally used to identify proteins acting in redundant pathways (Hartwell 2004). Here, we used the synthetic lethality scheme to uncover mutations whose harmful affects are normally masked by regulatory pathways. We also anticipated that this screen would lead to the identification of genes involved in Pds1p-independent mechanisms for Esp1p nuclear localization and/or activation. In this case, a synthetic interaction is likely to reflect the inactivation of pathways that are redundant or partially overlapping with Pds1p function.
The screen for synthetic interactions with pds1Δ was carried out by a modified synthetic genetic array (SGA) analysis (Tong et al. 2001; see legend to Figure 2). In the original method, a strain carrying a mutation in a query gene was mated with a collection of ∼4700 strains, each carrying a single deletion in a nonessential gene (designated genenΔ, where genen is one of the ∼4700 nonessential genes that is deleted). This array of heterozygous diploids was induced to undergo meiosis, and the inability to obtain a double mutant, namely a cell with the queried mutation and the deleted gene from the collection (genenΔ), was evidence for a synthetic lethal interaction. In this study we modified the SGA method and incorporated a plasmid-based step. Briefly, the queried mutation, in our case pds1Δ, was combined with mutations from the deletion collection in the presence of a centromeric plasmid, pPDS1, coding for URA3 and a wild-type copy of the PDS1 gene. Following meiosis and germination, pds1Δ genenΔ double-mutant strains carrying pPDS1 were tested for synthetic lethality by examining their ability to survive without the plasmid (Figure 2). The advantages of using a plasmid-based assay were threefold:
It eliminated many false positives that arose from the inability to obtain double mutants due procedural reasons unrelated to synthetic interactions.
It allowed us to circumvent synthetic interactions that cause lethality not during growth per se but at the time of spore germination, the requirements and regulation of which are poorly understood but could be significantly different from those for vegetative growth.
Cells lacking Pds1p are prone, in and of themselves, to high levels of chromosome instability and exhibit poor growth even at the permissive temperature (23°). Including a wild-type copy of the PDS1 gene ensured that cells were genetically stable throughout the experiment, thus reducing the likelihood of suppression or exacerbation of a synthetic interaction due to aneuploidy.
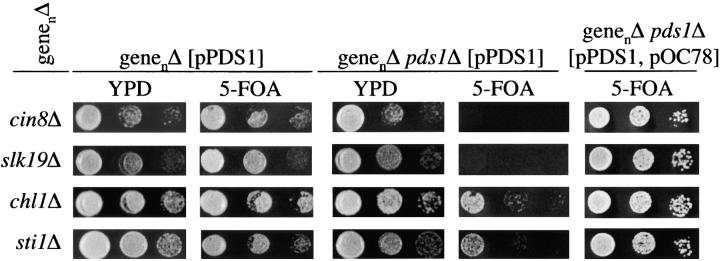
Figure 2.—
A screen for synthetic lethal interactions with pds1Δ using a modified SGA analysis. A pds1Δ strain (MATα MFα::MFαpromoterLEU2 can1Δ::MFApromoterHIS3 his3Δ ura3Δ met15Δ lys2Δ pds1::NAT, S288C background) carrying a centromeric plasmid encoding PDS1 and URA3 (pPDS1) was crossed individually to ∼4700 MATa strains of the yeast deletion collection, each containing a single deletion of a nonessential gene (designated genenΔ). Following diploid selection, the strains were sporulated and selected for double mutants (pds1Δ genenΔ) containing pPDS1 (for double-mutant selection procedure see Tong et al. 2001). Of the 4700 crosses, ∼90% gave rise to double-mutant strains containing the plasmid. Of those, 260 strains showed a putative synthetic interaction as scored by the inability to lose pPDS1 (see below). A total of 220 of these strains were further examined by tetrad analysis. For each of these strains, four double-mutant isolates (pds1Δ genenΔ) and two single-mutant isolates (genenΔ) were assayed by three 10-fold serial dilutions for their ability to survive in the absence of Pds1p function by counterselecting for pPDS1 on 5-FOA media. Because 5-FOA is toxic to cells expressing URA3, only cells that have spontaneously lost pPDS1 would be able to grow on the 5-FOA plates. The inability to grow on 5-FOA, indicative of a requirement for Pds1p for growth, was manifested by either synthetic lethality (for example, see cin8Δ or slk19Δ) or severe synthetic sickness (see chl1Δ or sti1Δ). Double-mutant combinations that were unable to grow on 5-FOA were transformed with pOC78, a centromeric plasmid coding for PDS1 LEU2 HIS3. If the inability of the genenΔ pds1Δ pPDS1 strain to grow on 5-FOA was due to a requirement for PDS1 (and not due to the integration of the URA3 gene into the chromosome, for example), then the presence of pOC78 should allow these cells to grow on 5-FOA. Of the 220 strains examined by tetrad analysis, 21 showed a true synthetic interaction. The identity of the gene disruptions in these strains was verified by sequencing. The high false-positive rate, which is in line with recent reports (Tong et al. 2004), may be due to technical challenges associated with the automated procedure (Tong et al. 2001) that can be affected by various factors such as growth rate differences and morphology effects on transfer efficiency.
