Abstract
Landscape genetics is a new discipline that aims to provide information on how landscape and environmental features influence population genetic structure. The first key step of landscape genetics is the spatial detection and location of genetic discontinuities between populations. However, efficient methods for achieving this task are lacking. In this article, we first clarify what is conceptually involved in the spatial modeling of genetic data. Then we describe a Bayesian model implemented in a Markov chain Monte Carlo scheme that allows inference of the location of such genetic discontinuities from individual geo-referenced multilocus genotypes, without a priori knowledge on populational units and limits. In this method, the global set of sampled individuals is modeled as a spatial mixture of panmictic populations, and the spatial organization of populations is modeled through the colored Voronoi tessellation. In addition to spatially locating genetic discontinuities, the method quantifies the amount of spatial dependence in the data set, estimates the number of populations in the studied area, assigns individuals to their population of origin, and detects individual migrants between populations, while taking into account uncertainty on the location of sampled individuals. The performance of the method is evaluated through the analysis of simulated data sets. Results show good performances for standard data sets (e.g., 100 individuals genotyped at 10 loci with 10 alleles per locus), with high but also low levels of population differentiation (e.g., FST < 0.05). The method is then applied to a set of 88 individuals of wolverines (Gulo gulo) sampled in the northwestern United States and genotyped at 10 microsatellites.
RECENT developments in molecular markers and statistical tools, combined with powerful computers have led to the emergence of a new scientific field, landscape genetics, which is an amalgamation of population genetics and landscape ecology (Manel et al. 2003). This discipline aims to provide information on how landscape and environmental features influence gene flow, population structure, and local adaptation. It also aids in identifying cryptic genetic discontinuities, which are breaks in gene flow without any obvious cause, or secondary contact among previously isolated populations. The spatial delineation of genetic discontinuities within a species allows that of operational units, an important issue for species management (i.e., for pest control, as well as the monitoring of game or threatened species). Moreover, identifying the abiotic and biotic factors involved in evolutionary processes is essential for modeling and predicting the evolution of genetic diversity under different scenarios, especially those related to environmental changes due to human activity (e.g., habitat fragmentation). Landscape genetics usually makes use of data obtained at highly variable markers (e.g., microsatellites) and collected at a finer scale than that typical of phylogeography. Therefore, in contrast to phylogenetics, landscape genetics tends to focus on the understanding of the microevolutionary processes that generate genetic structure across space. The two key steps of landscape genetics are the detection and location of genetic discontinuities and the correlation of these discontinuities with landscape and environmental features (e.g., mountains, rivers, roads, gradient of humidity, and deforested areas) (Manel et al. 2003). Ideally, the first step should be based on methods that do not require assumptions of population boundaries beforehand. This implies that the individual is the operational unit of study. However, this unit can be extended to a priori defined populations if enough populations can be sampled and individuals are not too sparsely distributed in space within each population sample.
Several recent methods based on cluster models and likelihood computation have the potential to both group individuals into populational units and detect migrants between those units, without requiring the a priori definition of populational limits (Pritchard et al. 2000; Dawson and Belkhir 2001; Falush et al. 2003). However, these methods do not explicitly take into account the spatial nature of the problem of detecting and locating genetic discontinuities. In formal terms, they are all based on the assumption that the variable coding the assignment to a population is a priori independent and identically distributed among individuals. As a consequence, they do not make use of spatial coordinates of sampled individuals, except in some ad hoc postprocessing schemes like those consisting of drawing by hand the spatial convex hull of each inferred population. Hence these methods cannot objectively identify the spatial location of genetic discontinuities between populations.
Although a large body of statistical literature is available on the clustering of spatially explicit data (Lawson and Denison 2002), the models available are devoted to the analysis of quantitative and univariate data, whereas genetic data are categorical and strongly multivariate by nature. The work of Vounatsou et al. (2000) should, however, be mentioned, since it aims to relate haplotype frequencies to spatial coordinates and environmental covariates. Nevertheless, this method starts from a known clustering of data, which is injected as a prior information on the spatial dependence through a conditional autoregressive model. In a different spirit, Dupanloup et al. (2002) proposed to cluster populations by maximization of a differentiation criterion between population clusters, the criterion being the proportion of total genetic variance due to differences between clusters. As the effective maximization is numerically prohibitive, Dupanloup et al. (2002) suggest using a simulated annealing approach in which the random search strategy makes use of the spatial coordinates of the population samples (note that the unit of treatment could be an individual rather than a population). This can lead to certain local maxima easy to reach from a given spatial sampling configuration and to the identification of relevant genetic discontinuities between groups of populations. However, their criterion does not rely on the coordinates in its definition; therefore the global maximum searched does not depend itself on the coordinates, and the method turns out to be spatial mainly through the heuristic optimization strategy, whose convergence properties still have to be assessed.
In this article, we describe a new statistical model that aims at inferring and locating genetic discontinuities between populations in space from individual multilocus genetic data. Our central assumption throughout this work is that some spatial dependence is often present among individuals. On the basis of this sensible assumption, we developed a hierarchical spatial model in which we formally inject a priori information on how the individuals are spatially organized. In addition to the detection of genetic discontinuities between populations, our method also addresses the following points: (i) denoising blurred coordinates of sampled individuals, (ii) estimating the number of populations in the studied area, (iii) quantifying the amount of spatial dependence in the data, (iv) assigning individuals to their population of origin, and (v) detecting individual migrants between populations.
HIERARCHICAL SPATIAL MODEL
The global set of sampled individuals is viewed as representative of one or several panmictic populations separated by geographic borders across space. Our modeling strategy is hierarchical in the sense that we first specify how the populations are spatially organized and then we specify the statistical genetic properties of each population conditionally on this spatial organization.
Hidden model of spatial organization through Voronoi tessellation:
Let Δ be the geographical region under study. We denote by z = (z1, … , zn) the vector of genotypes of the n diploid individuals (although other ploidies could be considered) observed at L loci, zi being a collection of pairs of alleles zi,l = {ai,l, bi,l}, with l = 1, … , L, and we denote by t = (t1, … , tn) the vector of the two-dimensional spatial coordinates of these individuals.
We consider that there are K different populations present in the spatial domain under study and that those populations occupy some subdomains Δ1, … , ΔK. The Δk form a partition of Δ, namely Δ = Δ1 ∪ … ∪ ΔK with Δk ∩ Δl = 0, for k ≠ l. We consider the setting where we have no knowledge about the shape and location of these subdomains, and part of this article is devoted to their estimation from spatial and genetic data t and z. A geographical subdomain being possibly extremely complex, we need to make a few assumptions on the shape and locations of the Δk, to reduce the complexity, namely the number of parameters, of the problem. For several reasons discussed later, we assume that each subdomain Δk can be approximated by a union of convex polygons. This assumption is not restrictive as any complex domain can be arbitrarily well approximated by such union of convex polygons provided enough polygons are considered. As we do not know where such polygons should be placed to approximate some true spatial organization of the population under study, we model the locations of these polygons as random variables with uniform distribution over the whole spatial domain.
