Abstract
Objectives. Obesity has emerged as one of the most important public health issues in the United States. We assessed obesity prevalence rates and their trends among major US occupational groups.
Methods. Self-reported weight and height were collected annually on US workers, aged 18 years or older, from the 1986 to 1995 and the 1997 to 2002 National Health Interview Surveys. Overall, occupation-, race-, and gender-specific rates of obesity (defined as a body mass index>30.0 kg/m2) were calculated with data pooled from both study periods (n>600000). Annual occupation-specific prevalence rates were also calculated, and their time trends were assessed.
Results. Obesity rates increased significantly over time among employed workers, irrespective of race and gender. The average yearly change increased from 0.61% (±.04) during the period from 1986 to 1995 to 0.95% (±.11) during the period from 1997 to 2002. Average obesity prevalence rates and corresponding trends varied considerably across occupational groups; pooled obesity prevalence rates were highest in motor vehicle operators (31.7% in men; 31.0% in women).
Conclusions. Weight loss intervention programs targeting workers employed in occupational groups with high or increasing rates of obesity are urgently needed.
In the United States, obesity has risen at an unprecedented rate during the past 20 years,1 and current research indicates that the situation is worsening rather than improving. From 1960 to 1980, the prevalence of obesity among adults in the United States was relatively stable; however, recent findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) showed that 3 out of every 10 US adults are obese.2 In addition to increasing mortality from all causes, obesity is linked to an increased risk of developing hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, gallbladder disease, osteoarthritis, coronary heart disease, stroke, asthma, and sleep apnea.3–7 Additionally, new evidence suggests that obesity is a risk factor for endometrial, breast, prostate, and colon cancers. 8–10
The relationship between obesity and occupation has not been fully investigated. Work-related factors, such as job and position, job stress, and extended work (including overtime night work and sedentary work) may promote weight gain and abdominal fat accumulation.11–14 One of the national Healthy People 2010 Objectives is to reduce the prevalence rate of obesity among adults to less than 15%,15 therefore, because treatment often fails, research efforts focused on prevention are required. Weight loss intervention and education programs targeting workers employed in various occupational groups are urgently needed, but, unfortunately, nationally representative data identifying occupational groups with the highest obesity rates are not presently available.16,17 It is also not known which occupational groups are experiencing large increases in obesity rates. Our research objective was to evaluate overall, gender- and race-specific obesity rates and their 17-year trends, including the past decade, within 41 occupational groups using nationally representative samples of the US worker population.
METHODS
The National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) is a continuous multipurpose and multistage probability area survey of the US civilian noninstitutionalized population living at addressed dwellings.18 Each week, a probability sample of households is interviewed by trained personnel to obtain information about the characteristics of each member of the household.19 In the majority of cases (63%) in the 1986 to 1996 NHIS surveys, the participants themselves answered all the questions; for the remaining participants, the responses were obtained from their relatives or other proxies. However, beginning with the 1997 NHIS survey, all survey responses were self-reported. For simplicity, in the present study, both self-reported or proxy-reported data are referred to as “reported.” In the period from 1986 to 1996, annual NHIS survey response rates ranged from 95% to 98%20; in the period from 1997 to 2002, these rates fell to 70%–80%, reflecting the trend of lower response rates in all national surveys.21,22
Body mass index (BMI) is commonly used to define obesity and has been found to closely correlate with the level of body fat.23 BMI was calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. Respondents were classified as obese if their BMI was greater than 30.0 kg/m2.24 From 1986 to 1995, the NHIS reported weight and height values for all participants. Data from the 1996 survey year are not presented because, for that year, the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) reported data only for participants with a weight between 98 and 289 pounds and a height between 59 and 76 inches; BMI for the 1996 participants outside of these weight and height ranges were not made available by NCHS. Starting in 1997, the NHIS was redesigned and the NCHS made available the BMI values for all participants, even those with weight and height outside the above ranges.25 Because of these differences in the reporting, and because of the major redesign of the sampling and interview format, we analyzed data separately for NHIS survey periods 1986 to 1995 and 1997 to 2002.
In the 1986 to 1995 NHIS, employment information was collected on all subjects aged 18 years or older who reported working during the 2 weeks prior to the survey26,27; starting in 1997, NCHS collected employment information from adults who stated that they were working during the week before the NHIS survey. Both of these definitions included paid and unpaid work. Forty-one standardized occupational codes derived from more detailed US Census occupational codes were provided in the NHIS database from 1986 to 1995 and from 1997 to 2002.28,29 We grouped survey participants in the trend data analysis into White, Black, or “other race” category. “Other race” included other, Aleutian Eskimo/American Indian, Asian/Pacific Islander, and unknown/multiple races.
Because of the complex sample survey design, analyses were completed with the SUDAAN package to take into account sample weights and design effects.30 For pooled prevalence estimates, sample weights were adjusted to account for the aggregation of data over multiple survey years by dividing the original weight by 10 (the number of years combined in survey years 1986 through 1995) and by 6 (the number of years combined in survey years 1997 through 2002).18 To assess obesity trends within each survey period, a weighted linear regression model was fitted to the annual design-adjusted rates within occupational groups. The weight used for each annual rate was the inverse of its variance.
RESULTS
A total of 603 139 persons aged 18 years and older reported working within the 2 weeks prior to their participation in the 1986 to 1995 NHIS surveys, and in the 1 week prior to their participation in the 1997 to 2002 NHIS surveys. Among the 488 612 workers in the 1986 to 1995 survey period, the mean age (±SD) was 38.9 ±12.8, with a total of 226 128 women (46.3%); the mean age of the 114 527 workers from the 1997 to 2002 period was 40.3 ±12.7, including 57198 women (49.9%).
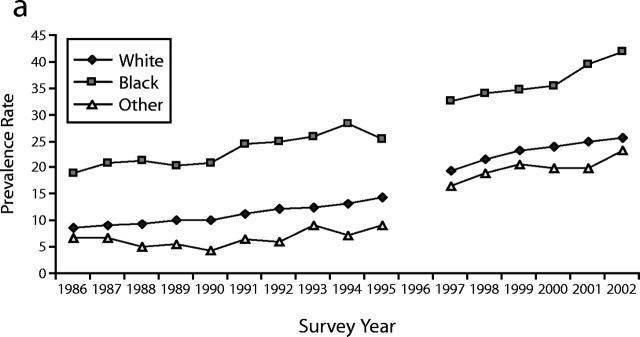
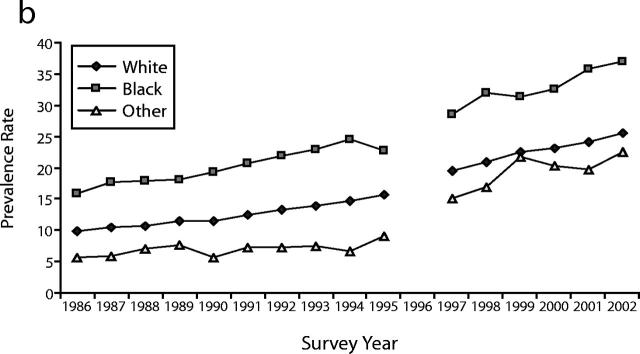
The average yearly change (±SE) in obesity rates increased from 0.61% (±.04) in the 1986 to 1995 period to 0.95% (±.11) in the 1996 to 2002 period. Annual obesity rates increased significantly among all gender-race groups in the survey periods 1986 to 1995 and 1997 to 2002 (Figure 1 ▶). In all survey years, annual obesity rates were highest in Black workers (particularly women) and lowest among those in the “other race” category.
FIGURE 1—
Trends in gender- and race-specific prevalence rates of obesity among working adults, (a) men and (b) women: the National Health Interview Survey, 1986 to 2002.