The modified SGA screen was carried out twice, resulting in 260 putative synthetic interactions (e.g., synthetic lethality or synthetic sickness), with only a 10% overlap between the two screens. A total of 220 diploid parents containing pPDS1 were subjected to tetrad analysis as described in the legend to Figure 2. Each genenΔ mutant strain was tested for growth by itself and in combination with the pds1Δ mutation with pPDS1 (on YPD) or without pPDS1 [on plates containing 5-fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA), which allows growth of cells that have lost the URA3-containing plasmid; Figure 2]. To ensure that the 5-FOA sensitivity reflected dependence on PDS1, all double-mutant combinations carrying pPDS1 were further tested for their ability to grow on 5-FOA when another centromeric plasmid carrying PDS1 and a selectable marker other than URA3 was introduced (see legend for Figure 2). Under this condition, all strains with double-mutant combinations that resulted in synthetic lethality or sickness should be able to lose pPDS1 and grow on 5-FOA. On the basis of the growth phenotype, interactions were classified as “synthetically lethal” (for examples, see Figure 2, cin8Δ and slk19Δ), “synthetically sick” (Figure 2, chl1Δ and sti1Δ), or “noninteractors” (i.e., if growth in the presence or absence of pPDS1 were indistinguishable; not shown). The side-by-side analysis of the genenΔ mutant strain and the genenΔ pds1Δ double-mutant strain allowed us to eliminate false positives that resulted from a severe growth defect of the genenΔ mutation alone.
In all, 21 of the 220 mutations tested were verified as having a bona fide synthetic interaction with pds1Δ. The full list of synthetic interactions is shown in Table 1. These could be divided into five functional groups: microtubule dynamics, chromosome segregation, cell cycle regulators, heat-shock proteins, and proteins of unknown function. One gene identified in this screen that was previously unnamed was designated as SWS2, for sick without securin. Importantly, our screen was based on the premise that the absence of Pds1p function would uncover proteins involved in spindle- or DNA-related processes. This approach was validated by the isolation of mutant strains defective in microtubule-associated proteins (e.g., cin8Δ) that were known to require the spindle checkpoint pathway for viability (Geiser et al. 1997).
TABLE 1.
Synthetic interaction results
| ORF | Gene name |
Functiona | SI with pds1Δb |
SI with mad2c,d |
SI with rad9Δc,e |
SI with mrc1Δc,f |
Rescue of SI with pds1Δ by 2μESP1g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microtubule dynamics | |||||||
| YMR198W | CIK1 | Kar3 kinesin-binding protein | Lethal | Lethal | None | Sick | No |
| YOR349W | CIN1 | Tubulin-folding chaperone | Lethal | Lethal | None | None | No |
| YPL241C | CIN2 | Tubulin-folding chaperone | Lethal | None | None | None | No |
| YEL061C | CIN8 | Spindle-associated kinesin | Lethal | Lethal | None | None | No |
| YML094W | GIM5 | Tubulin folding | Lethal | Sick | None | None | No |
| Chromosome segregation | |||||||
| YPL008W | CHL1 | Helicase, sister chromatid cohesion | Sick | None | None | None | No |
| YPR135W | CTF4 | Associated with DNA polα | Sick | None | None | Lethal | No |
| YRM078C | CTF18 | Alternative RF-C subunit | Lethal | None | None | None | No |
| YPL018W | CTF19 | Kinetochore protein | Lethal | Lethal | None | None | No |
| YCL016C | DCC1 | Alternative RF-C subunit | Lethal | None | None | None | No |
| YOR195W | SLK19 | Kinetochore and spindle associated | Lethal | None | None | None | No |
| Cell cycle | |||||||
| YPR119W | CLB2 | Mitotic cyclin | Sick | None | None | None | No |
| YCR065W | HCM1 | Transcription factor | Sick | Sick | None | None | No |
| Heat Shock | |||||||
| YMR186W | HSC82 | Hsp90-type chaperone/heat shock | Sick | None | None | None | Yes |
| YOR027W | STI1 | Hsp90 cochaperone | Sick | None | None | None | Yes |
| YPL106C | SSE1 | Hsp70-type chaperone/heat shock | Lethal | None | None | None | No |
| Unknown function | |||||||
| YOR080W | DIA2 | F-box protein | Lethal | None | Lethal | None | No |
| YLR204W | QRI5 | Unknown | Sick | None | None | None | No |
| YNL081C | SWS2 | Unknown | Sick | None | None | None | No |
| YIL040W | APQ12 | Unknown | Lethal | Lethal | None | None | No |
| YDR200C | VPS64 | Mating-pheromone response | Sick | Lethal | None | None | No |
SI, synthetic interaction.