More formally, we consider that there is a point process (a set of random points in the spatial domain, the number of points itself being random) that has realization denoted by (u1, … , um). Each ui (referred to hereafter as nucleus) defines a set Ai around it, defined as Ai = {s, dist(s, ui) ≤ dist(s, uj), ∀j = 1, … , m}. Namely, Ai is the set of geographical sites closer to ui than to any other points among (u1, … , um). Each Ai is a convex polygon and the set A1, … , Am is known as the Voronoi tesselation of Δ, as it splits Δ in m nonoverlapping subdomains. We now assume that each of these Ai contains individuals of one subpopulation only. Hence, each Ai can be labeled by a number between 1 and K that we denote by c(ui).
In mathematical terms, we parameterized these subdomains assuming that they are unions of some underlying Voronoi cells induced by a homogeneous Poisson point process. For any arbitrary point x in Δ, c(x) is defined as the population of its closest nucleus. The domain finally covered by population k is the union of cells of the same population, namely 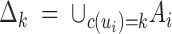 . The belonging of any point of the domain to the populations can be thought of as a coloring; hence this model is sometimes referred to as colored Voronoi tiling. (See Figure 1 for an illustration with K = 2 and m = 5.) It is widely used in earth sciences to model spatial organization of categorical variables such as geological formations, or soil occupation (Lantuéjoul 2002), and has also been used in genetics in a different framework by Dupanloup
et al. (2002).
. The belonging of any point of the domain to the populations can be thought of as a coloring; hence this model is sometimes referred to as colored Voronoi tiling. (See Figure 1 for an illustration with K = 2 and m = 5.) It is widely used in earth sciences to model spatial organization of categorical variables such as geological formations, or soil occupation (Lantuéjoul 2002), and has also been used in genetics in a different framework by Dupanloup
et al. (2002).
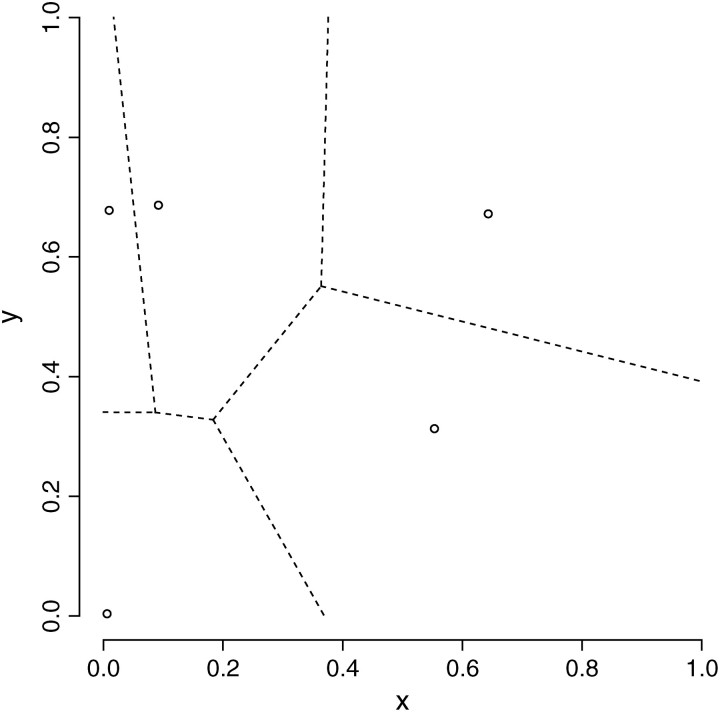
Figure 1.—
Random tessellation of a unit square into two spatial domains through a colored Voronoi tiling. Left, realization of a Poisson point process with Voronoi tessellation induced. Right, partition obtained after union of tiles belonging to the same population (coded as two colors).
We assume that all populations have a priori equal probability; therefore, we assume that each tile belongs to a population with probability 1/K, independently. Although reasonably simple, our model allows departure from the so-called independent identically distributed (i.i.d.) mixture model commonly used in nonspatial cluster models (Pritchard et al. 2000; Falush et al. 2003). In the latter method, the joint prior probability that individual i belongs to population k and individual i′ belongs to population k′ is equal to 1/K2 (the product of the marginals) whatever the geographical distance between the individuals may be.
In the colored Voronoi tiling model that we propose to use, the marginal is uniform, but the joint probability does not factorize. More specifically, the joint probability that any two individuals belong to the same population decreases with the geographical distance between them. In other words, i.i.d. mixture models such as those of Pritchard et al. (2000) or Falush et al. (2003) put equal prior weights to all partitions, whereas our model tends to favor partitions that are spatially organized. To a certain extent, our model is very similar in spirit to those used in image analysis, where the purpose is to retrieve a true scene blurred by a certain noise. In this context, it is widely admitted that even when very little is known about the true scene, it is useful to use a prior assuming some spatial organization; see Besag (1986) or Hurn et al. (2003) for a recent review. The advantages of our spatial model are (1) the possibility for better classification with limited data due to a more informative prior and (2) the direct inference about range boundaries. However, with large amounts of data (and a given K), the posterior assignments of individuals should be the same under the spatial model as for the nonspatial model.
The amount of spatial dependence prescribed by the colored Voronoi tesselation depends on how the domains Δk are themselves fragmented in smaller polygons Ai. Let us denote by λ the rate of the Poisson process u1, … , um. This parameter controls the number of polygons in Δ and hence the amount of spatial dependence in the hidden clustering. Low values of λ correspond to weakly fragmented partitions of Δ and thus to strong dependence of the hidden spatial organization of populations, whereas large values of λ correspond to high fragmentation and weak spatial dependence. When the number of points m is very large, each tile contains only one sampled individual and our tessellation model behaves like an i.i.d. mixture model similar to the prior on the clustering used by Pritchard et al. (2000), Corander et al. (2003), or Falush et al. (2003).
It is worth noting that the model allows the definition of complex spatial domains including situations for which those domains appear as unconnected pieces in the sampling window (see Figure 2). Hence, our model should not overestimate the number of populations in these particular although potentially frequent cases. Moreover, as is shown later, this feature makes it possible to visually detect migrants and identify their spatial domain of origin.
Figure 2.—
Illustration of the need for a tessellation prior allowing nonconnected components.