For each gender and each 1 of the 41 occupational groups, Tables 1 ▶ and 2 ▶ show: the sample size; the percentage of Black workers for each occupational group (given that Black workers had the highest rates of obesity); the pooled and annual prevalence rates of obesity; and the slope (i.e., yearly change in obesity rate) of the weighted linear regression of rate of obesity over time, its standard error, and the corresponding P value. Slopes were not calculated for a particular occupational group when the sample size for any given survey year was below 46. Pooled and annual obesity rates preceded by an asterisk have a relative standard error [defined as 100 × SE (rate)/rate] of greater than 30% and, following the practice of the NCHS, should be considered imprecise estimates.31
TABLE 1—
Pooled and Annual Prevalence Rates of Obesity in 41 Occupational Categories: the National Health Interview Survey, 1986–1995
| Annual Prevalence Rate of Obesity | ||||||||||||||||
| Occupation | Sample No. | Estimated US Population | Percentage Black | Overall Prevalence | 1986 | 1987 | 1988 | 1989 | 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | Slope ± SE | P |
| Men | ||||||||||||||||
| Officials and administrators (public administration) | 1341 | 320 864 | 7.2 | 14.95 | 10.3 | 13.2 | 12.4 | 16.0 | 16.3 | 13.3 | 13.4 | 14.4 | 19.3 | 19.2 | 0.631 ± 0.245 | .03 |
| Managers and administrators (except public administration) | 30 273 | 7 217 767 | 4.9 | 13.11 | 11.4 | 10.6 | 11.5 | 12.7 | 12.6 | 12.8 | 13.2 | 15.0 | 15.5 | 15.6 | 0.578 ±0.064 | .00 |
| Management-related occupations | 7822 | 1 882 304 | 6.0 | 11.97 | 12.2 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 9.9 | 10.6 | 10.3 | 12.6 | 14.2 | 14.6 | 15.3 | 0.545 ± 0.170 | .01 |
| Engineers | 7578 | 1 821 250 | 3.8 | 10.37 | 9.2 | 8.8 | 10.9 | 8.3 | 8.6 | 10.5 | 10.8 | 9.6 | 12.2 | 15.2 | 0.389 ±0.179 | .06 |
| Architects and surveyors | 729 | 174 141 | 3.5 | 8.34 | 8.3a | 14.5a | 4.8a | 8.7a | 4.7a | 12.6 | 8.1a | 10.7a | 6.0a | 9.7a | b | b |
| Natural, mathematical/computer scientists | 3835 | 939 904 | 5.3 | 10.43 | 5.8 | 9.7 | 9.8 | 10.0 | 7.8 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 15.1 | 12.3 | 0.641 ±0.192 | .01 |
| Health-diagnosing occupations | 2813 | 664 264 | 3.4 | 6.15 | 2.8 | 4.1 | 10.2 | 4.8 | 5.9 | 5.0 | 4.8 | 10.1 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 0.335 ±0.224 | .17 |
| Health assessment/treating occupations | 1349 | 323 775 | 8.0 | 11.03 | 6.9 | 4.7 | 7.8 | 14.5 | 10.7 | 15.9 | 9.9 | 16.7 | 13.1 | 9.5 | 0.791 ±0.344 | .05 |
| Teachers, librarians, counselors | 6904 | 1 643 367 | 7.4 | 12.66 | 7.9 | 10.5 | 12.1 | 12.1 | 13.5 | 12.2 | 12.9 | 14.5 | 12.3 | 17.8 | 0.613 ±0.171 | .01 |
| Writers, artists, entertainers, athletes | 4206 | 1 032 077 | 6.5 | 9.68 | 8.3 | 5.7 | 7.5 | 10.6 | 9.0 | 7.4 | 12.0 | 12.2 | 15.1 | 8.4 | 0.593 ±0.265 | .06 |
| Other professional specialty occupations | 5612 | 1 332 807 | 7.9 | 11.86 | 8.8 | 9.9 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 10.4 | 12.8 | 12.9 | 13.9 | 15.4 | 13.7 | 0.719 ±0.094 | .00 |
| Health technologists/technicians | 1046 | 257 832 | 12.6 | 12.37 | 9.3a | 5.a4 | 11.7 | 9.1 | 6.3a | 7.3 | 17.8 | 11.7 | 18.4 | 16.2 | b | b |
| Technologists, technicians (except health) | 7621 | 1 854 827 | 6.7 | 11.72 | 10.1 | 9.5 | 9.4 | 9.9 | 11.8 | 11.0 | 12.1 | 13.9 | 13.0 | 15.3 | 0.586 ±0.088 | .00 |
| Supervisors and proprietors | 9661 | 2 325 275 | 3.8 | 13.02 | 9.9 | 10.9 | 10.2 | 11.5 | 11.2 | 15.7 | 14.5 | 14.4 | 14.7 | 15.8 | 0.710 ±0.127 | .00 |
| Sales representatives, commodities and finance | 9883 | 2 380 853 | 3.6 | 12.13 | 9.9 | 10.4 | 11.3 | 12.3 | 10.6 | 9.9 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 15.0 | 15.9 | 0.568 ±0.145 | .00 |
| Other sales personnel | 8391 | 2 018 715 | 7.9 | 12.07 | 7.1 | 10.1 | 9.9 | 11.6 | 10.8 | 12.3 | 13.5 | 14.7 | 13.0 | 16.3 | 0.762 ±0.114 | .00 |
| Computer equipment operators | 920 | 222 071 | 12.8 | 12.53 | 10.1 | 9.1 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 13.2 | 12.3 | 15.1 | 16.3 | 21.0 | 13.9a | b | b |
| Secretaries, stenographers, and typists | 340 | 79 564 | 16.6 | 11.01 | 0.0 | 8.4a | 12.1a | 17.3a | 7.0a | 12.7a | 15.7a | 4.9a | 10.0a | 22.0a | b | b |
| Financial records processing occupations | 889 | 215 674 | 8.4 | 9.81 | 4.4 | 7.4 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 10.1 | 9.4 | 12.7 | 11.9 | 12.7 | 14.8 | 0.984 ±0.129 | .00 |
| Mail and message distribution personnel | 2482 | 570 995 | 17.4 | 11.88 | 6.6 | 7.2 | 12.1 | 12.4 | 13.2 | 12.5 | 15.0 | 10.5 | 13.4 | 18.2 | 0.918 ±0.243 | .01 |
| Other administrative support personnel | 10 893 | 2 629 800 | 12.5 | 13.56 | 10.4 | 12.5 | 9.4 | 9.4 | 11.3 | 13.0 | 16.2 | 16.4 | 16.7 | 17.5 | 0.940 ±0.202 | .00 |
| Private household occupations | 153 | 34 702 | 18.6 | 15.80 | 24.9a | 26.7a | 17.0a | 1.2a | 18.1a | 10.2a | 17.8a | 26.4a | 7.3a | 16.3a | b | b |