Function is based on the gene ontology annotation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae database (http://www.yeastgenome.org/) and references therein.
pds1Δ strain used was described in legend to Figure 2.
Crosses to mad2Δ, rad9Δ, and mrc1Δ strains were done with single mutants (genenΔ) that came out of the tetrad analysis done in the cross with pds1Δ.
Deletion of the MAD2 gene results in the inactivation of the spindle checkpoint pathway. The mad2Δ strain used was MATα can1Δ leu2Δ his3Δ lys2Δ ura3Δ mfa1Δ::MFApr-HIS3 mad2::NAT[pRL18] (pRL18: CEN URA3 MAD2 plasmid). Strain and plasmid were a gift from Dan Burke (University of Virginia).
Deletion of the RAD9 gene results in the inactivation of the DNA damage checkpoint pathway. The rad9Δ strain used was MATa ura3Δ leu2Δ his3Δ met15Δ rad9::NAT [pRAD9] (pRAD9: CEN URA3 RAD9 plasmid). pRAD9 was a gift from Steve Elledge (Harvard Medical School).
Deletion of the MRC1 gene results in the inactivation of the DNA replication checkpoint pathway. The mrc1Δ strain used was MATa ura3Δ leu2Δ his3Δ met15Δ mrc1::NAT [pMRC1] (pMRC1: CEN URA3 MRC1 plasmid). pMRC1 was a gift from Steve Elledge (Harvard Medical School).
Plasmid 2μESP1 is a pRS426 (2μURA3)-based plasmid encoding for ESP1 in which the URA3 gene was substituted for LYS2 by PCR-mediated recombination. This plasmid was transformed into pds1Δ genenΔ lys2 strains carrying pPDS1 that were isolated in the original tetrad analysis.
Next, we wished to determine which of the synthetic interactions listed in Table 1 was due to checkpoint failure. To this end, each of the single genenΔ strains was crossed to a strain defective in the spindle checkpoint pathway (mad2Δ), the DNA damage checkpoint pathway (rad9Δ), or the DNA replication checkpoint pathway (mrc1Δ). In each case, the checkpoint mutant strain harbored a wild-type copy of the mutant checkpoint gene (MAD2, RAD9, or MRC1, respectively) on a CEN URA3 plasmid. A synthetic interaction was evident by the ability of the double mutant (i.e., genenΔ with a checkpoint mutant) to grow in the presence, but not in the absence, of the plasmid, as described above (legend of Figure 2). As shown in Table 1, 11 mutants exhibited a synthetic interaction with at least 1 checkpoint mutant. As expected, mutations in most of the genes coding for microtubule-associated proteins showed a synthetic interaction (lethality or sickness) with mad2Δ. Moreover, among those that showed a synthetic interaction with any checkpoint mutant, most were with mad2Δ (8 of 11). This is consistent with the more prominent role played by Pds1p in the spindle assembly checkpoint than in the DNA replication or DNA damage checkpoint pathways. Interestingly, mutations in two genes coding for proteins of unknown function, APQ12 and VPS64 (also known as FAR9), also exhibited synthetic interactions with mad2Δ, suggesting that the proteins encoded by these genes may play a role in kinetochore or spindle function. Apq12p is an endoplasmic-reticulum-associated protein of unknown function (T. Slaby and O. Cohen-Fix, unpublished results) and Vps64p/Far9p was previously shown to have a role in the response to mating-pheromone-induced arrest (Kemp and Sprague 2003). Thus, in both cases, a connection to the spindle checkpoint pathway is intriguing. Likewise, a mutation in a gene coding for another protein of unknown function, Dia2p, a predicted F-box protein, was synthetically lethal with rad9Δ. Mutation of DIA2 causes a mild invasive growth phenotype (Palecek et al. 2000) and a modest stabilization of ectopically expressed cyclin E (Koepp et al. 2001). Intriguingly, both the pds1Δ dia2Δ and the rad9Δ dia2Δ synthetic lethal interactions were observed only in crosses with dia2Δ cells that had been propagated for numerous cell divisions, a finding that reflects the progressive accumulation of DNA damage that occurs in the absence of Dia2p (D. Blake and M. Tyers, unpublished results).