Although it can sometimes be relevant to model animal territories as Voronoi cells (Blackwell 2001), we do not give to the cells any strong biological interpretation, neither do we see this tiling model as a realistic representation of the true organization of populations. This prior on the partition allows penalizing only very loosely spatially organized clustering, as we believe that populations tend to be spatially organized in real life. However, our model does not penalize too strongly connected components of small to moderate sizes. This feature complies well with the fact that our prior knowledge on the level of spatial fragmentation of populations is usually rather limited. Therefore, the colored Voronoi tiling model is a good trade-off between numerical tractability and more complicated partition models like those of Nicholls (1997), Møller and Waagepetersen (1998), or Møller and Skare (2001).
Model for frequencies:
It is commonly assumed in population genetics that the allele frequencies follow independent Dirichlet distributions, namely
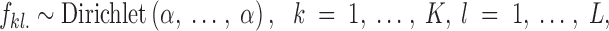 |
1 |
where fkl. denotes the vector whose entries are fklj (frequency of allele j at locus l in population k), (e.g., Rannala and Moutain 1997; Pritchard et al. 2000; Estoup et al. 2004). This model (referred to hereafter as D-model and spatial D-model when embedded in our spatial scheme) is attractive, because of its conjugacy properties and its biological relevance according to the theory of evolutionary neutral mutation process of Kimura (Tavaré and Zeitouni 2001). However, it does not take into account the fact that allele frequencies tend to be similar in different populations.
Following this line of thought, Falush et al. (2003) introduced interpopulation correlation in frequencies by introducing a hypothetical ancestral population with allele frequencies fAlj, l = 1, … , L, j = 1, … , Jl (frequency of allele j at locus l in the ancestral population, where Jl is the number of alleles at locus l), from which present populations have diverged according to drift factors d1, … , dK. In this second model (referred to as F-model and spatial F-model when embedded in our spatial scheme), the frequencies at each locus in the ancestral population follow a Dirichlet(1, … , 1) distribution. Falush et al. (2003) relate frequencies in the present populations to those of the ancestral population and to the drift factors through
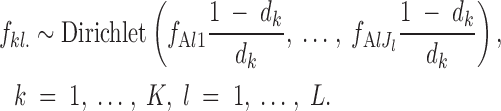 |
2 |
This equation accounts for the fact that if a set of populations have split from an ancestral population at a given time, their allele frequencies will differ. The amount of differentiation depends on many factors that are quantitatively unknown. The vector d1, … , dK parameterizes our uncertainty about the level of differentiation.
Anticipating the discussion that follows, we may fear that the F-model embedded in our full Bayesian inferential scheme, including inference of K (see below), may be excessively flexible, since in contrast to Falush et al. (2003), we do not prescribe how many populations there are, and neither does the F-model state how differentiated these populations are. This may lead to inference of spurious populations. Therefore, although the F-model sounds theoretically more appealing than the D-model, we keep attention on both models throughout this article.
Conditional model for genotypes:
Given the partition and the allele frequencies fklj, we assume that the genotypes in each population are independent draws from the discrete multivariate distribution specified by the fklj, which is equivalent to the assumption of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium within, and linkage equilibrium, between loci.
FULL BAYESIAN SPECIFICATION
All nonobserved quantities involved are treated as unknown. For full Bayesian inference we place priors on them, and the model can be summarized as follows.
Number of populations:
K ∼ Uniform({Kmin, … , Kmax}). This is a weakly informative prior for which the only subjective inputs are Kmin, usually set to 1, and Kmax, set to a large value as compared to the maximum number of populations that can be reasonably expected, so that the choice is numerically inconsequential.
Number and location of tiles:
We consider that m ∼ Poisson(λ) and that u1, … , um
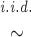 UniformD. This is the usual homogeneous Poisson process. The complete randomness of the locations of the points makes this prior noninformative about the locations of the borders between populations, and it is numerically convenient. The unknown amount of spatial organization is controlled by λ, on which we place a flat hyper-prior, assuming that λ ∼ u([0, λmax]). As previously mentioned, for large λ-values, the tessellation model behaves like an i.i.d. mixture model. As λmax should be taken large enough to cover a large range of spatial organization from strong (λ ≈ 0) to weak spatial organization, we suggest taking λmax equal to the number of sampled individuals.
UniformD. This is the usual homogeneous Poisson process. The complete randomness of the locations of the points makes this prior noninformative about the locations of the borders between populations, and it is numerically convenient. The unknown amount of spatial organization is controlled by λ, on which we place a flat hyper-prior, assuming that λ ∼ u([0, λmax]). As previously mentioned, for large λ-values, the tessellation model behaves like an i.i.d. mixture model. As λmax should be taken large enough to cover a large range of spatial organization from strong (λ ≈ 0) to weak spatial organization, we suggest taking λmax equal to the number of sampled individuals.
Colors of tiles:
c1, … , cm
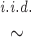 Uniform1, … , K.
Uniform1, … , K.
Subdomains of populations:
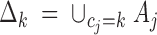 for k = 1, … , K, where (A1, … , Am) are the Voronoi tiles induced by (u1, … , um).
for k = 1, … , K, where (A1, … , Am) are the Voronoi tiles induced by (u1, … , um).
Drift:
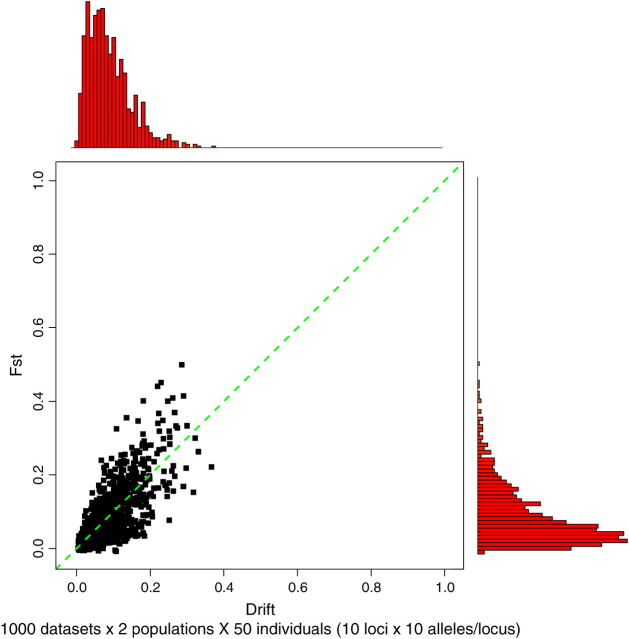
The drift parameters prescribe the amount of genetic differentiation between the present-time populations and the ancestral population and, hence, between the present-time populations themselves. Although it may be sometimes possible to have a rough idea of the amount of differentiation between populations under study (e.g., in terms of classical measures, such as FST), it seems, however, difficult to express this prior knowledge in terms of a prior on the drift parameters. To assess the relation between the drift factors and the differentiation we carried out a small set of simulations. We simulated 1000 data sets, each made of two populations of 50 individuals genotyped at 10 loci with 10 alleles per locus. All frequencies were preliminarily sampled from the F-model with drift d1 = d2 uniform on [0, 1]. The level of differentiation between population samples was measured using the parameter FST estimated following Weir and Cockerham (1984). Results show a close linear relation between d and FST. It therefore sounds natural to place a prior on dk, putting most weight on the left side of [0, 1] with a negligible weight for values >0.3, instead of a prior uniform on [0, 1]. An independent Beta(2, 20) prior complies well with these requirements (see Figure 3). Note that a limited number of test simulations indicated that the choice of prior on dk did not affect the results of the overall algorithm (results not shown).