| Police and firefighters | 4258 | 1 023 980 | 12.5 | 17.70 | 15.2 | 13.8 | 15.6 | 18.0 | 13.9 | 19.3 | 18.2 | 18.6 | 18.7 | 24.2 | 0.871 ±0.229 | .01 |
| Other protective service occupations | 2718 | 636 439 | 21.2 | 19.16 | 13.7 | 13.2 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 16.9 | 21.0 | 20.8 | 21.0 | 23.8 | 21.7 | 1.066 ±0.231 | .00 |
| Food service personnel | 7182 | 1 719 150 | 16.1 | 9.94 | 7.1 | 9.1 | 9.1 | 9.2 | 9.4 | 10.1 | 10.1 | 12.4 | 10.1 | 12.0 | 0.384 ±0.093 | .00 |
| Health service personnel | 896 | 207000 | 30.4 | 16.58 | 14.3a | 18.0 | 10.3a | 17.0a | 17.1 | 16.6 | 15.8 | 17.1 | 20.9 | 16.8 | b | b |
| Cleaning and building service personnel | 7421 | 1 666 428 | 21.3 | 14.52 | 11.9 | 14.2 | 11.6 | 15.0 | 14.4 | 14.0 | 16.1 | 17.2 | 14.2 | 16.3 | 0.414 ±0.152 | .03 |
| Personal service workers | 1808 | 429 701 | 15.2 | 9.71 | 3.3a | 9.6 | 6.3a | 8.6 | 6.2a | 5.8a | 14.9 | 10.4 | 11.5 | 17.7 | 0.973 ±0.340 | .02 |
| Farm operators and managers | 5041 | 1 110 014 | 2.0 | 15.37 | 11.9 | 14.2 | 14.1 | 14.5 | 16.1 | 14.6 | 15.3 | 20.9 | 14.8 | 20.6 | 0.620 ±0.214 | .02 |
| Farm workers and other agricultural workers | 5714 | 1 288 324 | 10.5 | 12.36 | 10.4 | 9.0 | 12.1 | 11.2 | 13.8 | 13.3 | 12.2 | 10.4 | 15.9 | 14.4 | 0.490 ±0.192 | .03 |
| Forestry and fishing occupations | 742 | 186 114 | 10.4 | 15.10 | 10.7a | 12.3a | 9.8a | 12.0a | 12.7a | 24.0 | 16.9 | 17.6 | 24.2 | 13.2a | 0.966 ±0.430 | .06 |
| Mechanics and repairers | 16727 | 3 953 408 | 7.5 | 14.51 | 12.8 | 12.6 | 11.4 | 14.6 | 14.2 | 14.5 | 14.9 | 16.6 | 15.9 | 18.0 | 0.601 ±0.108 | .00 |
| Construction and extractive trades | 20 296 | 4 815 157 | 6.9 | 12.19 | 10.8 | 11.5 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 11.3 | 11.7 | 14.1 | 15.8 | 13.4 | 13.4 | 0.517 ±0.142 | .01 |
| Precision production occupations | 12 183 | 2 845 536 | 7.2 | 14.62 | 11.7 | 13.0 | 12.4 | 15.0 | 14.5 | 14.4 | 15.1 | 18.0 | 16.6 | 16.2 | 0.576 ±0.102 | .00 |
| Machine operators/tenders (except precision) | 13 316 | 3 094 652 | 13.2 | 14.50 | 10.5 | 12.4 | 13.0 | 13.8 | 14.8 | 15.0 | 15.3 | 15.7 | 18.2 | 16.4 | 0.671 ±0.085 | .00 |
| Fabricators, assemblers, inspectors, samplers | 6702 | 1 557 173 | 11.6 | 14.41 | 11.6 | 13.7 | 12.2 | 13.3 | 13.2 | 15.3 | 15.6 | 15.5 | 15.6 | 18.1 | 0.568 ±0.103 | .00 |
| Motor vehicle operators | 13 567 | 3 136 798 | 15.3 | 19.83 | 17.7 | 16.2 | 18.4 | 18.0 | 19.6 | 20.7 | 19.7 | 19.5 | 23.7 | 24.1 | 0.713 ±0.140 | .00 |
| Other transportation (except motor vehicles) | 698 | 168 742 | 7.5 | 18.20 | 10.8a | 11.9a | 20.4 | 18.6 | 16.0 | 17.6a | 29.3 | 10.9a | 24.7 | 18.6 | b | b |
| Material-moving equipment operators | 4396 | 1 018 823 | 13.4 | 19.18 | 16.8 | 16.9 | 16.9 | 15.6 | 20.8 | 18.7 | 26.1 | 19.2 | 21.1 | 20.7 | 0.670 ±0.267 | .04 |
| Construction laborers | 2890 | 676292 | 13.5 | 11.98 | 9.5 | 11.6 | 12.2 | 11.9 | 9.3 | 11.3 | 13.5 | 12.3 | 12.0 | 15.3 | 0.378 ±0.162 | .05 |
| Freight, stock, material handlers | 11 188 | 2 618 398 | 16.5 | 12.46 | 8.9 | 10.3 | 10.5 | 12.9 | 12.4 | 12.5 | 12.2 | 13.4 | 15.4 | 15.6 | 0.645 ±0.095 | .00 |
| Women | ||||||||||||||||
| Officials and administrators (public administration) | 1040 | 230 806 | 12.0 | 11.54 | 11.7a | 9.3a | 13.3 | 9.2a | 5.5a | 12.4 | 11.5 | 11.3 | 18.0 | 10.7 | b | b |
| Managers administrators (except public administration) | 17 747 | 4 057 038 | 6.9 | 10.26 | 8.0 | 9.4 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 10.4 | 9.7 | 11.3 | 11.7 | 10.2 | 13.7 | 0.501 ±0.119 | .00 |
| Management-related occupations | 9035 | 2 066 419 | 9.3 | 9.24 | 6.6 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 6.8 | 8.3 | 9.0 | 8.3 | 12.2 | 10.9 | 13.4 | 0.709 ±0.129 | .00 |
| Engineers | 694 | 159 477 | 7.5 | 5.75 | 0.0 | 2.1a | 6.2a | 3.1a | 8.4a | 4.3a | 4.0a | 9.2a | 9.8a | 9.9a | b | b |
| Architects and surveyors | 109 | 24 678 | 3.3 | 1.67a | 0.0 | 6.3a | 5.4a | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.6a | b | b |
| Natural, mathematical/computer scientists | 1830 | 423 638 | 8.7 | 7.85 | 1.4a | 5.5a | 11.4 | 7.2 | 8.4 | 6.7 | 11.3 | 8.1 | 6.4 | 8.8 | 0.580 ±0.290 | .08 |
| Health-diagnosing occupations | 735 | 167 635 | 6.6 | 4.27 | 3.0a | 5.4a | 4.2a | 6.6a | 2.8a | 4.1a | 4.6a | 3.7a | 4.7a | 3.6a | b | b |
| Health assessment/treating occupations | 9457 | 2 15 290 | 9.4 | 11.57 | 9.0 | 8.9 | 10.4 | 9.9 | 9.3 | 13.0 | 12.7 | 13.5 | 14.9 | 12.8 | 0.624 ±0.127 | .00 |
| Teachers, librarians, counselors | 15 718 | 3 551 611 | 9.3 | 10.33 | 8.6 | 7.9 | 9.6 | 8.6 | 8.8 | 10.4 | 11.3 | 12.2 | 11.4 | 13.4 | 0.563 ±0.095 | .00 |
| Writers, artists, entertainers, athletes | 3999 | 936 020 | 4.4 | 6.59 | 5.1 | 4.1 | 6.5 | 7.1 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 7.3 | 5.6 | 7.0 | 8.2 | 0.317 ±0.110 | .02 |
| Other professional specialty occupations | 3956 | 882 293 | 13.6 | 11.22 | 9.9 | 7.8 | 7.4 | 10.4 | 11.0 | 12.4 | 11.4 | 13.5 | 14.2 | 11.7 | 0.674 ±0.159 | .00 |
| Health technologists/technicians | 5033 | 1 109 678 | 14.9 | 15.10 | 14.7 | 13.4 | 14.5 | 14.6 | 12.7 | 15.7 | 14.4 | 14.2 | 17.3 | 18.5 | 0.395 ±0.158 | .04 |