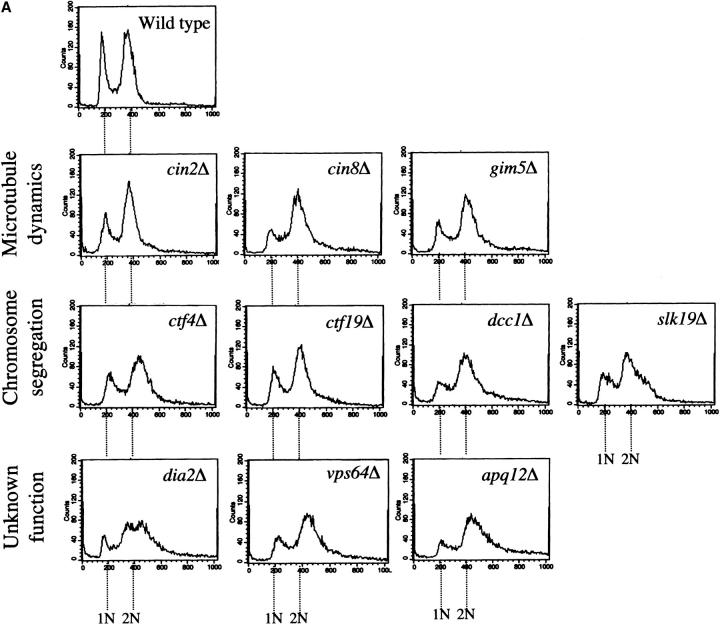
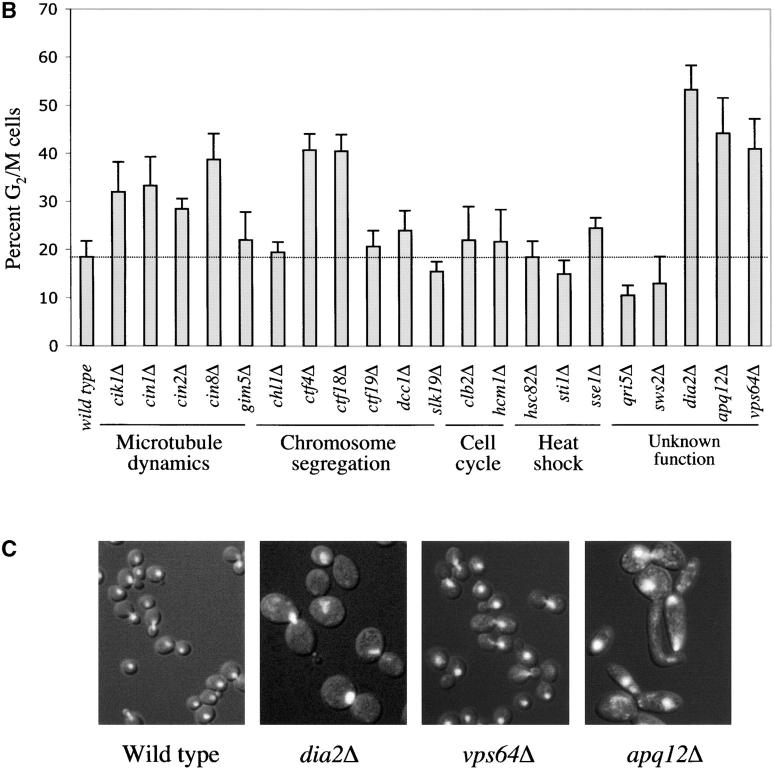
The synthetic lethality with pds1Δ and mutations in checkpoint genes suggested that in a checkpoint-proficient background, several of the mutations isolated in this screen might exhibit cell cycle delays, especially in G2/M, where the aforementioned checkpoint pathways are known to act. This was of particular interest in the case of apq12Δ, vps64Δ, and dia2Δ, mutations that were previously uncharacterized with regards to cell cycle profiles. To test this possibility, the cell cycle distribution of unperturbed logarithmic-phase cultures of the single mutants (i.e., a wild-type PDS1 and checkpoint-proficient background) was determined by flow cytometry analysis (Figure 3A) and cell morphology analysis (Figure 3B). As expected, many of the mutations in processes related to microtubule dynamics and chromosome segregation (Table 1) exhibited a G2/M accumulation either by flow cytometry or by cell morphology (Figure 3, A and B). This was also true for dia2Δ, apq12Δ, and vps64Δ, further supporting an involvement in DNA metabolism (for Dia2p) or spindle/kinetochore function (for Apq12p and Vps64p), as suggested by their genetic interactions with the respective checkpoint pathway mutations. Interestingly, the growth defect in dia2Δ, apq12Δ, or vps64Δ was also manifested in their relatively large cell size (Figure 3C), typical of cells that are experiencing a cell cycle delay. Taken together, these results strongly suggest that Dia2p, Apq12p, and Vps64p are involved in processes that affect cell cycle progression.