Figure 3.—
Relationship between drift factor and FST. Results are from simulated data. The drifts d1 and d2 were equal and sampled from a Beta(2, 20) prior (x-axis).
Frequencies in the ancestral population:
fAl1, … , fAlJl ∼ Dirichlet(1, … , 1), l = 1, … , L.
Frequencies in the present population:
fkl. ∼ Dirichlet fAl11 − dk/dk, … , fAlJl1 − dk/dk, k = 1, … , K, l = 1, … , L.
Locations of individuals:
The recorded location ti of sampled individual i may not be representative of the true location of the individual. Consider, for instance, the case of sedentary animals (where the true location makes sense) that have moved during capture, or the case of units localized at a coarse administrative level only, or simply the case of measurement errors. To account for this uncertainty, each ti stands for the observed location whereas the true location is denoted by si. These unobserved si are treated as unknown hereafter and are part of the parameters to be estimated. The true coordinates si are naturally related to observed coordinates ti through
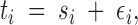 |
3 |
where εi is an i.i.d. additive noise chosen in a suitable parametric distribution. Even when the coordinates are recorded with a good precision with respect to the size of the domain under study, it is useful to introduce such an additive noise to allow individuals with the same coordinates to belong to different populations.
MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO INFERENCE
We denote by θ = (K, m, u, c, d, f, fA, s) the vector of unknown parameters to be estimated. The likelihood of the data (t, z) is
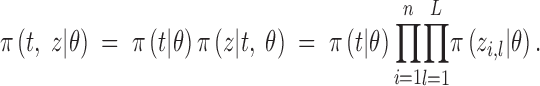 |
4 |
The terms of the product are given by the allelic frequencies:
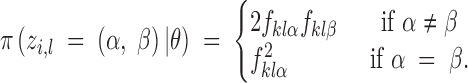 |
5 |
The inference of θ will be made through the investigation of its posterior distribution π(θ|t, z). We consider a hybrid algorithm based on sequential updates of the various blocks of parameters. All parameters are randomly initialized from the prior. Then the moves are proposed in a deterministic order as follows: (1) update d; (2) update fAl (these two steps are skipped in the D-model; see appendix, Details of MCMC computations); (3) update fkl.; (4) update cj for j = 1, … , m; (5) update uj for j = 1, … , m; (6) update si for i = 1, … , n; (7) discard or add a tile (increase or decrease m by 1); and (8) split one existing population into two or merge two into one (i.e., increase or decrease K by 1). Convergence follows from detailed balance, irreducibility, and aperiodicity (see appendix for computational details).
In practice the number of populations is first estimated by computing the mode of the posterior distribution: K̂ = ArgmaxK π[K|t, z] from a first run (θt)t=1,…,T. Then, because it is meaningless to compute empirical means on values of θt corresponding to different values of K, one can either work on subsamples of (θt)t=1,…,T obtained by restricting to the states corresponding to K = K̂ or simply rerun the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm with fixed K set to K̂.
As in all mixture problems, this model is not identifiable as the likelihood is invariant under any relabeling of the populations (Celeux 1997; Stephens 1997; Robert and Mengersen 1999; Celeux et al. 2000; Stephens 2000). Consequently, it may happen that along an MCMC run (especially if the numbers of loci and alleles are small), a move from say state ci = k to ci = l does not correspond to a reassignment of the ith cell but to a relabeling of the populations (switch between k and l). Although more theoretically rooted methods are available (Celeux et al. 2000; Stephens 2000) we used the expedient (when label switching was suspected), which consists of imposing after the run the following identifying constraints on the frequency of the first locus,
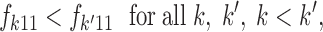 |
6 |
where the loci are sorted by an increasing number of alleles. This rule enabled us to fix the label-switching issue only when the frequencies did not overlap in the chains, and we found that it is advisable to check visually the trace of frequencies in the MCMC run to detect a possible switch.
We observed that label switching could be frequent when working with small data sets (<100 individuals, 1 or 2 loci, few polymorphisms) and becomes rare with larger and more traditional microsatellite data sets (e.g., at least 100 individuals genotyped at 10 loci with 10 alleles per locus). When such a relabeled sample is available, the conditional posterior π[c(s)|K = K̂, z, t] is estimated by the corresponding empirical mean. Similarly, d, fA, and f are estimated by their means over the corresponding populations.
The whole algorithm has been programmed in Fortran 77, making use of the numerical library for random number generation, Randlib1.3. The machine time required for 105 iterations on a data set of 1000 individuals genotyped at 10 loci with 10 alleles per locus with 10 loci is typically of 1 hr on a PC equipped with a 2-GHz chip set.
RESULTS FROM SIMULATED DATA SETS
Number of populations:
A first interesting feature of this model is its ability to deal with an unknown number of populations. Because the effective value of the model depends on the precision in the estimation of K, this key point has been investigated by analyzing data sets simulated using the prior of the previously described spatial F-model. To retrieve the known K parameters that served to build the data set, we ran the MCMC scheme using the spatial F-model or the spatial D-model as a prior in the inference and computed K̂ after 50,000 iterations.
We first started by building 50 data sets of n = 50 individuals with K = 1 (only one population). For each data set, we get estimated K, and thus we end up with 50 estimated values corresponding to the 50 simulated data sets. This procedure has been repeated for various values of K with data sets of 50K individuals. Everywhere the number of loci was L = 10 and the number of alleles per locus was Jl=1,…,L = 10. The simulation process is described in the appendix.