| Technologists, technicians (except health) | 3559 | 826 693 | 8.4 | 8.71 | 6.0 | 6.9 | 5.4 | 7.4 | 7.5 | 9.3 | 9.9 | 10.2 | 12.4 | 11.6 | 0.738 ±0.099 | .00 |
| Supervisors and proprietors | 5598 | 1 278 544 | 6.2 | 11.78 | 10.6 | 8.6 | 9.9 | 11.5 | 12.5 | 11.5 | 12.6 | 12.0 | 13.3 | 14.0 | 0.497 ±0.093 | .00 |
| Sales representatives, commodities and finance | 5167 | 1193 821 | 4.7 | 6.58 | 4.5a | 3.8 | 5.9 | 4.8 | 5.7 | 6.5 | 8.3 | 8.2 | 8.6 | 9.2 | 0.635 ±0.085 | .00 |
| Other sales personnel | 16 605 | 3 796 117 | 11.0 | 10.83 | 8.2 | 9.6 | 8.2 | 9.9 | 10.0 | 11.8 | 11.9 | 13.1 | 12.7 | 13.2 | 0.594 ±0.084 | .00 |
| Computer equipment operators | 1810 | 400 929 | 14.5 | 9.99 | 7.1a | 6.5 | 9.0 | 9.8 | 11.3 | 14.2 | 10.4 | 15.4 | 13.6 | 4.8a | 0.329 ±0.364 | .39 |
| Secretaries, stenographers and typists | 18 167 | 4 131 183 | 8.6 | 9.58 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 9.0 | 10.7 | 10.0 | 12.2 | 13.8 | 14.4 | 0.889 ±0.084 | .00 |
| Financial records processing occupations | 8563 | 1 955 437 | 6.0 | 11.00 | 8.2 | 9.2 | 9.1 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 11.4 | 11.7 | 13.3 | 14.0 | 16.7 | 0.810 ±0.111 | .00 |
| Mail and message distribution personnel | 1538 | 328 665 | 22.5 | 13.60 | 7.2a | 8.7 | 15.1 | 8.7 | 13.0 | 16.0 | 15.1 | 15.1 | 23.1 | 15.9 | 1.155 ±0.341 | .01 |
| Other administrative support | 29 669 | 6 687 733 | 12.8 | 11.94 | 7.5 | 10.6 | 9.3 | 11.6 | 10.2 | 11.5 | 13.0 | 13.5 | 15.1 | 15.1 | 0.767 ±0.107 | .00 |
| Private household occupations | 3369 | 697 123 | 27.7 | 18.85 | 22.0 | 18.4 | 17.9 | 20.4 | 17.4 | 18.7 | 17.1 | 19.3 | 20.9 | 16.0 | –0.232 ±0.194 | .27 |
| Police and firefighters | 628 | 138 860 | 26.6 | 11.41 | 1.6a | 13.3a | 10.7a | 2.2a | 16.6 | 7.2a | 14.2a | 14.9a | 10.0 | 16.6 | b | b |
| Other protective service occupations | 721 | 159 289 | 22.3 | 15.42 | 6.2a | 9.4a | 18.4 | 17.1a | 14.1 | 19.0 | 16.7 | 17.6 | 16.3 | 16.7 | b | b |
| Food service personnel | 12 391 | 2 785 582 | 11.2 | 12.85 | 8.5 | 11.6 | 12.4 | 12.4 | 11.2 | 13.0 | 14.1 | 14.5 | 14.8 | 15.3 | 0.586 ±0.107 | .00 |
| Health service personnel | 8292 | 1 756 092 | 26.5 | 20.95 | 19.7 | 20.6 | 17.8 | 18.8 | 18.1 | 21.6 | 23.4 | 19.3 | 25.3 | 24.4 | 0.613 ±0.244 | .04 |
| Cleaning and building service personnel | 5523 | 1 149 738 | 26.4 | 19.70 | 17.6 | 18.9 | 17.8 | 21.6 | 15.7 | 22.3 | 22.3 | 18.2 | 19.8 | 22.4 | 0.374 ±0.290 | .23 |
| Personal service workers | 8514 | 1 908 222 | 11.3 | 13.73 | 13.3 | 14.1 | 11.8 | 12.3 | 10.0 | 14.4 | 14.1 | 14.7 | 16.4 | 15.3 | 0.438 ±0.200 | .06 |
| Farm operators and managers | 1033 | 221 061 | 0.9 | 11.69 | 5.4a | 8.9 | 9.2 | 11.9 | 12.1 | 16.2 | 16.8 | 10.0a | 14.5 | 14.3 | 0.965 ±0.271 | .01 |
| Farm workers and other agricultural workers | 1275 | 283 096 | 4.7 | 12.79 | 8.2a | 10.1 | 8.6 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 8.8 | 17.8 | 12.1 | 20.6 | 14.4 | 0.836 ±0.326 | .03 |
| Forestry and fishing occupations | 31 | 7307 | 14.2 | 15.30a | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 17.3a | 0.0 | 0.0 | 23.1a | 0.0 | 48.1a | 0.0 | b | b |
| Mechanics and repairers | 715 | 159 931 | 14.1 | 12.44 | 8.1a | 12.6a | 9.4a | 13.7a | 2.1a | 12.8 | 17.4 | 17.8 | 12.6 | 20.6 | 1.092 ±0.924 | .27 |
| Construction and extractive trades | 473 | 104 398 | 8.3 | 10.62 | 6.4a | 6.1a | 11.4a | 5.4a | 10.8a | 8.5a | 8.1a | 28.9a | 15.1a | 13.2 | b | b |
| Precision production occupations | 3844 | 847 349 | 11.6 | 14.35 | 13.7 | 13.2 | 11.6 | 13.5 | 12.8 | 13.4 | 14.6 | 16.7 | 17.1 | 17.4 | 0.585 ±0.139 | .00 |
| Machine operators/tenders (except precision) | 9280 | 2 008 473 | 17.9 | 16.39 | 14.0 | 14.7 | 15.2 | 14.8 | 15.4 | 18.0 | 18.2 | 18.2 | 19.7 | 17.4 | 0.553 ±0.108 | .00 |
| Fabricators, assemblers, inspectors, samplers | 4409 | 964 580 | 16.0 | 15.79 | 11.3 | 13.0 | 14.2 | 15.3 | 16.2 | 15.3 | 16.3 | 21.4 | 17.5 | 18.1 | 0.784 ±0.163 | .00 |
| Motor vehicle operators | 1728 | 376 126 | 15.4 | 22.61 | 21.4 | 18.3 | 14.8 | 20.7 | 22.1 | 25.5 | 24.9 | 25.2 | 26.2 | 25.9 | 1.196 ±0.287 | .00 |
| Other transportation, except motor vehicles | 23 | 5277 | 17.5 | 19.91a | 0.0 | 0.0 | 31.6a | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 40.7a | b | b |
| Material moving equipment operators | 255 | 55 875 | 18.5 | 16.54 | 6.4a | 16.3a | 13.0a | 32.4a | 10.8 | 6.6a | 36.5a | 13.3a | 21.4a | 4.1a | b | b |
| Construction laborers | 88 | 21 029 | 18.3 | 12.81a | 11.8a | 0.0 | 32.4a | 7.8a | 0.0 | 7.6a | 13.0a | 0.0 | 21.3a | 31.7a | b | b |
| Freight, stock, material handlers | 3507 | 765 254 | 15.2 | 14.20 | 12.8 | 10.9 | 15.6 | 15.1 | 13.3 | 14.2 | 16.0 | 15.3 | 14.8 | 13.9 | 0.311 ±0.179 | .12 |
aEstimates have a relative standard error > 30% and should be used with caution, as they do not meet NCHS standards of reliability or precision.31
b Trends were not calculated when the sample size for any individual survey year fell below 45.