Figure 3.—
Cell cycle distribution of mutants that show a genetic interaction with pds1Δ. Wild-type and mutant strains in A and B were grown to early log phase, fixed in 70% ethanol, and analyzed by flow cytometry (A) and fluorescent microscopy (B) for cell cycle distribution. (A) Only strains whose flow cytometry profiles are different from wild type are shown. Note the relatively high fraction of cells with 2N DNA content in the mutants shown relative to wild type. (B) Histograms represent the percentage of cells with a large bud and an undivided nucleus, indicative of a G2/M phase. (C) Images of wild-type, dia2Δ, vps64Δ, and apq12Δ cells. Bright white areas indicate DNA (DAPI staining).
While this manuscript was in preparation, Tong et al. (2004) reported the results of an extensive SGA analysis involving numerous checkpoint mutations. The Tong et al. (2004) screen, done without the plasmid loss step, uncovered synthetic interactions between mad2Δ and many of the gene disruptions reported here, but not with apq12Δ, vps64Δ, or dia2Δ. Furthermore, the Tong et al. (2004) screen reported synthetic interactions between double-mutant combinations involving checkpoint genes that were viable in our hands, including mad2Δ with chl1Δ, ctf18Δ, or dcc1Δ and rad9Δ with ctf18Δ or dcc1Δ. There could be at least two reasons for these differences:
Due to the temperature sensitivity of the pds1Δ strain, all of our analyses were done at 23°, whereas the Tong et al. (2004) assays were done at 30°. We know that at least one synthetic interaction, between apq12Δ and mad2Δ, is temperature dependent (T. Slaby and O. Cohen-Fix, unpublished results).
The Tong et al. (2004) analysis was done without a plasmid carrying a wild-type copy of the queried gene, and therefore it is possible that in some cases the observed synthetic interaction stemmed from a requirement for germination rather than for viability per se. In other words, certain double mutants may not have displayed a synthetic lethal interaction during vegetative growth had they been able to pass the germination step.
In our screen, the inclusion of the plasmid circumvents germination issues, as we were testing only double mutants that have passed this stage. In this regard, during tetrad analysis we observed that several double-mutant combinations displayed a higher-than-expected rate of spore death that was not observed when the double-mutant strain carried the plasmid.