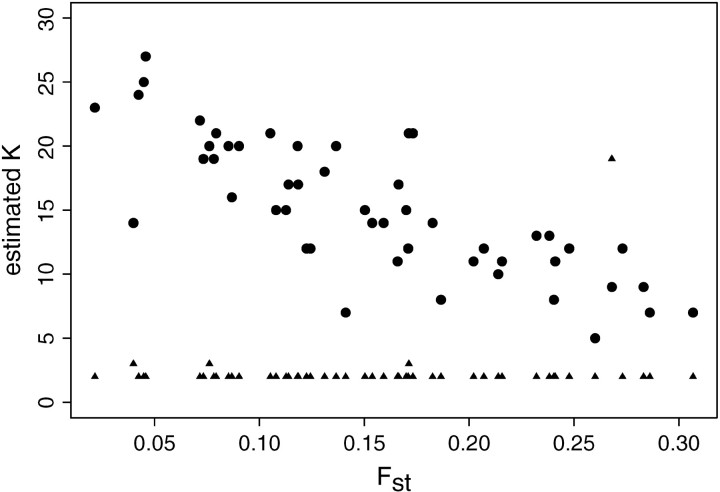
The histogram of estimated K is shown in Figure 4. It can be seen that the spatial D-model leads to excellent results and whatever the level of differentiation between populations is as measured by FST (see Figure 5). In contrast, very poor results were obtained when using the spatial F-model, although the latter model was used to simulate the test data sets. The model tends to overestimate systematically the true number of populations (see Figure 4) and the overestimation is stronger on weakly differentiated data sets (Figure 5). The spatial F-model proved to work well only for data sets with a high level of differentiation (FST > 0.5, data not shown). Results were improved for lower levels of differentiation by increasing the number of loci. However, even for L = 200 and Jl=1,…,L = 10, the spatial F-model seems to overestimate K by a factor of 5 when K = 2.
Figure 4.—
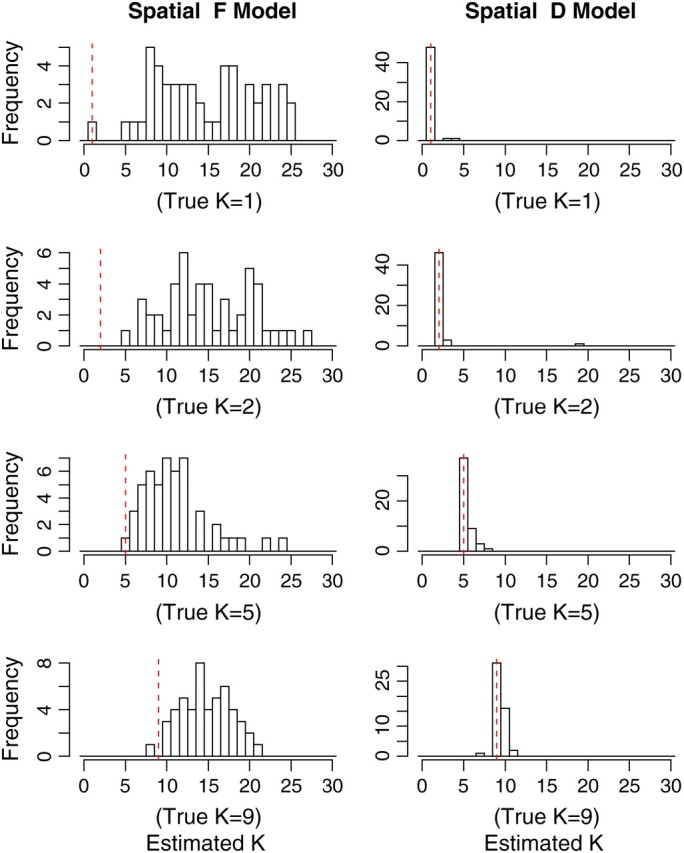
Estimated number of populations K̂. Each histogram shows estimates over 50 different simulated data sets with K = 1, 2, 5, 9, first using the spatial F-model (left) and then using the spatial D-model (right) as a prior for the allele frequencies. The vertical dashed line depicts the true value.
Figure 5.—
Empirical relationship between FST and the number of populations K̂ estimated using the spatial F-model (circle) and the spatial D-model (triangles) as a prior in the MCMC inference. The 50 simulated data sets are made of K = 2 populations, with L = Jl=1,…,L = 10.
Assignment to population of origin:
One other feature on which our model can be evaluated is its ability to assign individuals to their population of origin. We have several goals in mind here: (i) assessing the ability of the model to correctly classify individuals; (ii) comparing our model to nonspatial approaches suggested in the literature; and (iii) as the model is specifically tailored for populations displaying structure, we want to describe how the model behaves with respect to the amount of spatial and genetic structure present in the data. We simulated 1000 data sets using the spatial F-model, with 100 individuals organized in two populations (50 individuals per population), with 10 loci and 10 alleles per locus and then with only 3 loci and 10 alleles per locus. Each of these data sets has been first analyzed using the spatial F-model as a prior in the MCMC scheme. However, since we know from the results of the previous section that using the F-model can be misleading about the number of populations, we also analyzed our simulated data sets with the spatial D-model as a prior in the MCMC scheme.
An inference of all parameters (including the number of populations) could have been made. However, we wished to compare our method to methods that do not handle the inference of K. Therefore we chose to consider K as a known parameter and to compare the different methods when K is known and equal to 2. As already mentioned, most of the existing clustering models are based on i.i.d. mixtures. Therefore we have compared our spatial model to nonspatial clustering models obtained by replacing our spatial prior on the clustering variable c by an i.i.d. prior, giving the nonspatial F-model and nonspatial D-model. The nonspatial D-model turns out to be the model described by Pritchard et al. (2000) in the no-admixture case, whereas the nonspatial F-model can be viewed as a simplified version of the model of Falush et al. (2003), where linkage equilibrium is assumed.
Each data set has been analyzed in parallel by the four methods, from which we can derive the false classification rate defined as
 |
7 |
Results on the whole set of simulations and on various subsets with different levels of genetic and spatial structure are given in Table 1. The quantiles at levels (0.1, 0.25, 0.75) of the empirical distributions of FST and m were used to obtain subsets with various levels of genetic differentiation and of spatial organization, respectively. The quantiles at probabilities (0.1, 0.25, 0.75) were respectively (0.04, 0.06, 0.1) for FST and (12, 25, 80) for m. For instance, subsets for which the number of Voronoi tiles m were less than 12 correspond to highly spatially structured populations, whereas those for which m > 80 correspond to loose spatial organization. Examples illustrating simulated data sets with various levels of spatial organization are shown in Figure 6.
TABLE 1 .
