Figure 1.—
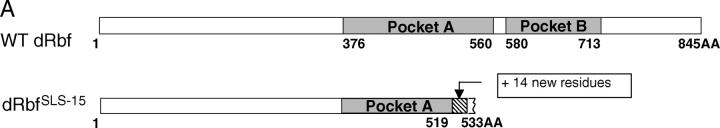
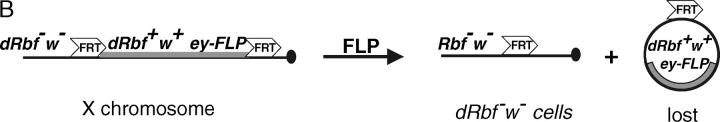
Schematics of the Rbf protein and Rbf rescue construct. (A) Diagram of the wild-type Rbf and RbfSLS-15 mutant proteins. The mutation analysis of the RbfSLS-15 transcripts revealed an 11-bp deletion resulting in a frameshift at amino acid residue 519, followed by the addition of 14 novel residues and truncation of the Rbf protein at residue 533. The truncated protein lacks Pocket B, a highly conserved RBF domain that is required for interactions with partner proteins and the execution of RBF function. (B) Diagram of the Rbf rescue construct and Rbf− clone generation. The RbfSLS-15 mutation combined with a Rbf rescue construct allows for the generation of Rbf− clones specifically in the eye, due to eye-specific FLP expression followed by recombination between the FRT sites and subsequent loss of the Rbf+ and w+ genes. All other tissues, which do not express FLP, remain Rbf+, resulting in a rescue of the organismal lethality normally associated with Rbf-deficient flies.