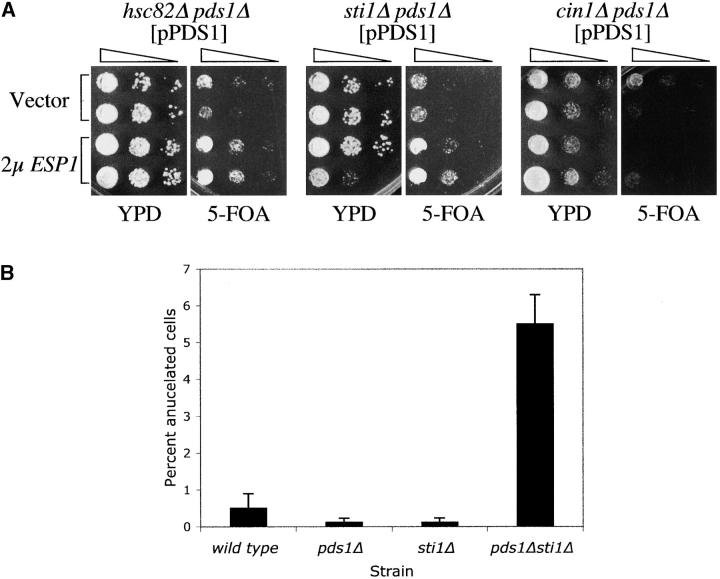
The role of Pds1p in Esp1p nuclear localization prompted us to examine whether any of the genes identified in this study were associated with Esp1p function. In the absence of Pds1p, cells are unable to grow at elevated temperatures due, at least in part, to Esp1p's inability to enter the nucleus (Jensen et al. 2001). This phenotype could be partially suppressed by overexpressing ESP1 (Jensen et al. 2001), suggesting that high levels of Esp1p can compensate for defects in pathways involved in Esp1p activation. Therefore, we examined whether elevated levels of Esp1p expressed from a high-copy plasmid (2μESP1) could rescue any of the synthetic interactions between pds1Δ and the mutants isolated in our screen. Indeed, the synthetic sickness between pds1Δ and mutations in two heat-shock genes, HSC82, encoding an Hsp90-type chaperone, and STI1, encoding a cochaperone of Hsc82p (Chang and Lindquist 1994; Chang et al. 1997), was suppressed by 2μESP1, as is evident by the ability of the pds1Δ hsc82Δ 2μESP1or pds1Δ sti1Δ 2μESP1 strains to survive in the absence of pPDS1 (Figure 4A). Interestingly, the synthetic interaction between pds1Δ and a disruption in another heat-shock gene, sse1Δ, was not suppressed by 2μESP1 (data not shown).
Figure 4.—
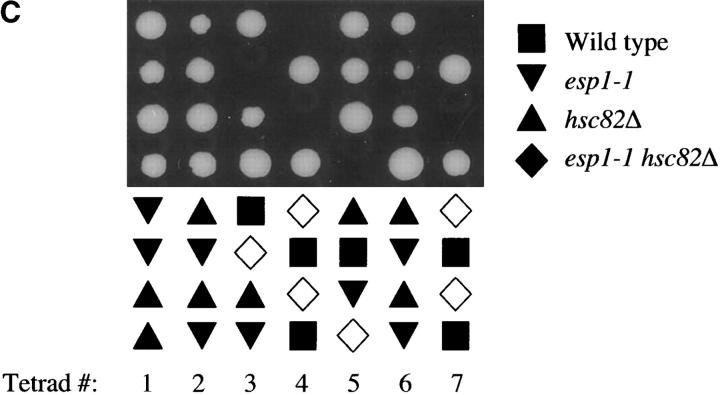
The genetic interactions between pds1Δ and mutants in genes coding for Hsp90-type chaperones reflect a role for the latter in Esp1p activity. (A) Double-mutant strains (pds1Δ genenΔ) carrying pPDS1 were transformed with 2μESP1 (described in Table 1) or with vector alone and analyzed for their ability to survive in the absence of Pds1p by growth on media containing 5-FOA. The synthetic lethality of two double mutants, hsc82Δ pds1Δ and sti1Δ pds1Δ, could be rescued by this approach. An example of a double mutant that was not rescued (cin1Δ pds1Δ) is also shown. (B) Percentage of anucleate cells (i.e., cells without a distinct DNA mass as determined by DAPI staining) was determined as described in Figure 3A. (C) An hsc82Δ/HSC82 esp1-1/ESP1 diploid strain was induced to undergo meiosis and form tetrads. The haploid meiotic products (spores) were dissected onto a rich media plate (YPD). The growth of spores from seven such tetrads is shown. The symbols denote the genotypes of these spores as determined subsequently. Open symbols indicate the predicted genotypes of spores that failed to germinate. Similar results were obtained when analyzing a sti1Δ/STI1 esp1-1/ESP1 diploid strain (data not shown).