Average false classification rates (in percentage) for all simulated data sets and subsamples with various levels of genetic and spatial structure
| Structure |
Spatial |
Nonspatial |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic | Spacial | F-model | D-model | F-model | D-model |
| Results with 10 loci | |||||
| All | All | 1.8 | 2.6 | 3.8 | 3.3 |
| FST < 0.04 | All | 7.8 | 14.2 | 15 | 13.5 |
| FST < 0.06 | All | 4.7 | 7.6 | 9 | 8.5 |
| FST > 0.11 | All | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| All | m < 12 | 2.3 | 1.9 | 11.4 | 6 |
| All | m < 25 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 4.4 |
| All | m > 80 | 2.2 | 3 | 2.8 | 3 |
| FST < 0.06 | m < 25 | 2.7 | 5.3 | 11.8 | 9.5 |
| FST < 0.04 | m < 12 | 3.5 | 1 | 24 | 16.7 |
| Results with 3 loci | |||||
| All | All | 11.3 | 12.5 | 17.5 | 17.5 |
The level of genetic and spatial structure increases with FST and decreases with m, respectively. Results are shown from 1000 simulated data sets of 100 individuals in two populations, with L = Jl=1,…,L = 10 and L = 3, Jl=1,…,L = 10.
Figure 6.—
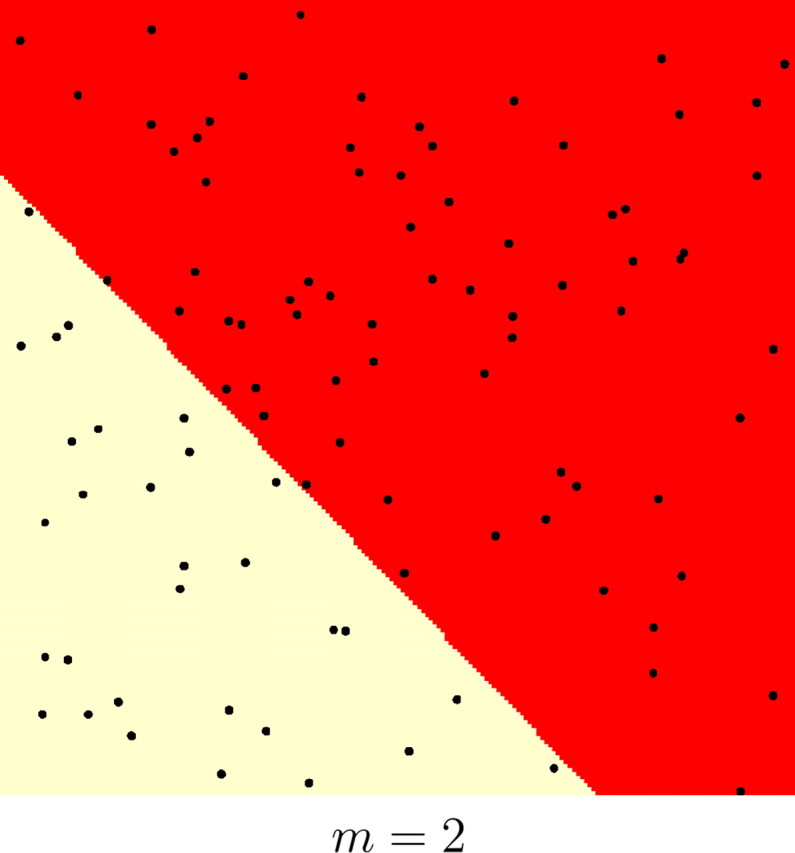
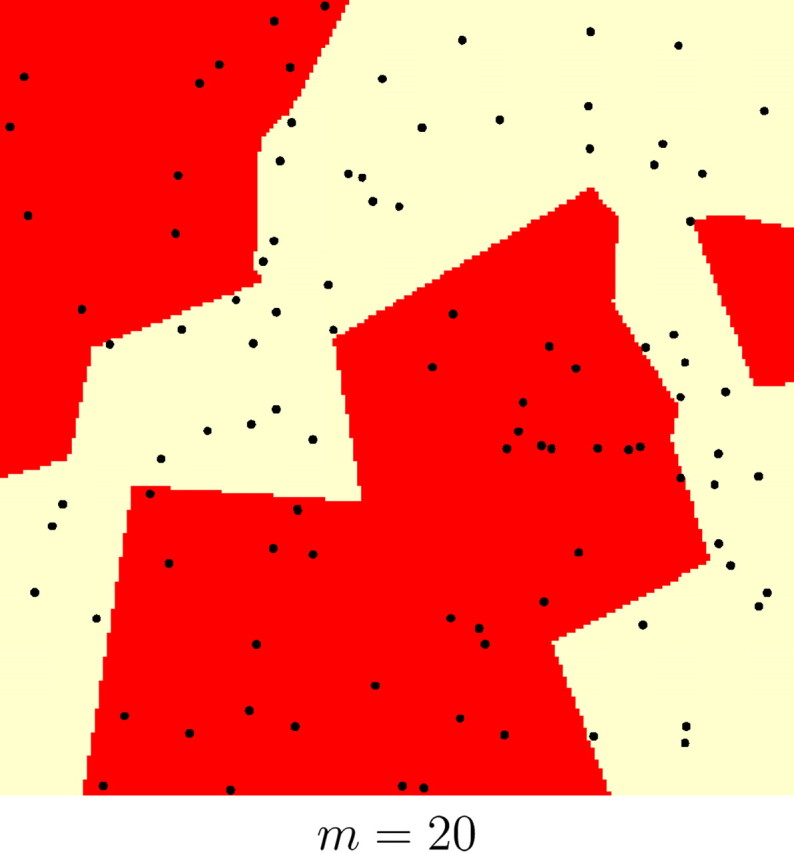
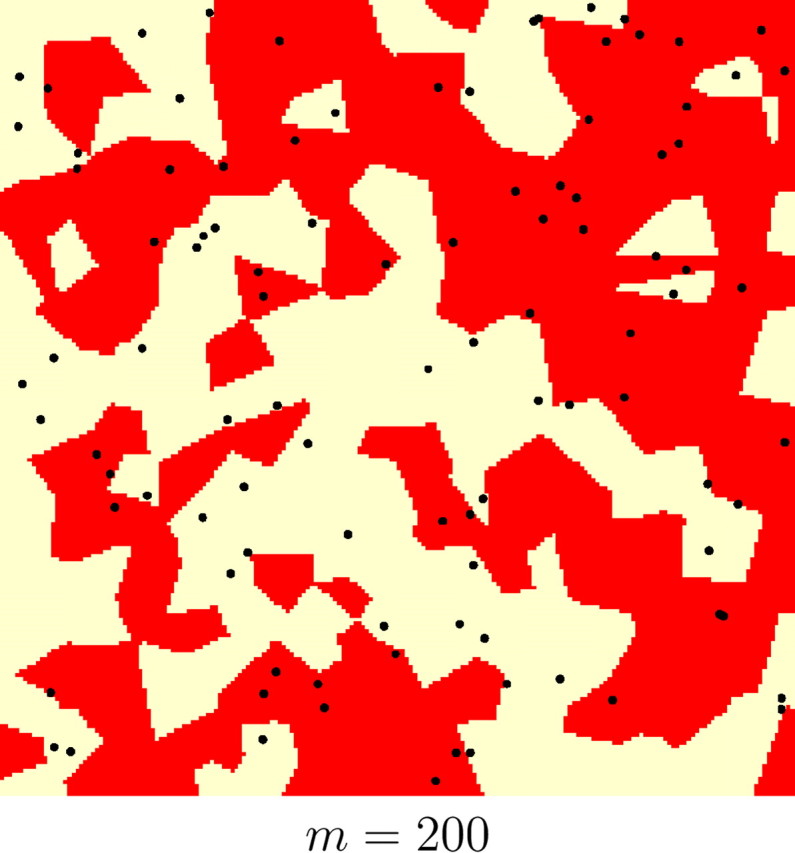
Examples of simulated spatial organization of 100 individuals (black dots) into two populations (coded as two colors) with various levels of spatial dependence. This level is controlled by parameter m (number of Voronoi tiles). The nuclei of the tiles are not depicted for clarity.