TABLE 2—
Pooled and Annual Prevalence Rates of Obesity in 41 Occupational Categories: the National Health Interview Survey, 1997–2002
| Annual Prevalence Rate of Obesity | ||||||||||||
| Occupation | Sample No. | Estimated US Population | Percentage Black | Overall Prevalence | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | Slope ±SE | P |
| Men | ||||||||||||
| Officials and administrators (public administration) | 335 | 401 695 | 12.70 | 27.79 | 26.5 | 25.3 | 21.1a | 18.4a | 32.8 | 38.0 | b | b |
| Managers administrators (except public administration) | 6005 | 7 316 851 | 5.40 | 22.34 | 17.4 | 22.4 | 25.0 | 20.3 | 24.1 | 24.6 | 1.152 ±0.556 | .11 |
| Management-related occupations | 1767 | 2 114 629 | 7.20 | 19.12 | 16.3 | 20.3 | 14.5 | 22.8 | 20.9 | 20.1 | 0.820 ±0.718 | .32 |
| Engineers | 1471 | 1 831 119 | 4.10 | 18.18 | 14.9 | 15.4 | 16.2 | 22.6 | 16.9 | 23.4 | 1.317 ±0.628 | .10 |
| Architects and surveyors | 158 | 185 661 | 4.50 | 14.54 | 9.4a | 21.1a | 11.1a | 12.6a | 13.6a | 14.1a | b | b |
| Natural, mathematical/computer scientists | 1543 | 1 794 908 | 4.90 | 18.85 | 18.5 | 19.1 | 15.1 | 15.5 | 25.1 | 18.6 | 0.439 ±0.885 | .65 |
| Health-diagnosing occupations | 579 | 745 432 | 2.20 | 11.19 | 7.2a | 8.0a | 17.1 | 17.1 | 8.6a | 10.8a | 0.642 ±0.851 | .49 |
| Health assessment/treating occupations | 357 | 412 753 | 9.00 | 22.20 | 22.3 | 12.0a | 25.6a | 23.1 | 17.4a | 31.2 | 1.360 ±1.668 | .46 |
| Teachers, librarians, counselors | 1798 | 2 073 333 | 8.00 | 20.37 | 17.8 | 20.2 | 21.6 | 19.7 | 21.1 | 21.4 | 0.574 ±0.249 | .08 |
| Writers, artists, entertainers, athletes | 1104 | 1 202 685 | 8.00 | 16.88 | 12.4 | 17.5 | 14.1 | 18.4 | 18.1 | 20.8 | 1.360 ±0.473 | .05 |
| Other professional specialty occupations | 1231 | 1 426 256 | 9.00 | 20.72 | 16.8 | 23.1 | 13.5 | 27.3 | 18.5 | 25.8 | 1.141 ±1.278 | .42 |
| Health technologists/technicians | 302 | 358 786 | 10.90 | 13.67 | 15.5a | 9.2a | 7.6a | 23.0a | 12.3a | 13.0a | b | b |
| Technologists, technicians (except health) | 1615 | 1 901 481 | 7.20 | 23.29 | 19.1 | 21.4 | 26.4 | 24.9 | 19.9 | 27.8 | 1.042 ±0.777 | .25 |
| Supervisors and proprietors | 1871 | 2 274 531 | 5.30 | 21.79 | 22.2 | 15.8 | 24.6 | 17.5 | 26.5 | 23.9 | 0.912 ±1.039 | .43 |
| Sales representatives, commodities and finance | 2097 | 2 570 730 | 4.50 | 19.02 | 18.9 | 16.7 | 20.5 | 22.3 | 17.7 | 18.3 | 0.049 ±0.514 | .93 |
| Other sales personnel | 1891 | 2 320 817 | 9.50 | 18.67 | 14.9 | 18.3 | 20.6 | 18.8 | 17.5 | 22.1 | 0.892 ±0.487 | .14 |
| Computer equipment operators | 155 | 180 586 | 13.10 | 24.94 | 20.0a | 18.5a | 28.9a | 25.3a | 29.9a | 33.1a | b | b |
| Secretaries, stenographers, and typists | 59 | 59 810 | 9.70 | 17.65a | 5.6a | 7.3a | 43.7a | 0.0 | 27.5a | 0.0 | b | b |
| Financial records processing occupations | 200 | 222 444 | 18.60 | 23.10 | 12.8a | 33.1a | 23.3a | 27.0a | 16.5a | 24.3a | b | b |
| Mail and message distribution personnel | 441 | 505 995 | 24.10 | 20.45 | 20.0 | 15.8 | 31.8 | 9.8 | 17.6 | 25.6 | 0.131 ±2.135 | .95 |
| Other administrative support personnel | 2593 | 2 949 184 | 14.80 | 22.88 | 18.9 | 18.3 | 25.0 | 22.2 | 25.0 | 27.0 | 1.677 ±0.463 | .02 |
| Private household occupations | 26 | 29 512 | 34.60 | 31.32a | 0.0 | 42.8a | 0.0 | 19.5a | 47.1a | 37.7a | b | b |
| Police and firefighters | 987 | 1 186 698 | 12.80 | 29.79 | 22.5 | 25.7 | 33.5 | 31.1 | 35.4 | 30.7 | 2.053 ±0.796 | .06 |
| Other protective service occupations | 646 | 696 744 | 22.50 | 27.58 | 21.2 | 31.0 | 19.2 | 27.1 | 38.5 | 28.3 | 1.681 ±1.456 | .31 |
| Food service personnel | 1825 | 2 080 815 | 14.60 | 18.49 | 16.2 | 13.1 | 23.5 | 18.4 | 17.3 | 22.4 | 1.205 ±0.843 | .23 |
| Health service personnel | 247 | 254 544 | 33.30 | 24.61 | 30.0 | 23.4a | 33.5a | 19.7a | 24.8 | 16.7a | b | b |
| Cleaning and building service personnel | 1507 | 1 612 197 | 19.60 | 22.99 | 18.0 | 21.4 | 22.2 | 22.6 | 25.6 | 27.8 | 1.751 ±0.218 | .00 |
| Personal service workers | 418 | 436 927 | 17.30 | 17.14 | 17.5a | 23.8 | 17.5 | 15.6a | 11.8a | 15.5a | –1.362 ±0.775 | .15 |
| Farm operators and managers | 627 | 764 784 | 1.00 | 21.62 | 14.9 | 19.9 | 23.8 | 26.9 | 23.1 | 22.6 | 1.692 ±0.741 | .08 |
| Farm workers and other agricultural workers | 1556 | 1 535 568 | 6.70 | 18.72 | 19.5 | 17.3 | 23.6 | 17.0 | 19.2 | 15.2 | –0.600 ±0.658 | .41 |
| Forestry and fishing occupations | 117 | 134 640 | 6.00 | 19.81 | 16.0a | 25.8a | 0.0 | 17.4a | 39.8a | 20.5a | b | b |
| Mechanics and repairers | 3626 | 4 333 134 | 7.90 | 22.94 | 21.1 | 23.2 | 21.8 | 21.5 | 24.3 | 25.5 | 0.701 ±0.275 | .06 |
| Construction and extractive trades | 4686 | 5 398 196 | 7.40 | 18.45 | 16.5 | 16.6 | 17.9 | 15.2 | 21.9 | 21.9 | 1.071 ±0.553 | .13 |
| Precision production occupations | 2223 | 2 641 979 | 7.20 | 25.00 | 18.7 | 23.4 | 25.6 | 31.0 | 26.3 | 25.2 | 1.628 ±0.773 | .10 |
| Machine operators/tenders (except precision) | 2605 | 2 947 586 | 11.80 | 23.37 | 24.2 | 20.0 | 25.5 | 24.9 | 20.6 | 25.2 | 0.024 ±0.662 | .97 |
| Fabricators, assemblers, inspectors, samplers | 1414 | 1 690 948 | 10.90 | 22.00 | 21.8 | 19.5 | 17.7 | 24.9 | 22.4 | 26.4 | 0.973 ±0.662 | .22 |
| Motor vehicle operators | 2989 | 3 426 058 | 14.40 | 31.66 | 27.9 | 31.5 | 29.5 | 30.9 | 34.2 | 35.9 | 1.391 ±0.347 | .02 |
| Other transportation (except motor vehicles) | 140 | 185 361 | 10.40 | 28.72 | 12.2a | 30.6a | 49.0a | 27.0 | 21.9a | 32.3a | b | b |
| Material-moving equipment operators | 927 | 1 094 993 | 12.90 | 28.24 | 23.1 | 27.4 | 30.4 | 25.6 | 32.8 | 30.1 | 1.410 ±0.652 | .10 |
| Construction laborers | 836 | 897 497 | 10.80 | 22.32 | 22.2 | 14.5 | 15.2 | 25.8 | 29.2 | 24.8 | 1.782 ±1.269 | .23 |
| Freight, stock, material handlers | 2355 | 2 815 269 | 18.00 | 22.09 | 19.4 | 21.6 | 23.1 | 15.1 | 27.0 | 26.4 | 1.050 ±1.207 | .43 |