The relatively mild sickness exhibited by the pds1Δ sti1Δ strain allowed us to test for further evidence in support of an Esp1p-related function for Sti1p. Cells compromised for Esp1p function are defective in sister chromatid separation, and Esp1p null cells exit mitosis in the complete absence of nuclear division, resulting in the accumulation of cells lacking a nucleus (anucleate cells; McGrew et al. 1992). Thus, if Pds1p and Sti1p contribute independently to Esp1p function, one would expect that the pds1Δ sti1Δ double-mutant strain would exhibit phenotypes reminiscent of loss of Esp1p activity. In keeping with this possibility, the pds1Δ sti1Δ strain showed levels of anucleate cells that were significantly higher than those of wild-type cells or either of the single-mutant strains alone (Figure 4B). These results suggest that Pds1p and Sti1p independently contribute to Esp1p activation and that in the absence of both proteins Esp1p activity is reduced, resulting in the appearance of anucleate cells.
Finally, if Sti1p and Hsc82p are involved in Esp1p function, one might expect that in their absence, the phenotype of a compromised esp1 allele may become more severe. To test this possibility, we crossed a sti1Δ or hsc82Δ strain to an esp1-1 strain and the resulting diploid strains were induced to undergo meiosis. Analysis of the meiotic products revealed that the sti1Δ esp1-1 or hsc82Δ esp1-1 double-mutant combination was drastically underrepresented (Table 2), representing only 3 of 103 spores and 3 of 60 spores, respectively. In contrast, the other expected genotypes (wild type and each of the single mutants) appeared in roughly equal numbers and accounted for >95% of the spores. In most cases, the genotype of spores that failed to germinate could be inferred to be sti1Δ esp1-1 or hsc82Δ esp1-1 (Figure 4C and data not shown). Taken together, these results suggest that the heat-shock/chaperone proteins Sti1p and Hsc82p play a role in promoting Esp1p function.
TABLE 2.
Synthetic interactions betweenesp1-1 and chaperone mutants
| Spore genotype | No. observed |
|---|---|
| A. hsc82Δ × esp1-1 | |
| hsc82Δ | 20 |
| esp1-1 | 20 |
| hsc82Δ esp1-1 | 3 |
| Wild type | 17 |
| Total no. of spores | 60 |
| B. sti1Δ × esp1-1 | |
| sti1Δ | 36 |
| esp1-1 | 28 |
| sti1Δ esp1-1 | 3 |
| Wild type | 36 |
| Total no. of spores | 103 |
For four of the gene disruptions identified in our screen (clb2Δ, sws2Δ, qri5Δ, and sse1Δ) neither their putative function nor our secondary screens (synthetic interactions with checkpoint mutants or high-copy ESP1) shed light on the cause for their synthetic lethality or sickness with pds1Δ. Clb2p is one of the yeast mitotic cyclins and the synthetic lethality between pds1Δ and clb2Δ has been reported previously (Ross and Cohen-Fix 2003). SWS2 and QRI5 encode mitochondria-associated proteins of unknown function (Huh et al. 2003), and their genetic interaction with PDS1 suggests that mitochondria may play a role in cell cycle regulation. Interestingly, flow cytomerty analysis suggested that sws2Δ and qri5Δ strains accumulate early in the cell cycle (data not shown). Finally, Sse1p is a heat-shock/chaperone protein of the Hsp70 family, and further studies are needed to determine how heat-shock proteins are involved in regulating cell cycle progression.
Uncovering genetic interactions with a mutation that confers genomic instability is challenging, as suppressors that could mask a severe growth deficiency can readily arise through aneuploidy. Nonetheless, our screen yielded 21 gene disruptions that showed genetic interactions with pds1Δ under very stringent conditions, namely tetrad analysis followed by a plasmid loss assay. A significant number (eight genes) were not previously known to have cell-cycle-related functions. We were able to identify new genes involved in spindle function or DNA metabolism, and we uncovered a previously unknown role for heat-shock/chaperone proteins in Esp1p function. Moreover, synthetic interactions with pds1Δ that were not mirrored by genetic interactions with other checkpoint mutants or suppressed by high levels of Esp1p may reflect novel roles of Pds1p; Pds1p may be involved in as-yet-uncharacterized checkpoint pathways or it may have additional targets that require the presence of Pds1p to sustain viability. Future work aimed at understanding these interactions at the molecular level is likely to yield insights into key cell cycle processes, such as spindle function and Esp1p activation, and possibly new roles for Pds1p in cell cycle regulation.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dan Burke and Steve Elledge for strains and plasmids, Priscilla Lau and Marc Angeli for assistance with SGA screens, Barbara Taylor for assistance with flow cytometry, and Andy Golden and members of the Cohen-Fix lab for helpful comments on the manuscript. This work was funded by a Leukemia and Lymphoma Society postdoctoral fellowship to K.E.R., a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council Studentship to L.B., Canadian Institutes of Health Research and Genome Canada grants to M.T., and an intramural National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases grant to O.C.-F.