Results from the whole data set show that spatial methods give lower FCR values than nonspatial methods and that this trend is strengthened for a low number of loci (e.g., three loci). The improvement of spatial as compared to nonspatial methods is the greatest when both the level of spatial organization is large (m < 12) and the level of differentiation is weak (FST < 0.04).
Hence, in addition to giving better results than the spatial F-model for the estimation of the number of populations, the spatial D-model compares favorably with the spatial F-model for the assignment of individuals to their populations, even when the data depart from the model assumed in the inference (cf. the data sets that were simulated according to the spatial F-model). Therefore in the following we focus on the spatial D-model only.
Mapping borders between populations:
Mapping borders between populations represents one of the major interests of our spatial model: it is presented through graphical outputs obtained from simulated data sets.
Individual genotypes were obtained with the software Easypop (Balloux 2001) by simulating two populations exchanging different numbers of migrants per generation. In a first data set (referred to hereafter as set A), the two populations are considerably differentiated (FST = 0.16), in a second set (B) the populations are less differentiated (FST = 0.06), and in a third data set (C), they are very weakly differentiated (FST = 0.01). In each set we have n = 200 individuals (with 100 individuals per population) and L = 10 loci with Jl=1,…,L = 10 alleles per locus. Individuals of each population were randomly located on each part of an oscillating curve on the unit square.
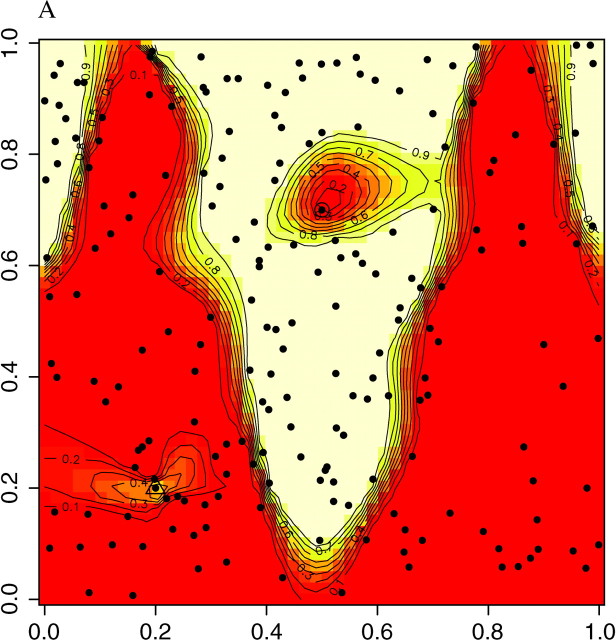
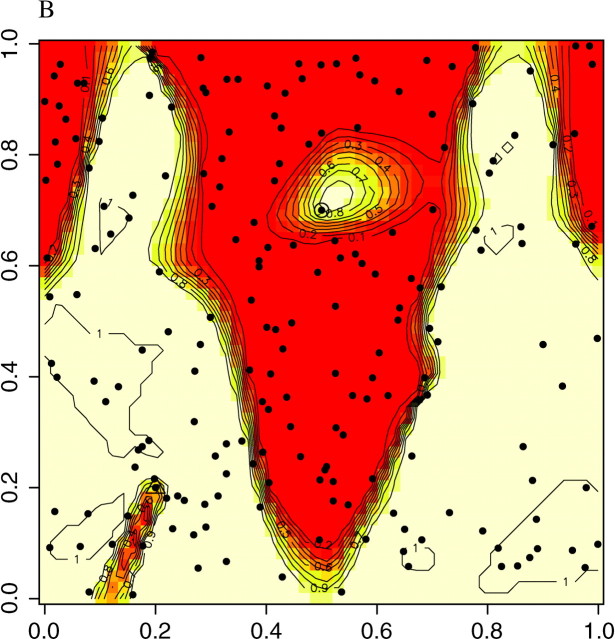
The ability of the model to find the actual partition of space is illustrated in Figure 7, set A, which displays the posterior probability π(c(s) = k|t, z) for any pixel to belong to the two populations. We observe that the true partition is very well detected. We obtained similar results on the two other data sets, although the boundary between the two domains was detected with less precision with data sets B and C (results not shown). We then quantitatively assessed how the level of differentiation influences the precision in the estimation of the border. This can be viewed from the map of δ(s), where δ(s) is any suitable measure of the dispersion of π[c(s)|t, z, K]. As π[c(s) = j|t, z, K] is a probability measure on {1, … , K} whose weights can be zero, the entropy is not defined, and therefore we used instead
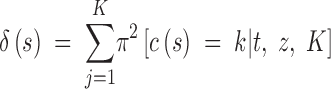 |
8 |
as an index of the dispersion of the distribution π[c(s) = k|t, z, K]. The right-hand side of Equation 8 is minimal when all the colors have equal probability, which corresponds to a flat posterior. Thus, the points s for which δ(s) is high are those confidently classified, whereas those where δ(s) is low correspond to poorly classified points that might correspond to transition regions or to sparsely sampled regions. The maps of δ(s) given in Figure 8 for the three data sets show that the lower values of δ(s) are along the true line of discontinuity (darker color), and that the accuracy in the estimation increases with the level of differentiation between populations.