| Women | ||||||||||||
| Officials and administrators (public administration) | 376 | 346 463 | 19.70 | 21.12 | 18.0 | 22.2 | 21.7 | 20.1a | 25.2 | 19.5 | 0.621 ±0.601 | .36 |
| Managers administrators (except public administration) | 4934 | 4 797 582 | 8.50 | 18.11 | 17.0 | 14.9 | 20.3 | 17.9 | 18.4 | 19.9 | 0.660 ±0.437 | .21 |
| Management-related occupations | 2936 | 2 897 763 | 11.70 | 17.78 | 12.6 | 15.4 | 21.7 | 14.7 | 18.1 | 24.1 | 1.671 ±0.746 | .09 |
| Engineers | 210 | 207 259 | 5.60 | 12.84 | 8.5a | 12.1a | 10.8a | 15.6a | 17.4a | 11.7a | b | b |
| Architects and surveyors | 39 | 40 444 | 2.60 | 7.29a | 0.0 | 4.0a | 0.0 | 15.6a | 27.7a | 0.0 | b | b |
| Natural, mathematical/computer scientists | 799 | 768 699 | 9.50 | 13.30 | 12.6 | 10.3 | 16.5 | 14.5 | 12.3 | 13.8 | 0.374 ±0.515 | .51 |
| Health-diagnosing occupations | 283 | 288 217 | 6.60 | 10.25 | 0.0 | 10.5a | 16.9a | 8.2a | 10.2a | 14.7a | b | b |
| Health assessment/treating occupations | 2610 | 2 758 450 | 9.20 | 19.83 | 18.6 | 20.5 | 18.8 | 20.8 | 21.7 | 18.6 | 0.243 ±0.345 | .52 |
| Teachers, librarians, counselors | 4400 | 4 477 066 | 9.40 | 16.84 | 15.7 | 14.4 | 16.6 | 16.6 | 18.9 | 18.6 | 0.818 ±0.234 | .03 |
| Writers, artists, entertainers, athletes | 1117 | 1 092 478 | 5.30 | 13.48 | 13.2 | 10.4 | 17.8 | 11.2 | 12.0 | 16.8 | 0.451 ±0.683 | .55 |
| Other professional specialty occupations | 1463 | 1 362 526 | 15.60 | 19.14 | 15.2 | 14.1 | 19.1 | 16.2 | 24.9 | 25.1 | 2.104 ±0.694 | .04 |
| Health technologists/technicians | 1391 | 1 416 593 | 13.70 | 23.48 | 21.4 | 21.9 | 23.5 | 23.3 | 27.3 | 22.9 | 0.638 ±0.427 | .21 |
| Technologists, technicians (except health) | 838 | 810 554 | 9.70 | 18.04 | 17.2 | 20.9 | 8.7 | 20.8 | 19.7 | 20.8 | 1.147 ±1.686 | .53 |
| Supervisors and proprietors | 1421 | 1 449 510 | 7.50 | 19.96 | 16.4 | 20.5 | 17.0 | 18.2 | 21.4 | 25.1 | 1.390 ±0.546 | .06 |
| Sales representatives, commodities and finance | 1503 | 1 483 280 | 6.00 | 13.68 | 9.0 | 15.9 | 13.3 | 15.0 | 12.8 | 16.6 | 1.159 ±0.534 | .10 |
| Other sales personnel | 3585 | 3 684 792 | 12.60 | 18.24 | 14.7 | 19.2 | 21.0 | 18.5 | 19.1 | 16.7 | 0.370 ±0.583 | .56 |
| Computer equipment operators | 236 | 224 232 | 15.40 | 23.76 | 20.3 | 19.2a | 27.7 | 49.3 | 17.3 | 32.1a | b | b |
| Secretaries, stenographers, and typists | 2532 | 2 572 819 | 8.70 | 19.63 | 21.2 | 17.1 | 21.6 | 19.1 | 17.9 | 21.3 | –0.047 ±0.534 | .93 |
| Financial records processing occupations | 1768 | 1 786 692 | 7.90 | 20.42 | 15.0 | 25.4 | 18.5 | 19.8 | 19.4 | 24.1 | 0.963 ±0.857 | .32 |
| Mail and message distribution personnel | 379 | 361 468 | 20.90 | 17.39 | 26.3 | 11.1a | 13.9a | 17.7 | 15.4a | 20.4 | 0.480 ±1.407 | .75 |
| Other administrative support personnel | 7941 | 7 864 575 | 14.40 | 22.46 | 18.7 | 23.6 | 19.8 | 23.2 | 23.9 | 24.9 | 0.970 ±0.449 | .10 |
| Private household occupations | 701 | 578 535 | 13.20 | 18.76 | 0.0 | 15.6 | 18.8 | 23.0 | 16.9 | 20.2 | b | b |
| Police and firefighters | 232 | 189 198 | 29.00 | 15.89 | 26.0a | 4.2a | 13.3a | 10.1a | 26.1a | 18.9a | b | b |
| Other protective service occupations | 256 | 232 682 | 27.20 | 30.45 | 22.4a | 27.3 | 24.0 | 33.8 | 27.1a | 47.2 | b | b |
| Food service personnel | 3030 | 3 032 388 | 11.10 | 20.10 | 18.5 | 19.3 | 22.0 | 17.8 | 22.2 | 20.5 | 0.437 ±0.407 | .34 |
| Health service personnel | 2423 | 2 156 950 | 27.90 | 32.43 | 26.9 | 26.9 | 30.4 | 36.7 | 35.4 | 36.6 | 2.354 ±0.486 | .01 |
| Cleaning and building service personnel | 1545 | 1 325 389 | 21.50 | 25.25 | 23.2 | 26.3 | 23.2 | 24.9 | 26.5 | 27.6 | 0.668 ±0.345 | .13 |
| Personal service workers | 2261 | 2 167 360 | 13.90 | 22.01 | 18.0 | 22.4 | 21.7 | 24.0 | 22.8 | 23.2 | 0.968 ±0.358 | .05 |
| Farm operators and managers | 130 | 147 997 | 0.00 | 18.35 | 11.4a | 29.7a | 15.5a | 25.2a | 15.6a | 13.1a | b | b |
| Farm workers and other agricultural workers | 358 | 344 144 | 4.40 | 22.76 | 14.2a | 23.5 | 24.9a | 30.8 | 22.1 | 21.7 | 1.372 ±1.138 | .29 |
| Forestry and fishing occupations | 7 | 5 587 | 43.50 | 9.32a | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 32.2a | 0.0 | 0.0 | b | b |
| Mechanics and repairers | 218 | 203 532 | 11.80 | 20.65 | 8.9a | 6.6a | 21.5a | 26.4a | 25.3a | 26.9a | b | b |
| Construction and extractive trades | 144 | 152 008 | 4.50 | 6.93a | 2.1a | 3.6a | 0.9a | 10.7a | 10.1a | 16.4a | b | b |
| Precision production occupations | 848 | 802 569 | 12.40 | 23.20 | 28.2 | 21.6 | 22.9 | 24.5 | 18.4 | 24.0 | –0.978 ±0.792 | .28 |
| Machine operators/tenders (except precision) | 1678 | 1 498 063 | 17.60 | 25.14 | 24.8 | 23.5 | 24.2 | 24.7 | 25.4 | 29.1 | 0.669 ±0.335 | .12 |
| Fabricators, assemblers, inspectors, samplers | 1045 | 970 146 | 16.80 | 25.30 | 23.1 | 21.6 | 21.0 | 23.2 | 32.5 | 30.7 | 2.075 ±0.854 | .07 |
| Motor vehicle operators | 499 | 472 407 | 18.20 | 31.02 | 15.2 | 18.1 | 37.0 | 33.5 | 37.3 | 42.6 | 5.722 ±1.080 | .01 |
| Other transportation (except motor vehicles) | 5 | 2608 | 76.80 | 64.08a | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | b | b |
| Material-moving equipment operators | 86 | 76 818 | 15.90 | 29.53 | 10.4a | 22.4a | 27.4a | 22.8a | 41.6a | 52.6a | b | b |
| Construction laborers | 23 | 19 105 | 9.10 | 21.09a | 15.1a | 14.8a | 47.5a | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20.0a | b | b |
| Freight, stock, material handlers | 948 | 905 494 | 14.10 | 19.12 | 15.4 | 19.5 | 15.3 | 22.1 | 21.7 | 19.9 | 1.061 ±0.595 | .15 |
aEstimates have a relative standard error > 30% and should be used with caution, as they do not meet NCHS standards of reliability or precision.31
b Trends were not calculated when the sample size for any individual survey year fell below 45.