References
- Agarwal, R., and O. Cohen-Fix, 2002. Phosphorylation of the mitotic regulator Pds1/securin by Cdc28 is required for efficient nuclear localization of Esp1/separase. Genes Dev. 16: 1371–1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R., Z. Tang, H. Yu and O. Cohen-Fix, 2003. Two distinct pathways for inhibiting pds1 ubiquitination in response to DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 45027–45033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. C., and S. Lindquist, 1994. Conservation of Hsp90 macromolecular complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 24983–24988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. C., D. F. Nathan and S. Lindquist, 1997. In vivo analysis of the Hsp90 cochaperone Sti1 (p60). Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 318–325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser, J. R., E. J. Schott, T. J. Kingsbury, N. B. Cole, L. J. Totis et al., 1997. Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes required in the absence of the CIN8-encoded spindle motor act in functionally diverse mitotic pathways. Mol. Biol. Cell 8: 1035–1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell, L., 2004. Genetics. Robust interactions. Science 303: 774–775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh, W. K., J. V. Falvo, L. C. Gerke, A. S. Carroll, R. W. Howson et al., 2003. Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature 425: 686–691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jager, H., A. Herzig, C. F. Lehner and S. Heidmann, 2001. Drosophila separase is required for sister chromatid separation and binds to PIM and THR. Genes Dev. 15: 2572–2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jallepalli, P. V., I. C. Waizenegger, F. Bunz, S. Langer, M. R. Speicher et al., 2001. Securin is required for chromosomal stability in human cells. Cell 105: 445–457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, S., M. Segal, D. J. Clarke and S. I. Reed, 2001. A novel role of the budding yeast separin Esp1 in anaphase spindle elongation: evidence that proper spindle association of Esp1 is regulated by Pds1. J. Cell Biol. 152: 27–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, H. A., and G. F. Sprague, Jr., 2003. Far3 and five interacting proteins prevent premature recovery from pheromone arrest in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23: 1750–1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepp, D. M., L. K. Schaefer, X. Ye, K. Keyomarsi, C. Chu et al., 2001. Phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination of cyclin E by the SCFFbw7 ubiquitin ligase. Science 294: 173–177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew, D. J., and D. J. Burke, 2003. The spindle assembly and spindle position checkpoints. Annu. Rev. Genet. 37: 251–282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longhese, M. P., M. Clerici and G. Lucchini, 2003. The S-phase checkpoint and its regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutat. Res. 532: 41–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrew, J. T., L. Goetsch, B. Byers and P. Baum, 1992. Requirement for ESP1 in the nuclear division of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 3: 1443–1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mei, J., X. Huang and P. Zhang, 2001. Securin is not required for cellular viability but is for normal growth of mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Curr. Biol. 11: 1197–1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo, J., and D. Toczyski, 2002. A unified view of the DNA-damage checkpoint. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14: 237–245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palecek, S. P., A. S. Parikh and S. J. Kron, 2000. Genetic analysis reveals that FLO11 upregulation and cell polarization independently regulate invasive growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 156: 1005–1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J. M., 2002. The anaphase-promoting complex: proteolysis in mitosis and beyond. Mol. Cell 9: 931–943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross, K. E., and O. Cohen-Fix, 2003. The role of Cdh1p in maintaining genomic stability in budding yeast. Genetics 165: 489–503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong, A. H., M. Evangelista, A. B. Parsons, H. Xu, G. D. Bader et al., 2001. Systematic genetic analysis with ordered arrays of yeast deletion mutants. Science 294: 2364–2368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong, A. H., G. Lesage, G. D. Bader, H. Ding, H. Xu et al., 2004. Global mapping of the yeast genetic interaction network. Science 303: 808–813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlmann, F., 2003. Chromosome cohesion and separation: from men and molecules. Curr. Biol. 13: R104–R114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H., D. Liu, Y. Wang, J. Qin and S. J. Elledge, 2001. Pds1 phosphorylation in response to DNA damage is essential for its DNA damage checkpoint function. Genes Dev. 15: 1361–1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, A., V. Guacci and D. Koshland, 1996. Pds1p is required for faithful execution of anaphase in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Biol. 133: 85–97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H., 2002. Regulation of APC-Cdc20 by the spindle checkpoint. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14: 706–714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]