During the period from 1986 to 1995, the highest pooled obesity rates were observed for male workers employed as motor vehicle operators (19.8%), material-moving equipment operators (19.2%), and other protective services employees (19.2%); for female workers, the highest pooled obesity rates were among motor vehicle operators (22.6%), health services workers (21.0%), and cleaning and building services workers (20.0%). Among men, the only occupational group with a pooled obesity prevalence rate below 7% was that of individuals employed in the health-diagnosing occupations (6.2%); female occupations with obesity prevalence rates below 7% included architects and surveyors (1.7%); health-diagnosing occupation employees (4.3%); engineers (5.8%); sales representatives and commodities and finance workers (6.6%); and writers, artists, entertainers, and athletes (6.6%). Irrespective of gender, there were no employed groups that experienced a reduction in obesity rates during this time period. Occupational groups with a significant increase of 1% or greater per year included male workers employed in the other protective service occupations (1.07 ±.23%, P < .001), female motor vehicle operators (1.20 ±.29%, P < .001), and female mail and message distributors (1.16 ±.34%, P < .01).
In the period from 1997 to 2002 (Table 2 ▶), the highest pooled obesity rates were observed for male workers employed as motor vehicle operators (31.7%), police and firefighters (29.8%), other transportation except motor vehicle moving operators (28.7%), and material-moving equipment operators (28.2%); and, for female workers, those employed as motor vehicle operators (31.0%), other protective service workers (30.5%), material-moving equipment operators (29.5%), and cleaning and building service workers (25.3%). In contrast to the earlier survey period, there were no occupational groups among the men with an obesity rate below 11%. Among women, only those employed in the health-diagnosing occupations (10.3%), as architects and surveyors (7.3%), and in the construction and extractive trades (6.9%) had obesity rates below 11%. There were no significant downward trends in obesity rates for any occupational group during the survey period from 1997 to 2002. Obesity rates among male workers employed as police or firefighters had an annual increase of 2.1% (±.8); female workers with annual increases above 2% included motor vehicle operators (5.7 ±1.1); health service workers (2.4 ±.5); other professional specialty occupation employees (2.1 ±.7); and fabricators, assemblers, inspectors, and samplers (2.1 ±.9).
DISCUSSION
Using data from a large, nationally representative sample of US workers, we found that obesity rates were higher for female workers than for male workers within most of the 41 occupational groups. Black female workers were found to have the highest prevalence of obesity relative to “other race” and White workers of both genders. However, it is important to note that over the past decade, obesity rates were rising in all worker groups, irrespective of race and gender. Among the various US working groups, the prevalence of obesity increased almost 10% between the survey years 1986 and 2002. This increasing obesity epidemic poses substantial challenges to the US workforce.
Obesity and its related health conditions directly damage the health and well-being of the current workforce and significantly contribute to long-term chronic disability.32–36 Additionally, the significant increase in the prevalence of obesity among children and adolescents indicates an even greater problem that employers will likely confront within the future workforce.37 Short-term disability claims attributed to obesity have increased 10-fold over the past decade, according to an UnumProvident study that analyzed its extensive disability database.38 Obesity-related disabilities cost employers an average of $8720 per employee every year.38 Designing and implementing worksite weight-loss programs that educate and help employees to achieve and maintain weight loss could substantially reduce the costly health burden on both employers and workers. This effort will not only prevent work-related illness, injury, and disability but also promote healthy lifestyles, which, in turn, will prevent and reduce chronic disease in working-age Americans, many of whom spend 8 to 12 hours per day at work.
Limitations
The NHIS data are cross-sectional data that permit only inferences of association of obesity in the 41 occupations analyzed. However, findings from this study are similar to those of others,33,34 in which the prevalence of obesity has been found to vary according to occupation. Consistent with the present findings, previous research has shown that race/ethnicity, social class, age, and/or sedentary jobs can contribute to an increase in obesity.32,33,37 Furthermore, it is possible that among obese people there exists bias by self-selection of occupation.
Although BMI has been shown, traditionally, to correlate with fat distribution, it must be noted that it does not take into account individuals who may have a large muscular habitus, nor does it directly measure percent body fat. However, most health organizations and scientists support the use of BMI to define overweight and obesity, particularly when direct measures of fat distribution are not available.39–41 Using a 2 or 1 week reference period prior to the NHIS interview to characterize occupational status might lead to misclassification of individuals with respect to their usual occupation. However, ongoing analyses of the NHIS data by the present team of investigators indicate a substantial concordance between self-reported current occupation and longest-held job.42
The present analysis suffers from many of the limitations seen in large population-based studies. Weight and height were collected in a self-reported or proxy fashion, which could have led to less precision in the calculation of the BMI.43,44 For example, previous research has suggested that people tend to underreport their weight and overreport their height, leading to the underestimation of BMI; additionally, the degree of under- and overreporting varies as a function of age, gender, race, ethnicity, and social class.45–47
The 1986 to 1995 NHIS employed proxy information when adults were not available for household interview. Proxy reports of weight and height may also be subject to bias. To reduce this potential bias, we reanalyzed our 1986 to 1995 data in the 61% of NHIS participants who directly reported weight and height during the interview. Results indicate that, for most occupations, the self-reported BMIs would be even higher than the combined proxy and self-reported BMIs. Examining the BMIs for all workers from 1986 to 1995, we found the average annual difference in the percentage of obesity between the nonproxy (self-reported) BMIs and the combined proxy and self-reported BMIs was 0.73%.
Finally, the change in the survey design methodology in 1996 prevented trend comparisons over the total 17-year time period. Moreover, small sample sizes could lead to less reliable estimates of obesity rates and trends in some worker subpopulations (e.g., private household occupations among men, and architects and surveyors among women).
Strengths
Despite the limitations presented, the use of large sample sizes, the nationally representative nature of the sample, oversampling of select subgroups (e.g., Blacks), and the annual assessment useful for assessing trends in prevalence of obesity within occupations allows this study to be favorably compared to other evaluations of the US obesity epidemic.
Irrespective of gender, individuals employed as motor vehicle operators were found to have the highest prevalence of obesity in both time periods. Among men, these pooled prevalence rates increased from 19.8% in the 1986 to 1995 survey period to 31.7% in the 1997 to 2002 survey period; corresponding rates for women were 22.6% and 31.0%, respectively. Developing weight-loss programs designed to take into account the job demands, physical demands, and even the socioeconomic and cultural backgrounds of motor vehicle operators could potentially help reduce this detrimental increase in obesity within this occupational group. Furthermore, examining occupations with a lower prevalence of obesity (such as female architects and surveyors or men employed in the health-diagnosing professions) could help researchers elucidate the relationship between occupation and optimal body weight.
Conclusions
The behavioral effects of physical activity on health are well established.48–51 Although the most promising weight-loss interventions focus on increasing physical activity in addition to implementing dietary changes, the increasing trend towards automation and other labor-saving strategies found at many work-sites will not foster physical activity conducive to weight loss. Primary and secondary prevention of obesity in occupational settings must therefore take into account the many societal and occupational factors that influence energy imbalance via multifaceted interventions (e.g., accountability of healthy food choices and food quantity, exercise programs). Such comprehensive, worksite-based interventions are urgently needed in order to slow the growing epidemic of obesity in the United States.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded in part through the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) (grant R01 OH003915).
Findings from this study were presented at the Annual Education Conference in 2004 of the Florida Public Health Association, Orlando, Florida, July 28, 2004; the Centers for Disease Control (CDC)/NIOSH conference “Steps to a Healthier US Workforce,” October 26–28, 2004; Washington, DC, Cafritz Conference Center; and at the 132nd Annual Meeting of the American Public Health Association in Washington, DC, November 8, 2004.
The data used in this article were made available in part by the Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social Research. The data for the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) were originally collected and prepared by the US Department of Health and Human Services and the National Center for Health Statistics.
Note. Neither the collector of the original data nor the Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social Research bears any responsibility for the analyses or interpretations presented in this article.
Human Participant Protection Because this study utilized anonymous data from a publicly available database, the protocol was reviewed and approved for exemption by the institutional review board of the University of Miami School of Medicine.
Peer Reviewed
Contributors A. J. Caban, L. E. Fleming, and D. J. Lee originated the study and led the writing of this article. W. LeBlanc and O. Gómez-Marín managed the data and performed statistical analyses. T. Pitman provided study support and data management. All authors helped conceptualize ideas, interpret findings, and provide critical review of the article.
References
- 1.Manson JE, Skerrett PJ, Greenland P, VanItallie TB. The escalating pandemics of obesity and sedentary lifestyle: a call to action for clinicians. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:249–258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA. 2002;288:1723–1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Silva MM, Matsuoka VF, Silva AR, Reimo R, Faintuch J, Zilberstein B, Gama-Rodrigues J. Sleep abnormalities in morbid obesity. Clin Nutr. 2003;22: S21–S22. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Abbasi F, Brown BW Jr, Lamendola C, McLaughlin T, Reaven GM. Relationship between obesity, insulin resistance, and coronary heart disease risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:937–943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Howard BV, Ruotolo G, Robbins DC. Obesity and dyslipidemia. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2003; 32:855–867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Boland LL, Folsom AR, Rosamond WD, for the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study Group. Hyperinsulinemia, dyslipidemia, and obesity as risk factors for hospitalized gallbladder disease. A prospective study. Ann Epidemiol. 2002;12:131–140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gelber AC. Obesity and hip osteoarthritis: the weight of the evidence is increasing. Am J Med. 2003; 114:158–159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Carmichael AR, Bates T. Obesity and breast cancer: a review of the literature. Breast. 2004;13:85–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mydlo JH, Gerstein MI, Harris CF, Braverman AS. Immune function, mitogenicity, and angiogenic growth factor concentrations in lean and obese rodent sera: implications in obesity-related prostate tumor biology. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2003;6:286–289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ozcelik B, Basbug M, Ozsahin O, Yilmazsoy A, Erez R. Effects of hypertension and obesity on endometrial thickness. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2003;109:72–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kornitzer M, Kittel F. How does stress exert its effects: smoking, diet and obesity, physical activity? Post-grad Med J. 1986;62:695–696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Langenberg C, Hardy R, Kuh D, Brunner E, Wadsworth M. Central and total obesity in middle aged men and women in relation to lifetime socioeconomic status: evidence from a national birth cohort. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2003;57:816–822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Goodman E, Slap GB, Huang B. The public health impact of socioeconomic status on adolescent depression and obesity. Am J Public Health. 2003;93: 1844–1850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wellman NS, Friedberg B. Causes and consequences of adult obesity: health, social and economic impacts in the United States. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2002;11:S705—S709.12534694 [Google Scholar]
- 15.US Department of Health and Human Services. Healthy People 2010: Understanding and Improving Health. 2nd ed. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2000.
- 16.Harrell JS, Johnston LF, Griggs TR, et al. An occupation based physical activity intervention program: improving fitness and decreasing obesity. AAOHN J. 1996;44:377–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brill PA, Giles WH, Keenan NL, et al. Effect of body mass index on activity limitation and mortality among older women: the National Health Interview Survey, 1986–1990. J Womens Health. 1997;6: 435–440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fowler FJ. The redesign of the National Health Interview Survey. Public Health Rep. 1996;111:508–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liao Y, Cooper RS, Cao G, et al. Mortality patterns among adult Hispanics: findings from the NHIS, 1986–1990. Am J Pub Health 1998;88:227–232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wagener DK, Winn DW. Injuries in the work-place: black-white differences. Am J Public Health. 1991;81:1408–1414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Atrostic BK, Bates N, Burt G, Silverstein A, Winters F. Nonresponse in federal household surveys: new measures and new insights. Paper presented at the International Conference on Survey Non-response; October, 1999; Portland, OR. Available at: http://www.fcsm.gov/committees/ihsng/portland_3__120299.pdf. Accessed July 8, 2004.
- 22.Gentlemen JF. Overview of the National Health Interview Survey. National Center for Health Statistics. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/ppt/bsc/OB193_BSC_JG.ppt. Accessed on: July 21, 2005.
- 23.Hill A, Roberts J. Body mass index: a comparison between self-reported and measured height and weight. J Public Health Med. 1998;21:116–117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1995;854:1–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.National Health Interview Survey, 2002. Code-book: 2002. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics (US). Available at: ftp://ftp.cdc.gov/pub/Health_Statistics/NCHS. Accessed July 8, 2004.
- 26.Zwerling C, Whitten PS, Davis CS, Sprince NL. Occupational injuries among older workers with visual, auditory, and other impairments: a validation study. J Occ Environ Med. 1998;40:720–723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Brackbill R, Frazier T, Shilling S. Smoking characteristics of US workers, 1978–80. Am J Ind Med. 1998;13:5–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.National Health Interview Survey, 1986. Codebook: 1986. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics (US). Available at: ftp://ftp.cdc.gov/pub/Health_Statistics/NCHS. Accessed July 8, 2004.
- 29.National Health Interview Survey, 2001. Codebook: 2001. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics (US). Available at: ftp://ftp.cdc.gov/pub/Health_Statistics/NCHS. Accessed July 8, 2004.
- 30.Software for Survey Data Analysis (SUDAAN), Version 8.0.0. Research Triangle Park, NC: Research Triangle Institute; 2001.
- 31.Lethbridge-Çejku M, Schiller JS, Bernadel L. Summary health statistics for US Adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2002. National Center for Health Statistics. Vital Health Stat 10. 2004;222:1–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lahti-Koski M, Vartiainen E, Mannisto S, Pietinen P. Age, education and occupation as determinants of trends in body mass index in Finland from 1982 to 1997. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000;24: 1669–1676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sarlio-Lahteenkorva S, Silventoinen K, Lahelma E. Relative weight and income at different levels of socioeconomic status. Am J Public Health 2004;94: 468–472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sturm R, Ringel JS, Andreyeva T. Increasing obesity rates and disability trends. Health Affairs. 2004;23: 199–205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Narbro K, Agren G, Jonsson E, et al. Sick leave and disability pension before and after treatment for obesity: a report from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999;23: 619–624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Regan J, Hamer G, Wright A. The epidemic of obesity: when a disease is not a disability. Tenn Med. 2003;96:564–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999–2000. JAMA. 2002; 288:1728–1732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.UnumProvident Obesity-Related Disability Claims Study. Available at: http://www.unumprovident.com/newsroom/news/corporate/obesity.aspx. Accessed July 8, 2004.
- 39.Lean MEJ, Han TS, Seidell JC. Impairment of health and quality of life using new federal guidelines for the identification of obesity. Arch Intern Med. 1999; 159:837–843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.National Institutes of Health. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults. Bethesda, Md: Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; 1998.
- 41.Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM. Criteria for definition of overweight in transition: background and recommendations for the United States. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72:1074–1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gómez-Marín O, Fleming LE, LeBlanc W, Lee DJ, Pitman T, Caban AJ. Longest-held job in US occupational groups: The National Health Interview Survey (NHIS). J Occup Environ Med. 2005;47:79–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Patrick DL, Bushnell DM, Rothman M. Performance of two self-report measures for evaluating obesity and weight loss. Obes Res. 2004;12:48–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Morgan PJ, Jeffrey DB. Restraint, weight suppression, and self-report reliability: how much do you really weigh? Addict Behav. 1999;24:679–682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kuczmarski MF, Kuczmarski RJ, Najjar M. Effects of age on validity of self-reported height, weight, and body mass index: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. J Am Diet Assoc. 2001;101:28–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Engstrom JL, Paterson SA, Doherty A, Trabulsi M, Speer KL. Accuracy of self-reported height and weight in women: an integrative review of the literature. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2003;48:338–345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Spencer EA, Appleby PN, Davey GK, Key TJ. Validity of self-reported height and weight in 4808 EPIC-Oxford participants. Public Health Nutr. 2002;5: 561–565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhang Q, Wang Y. Socioeconomic inequality of obesity in the United States: do gender, age, and ethnicity matter? Soc Sci Med. 2004;58:1171–1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Belza B, Warms C. Physical activity and exercise in women’s health. Nurs Clin North Am. 2004;39: 181–193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wang F, McDonald T, Champagne LJ, Edington DW. Relationship of body mass index and physical activity to health care costs among employees. J Occup Environ Med. 2004;246:428–436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Brown DW, Brown DR, Heath GW, et al. Associations between physical activity dose and health-related quality of life. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36: 890–896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]