Figure 7.—
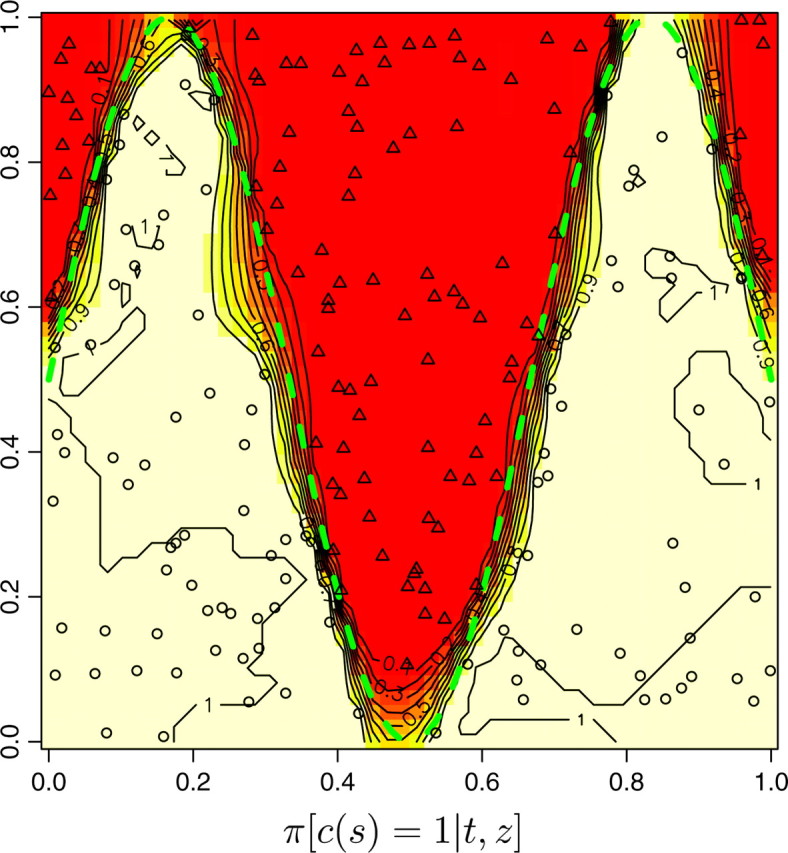
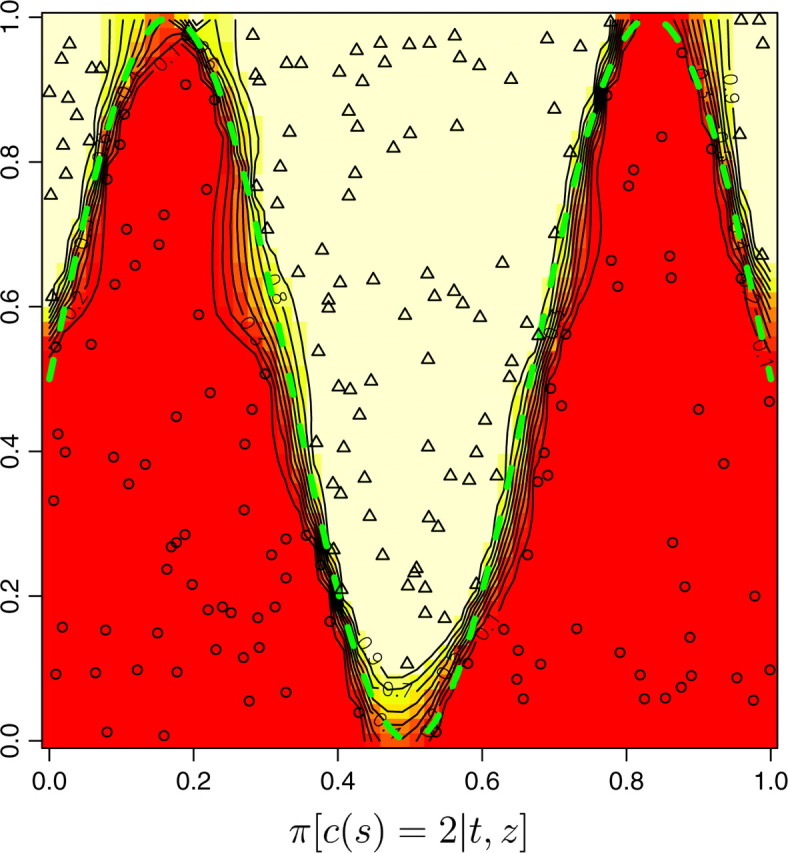
Maps of posterior probabilities, simulated data set A. The dashed green line depicts the true sine-shaped line of discontinuity. FST = 0.16, L = Jl=1,…,L = 10.
Figure 8.—
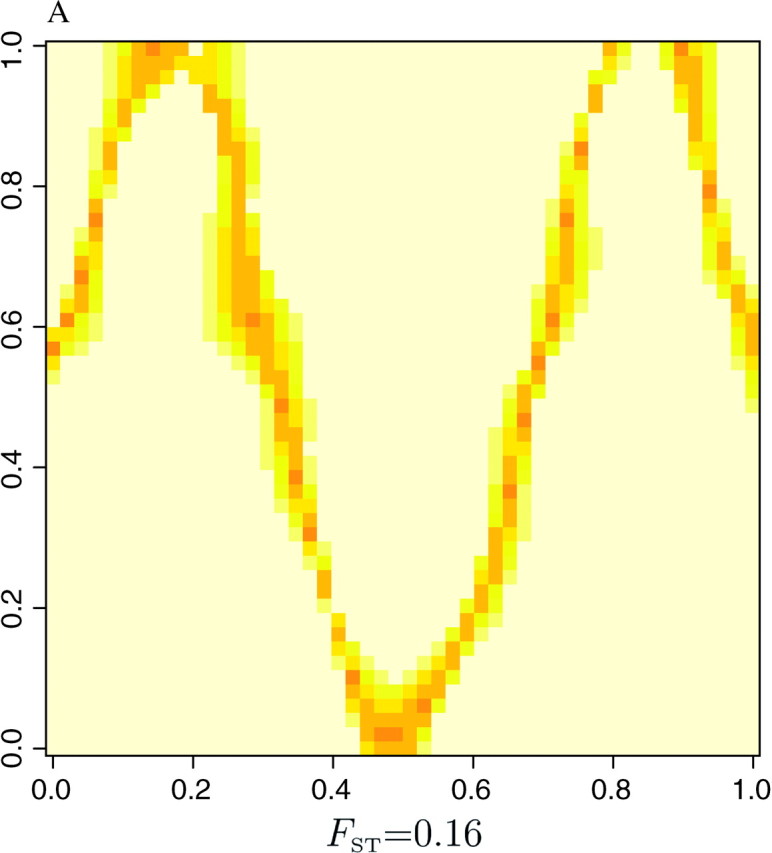
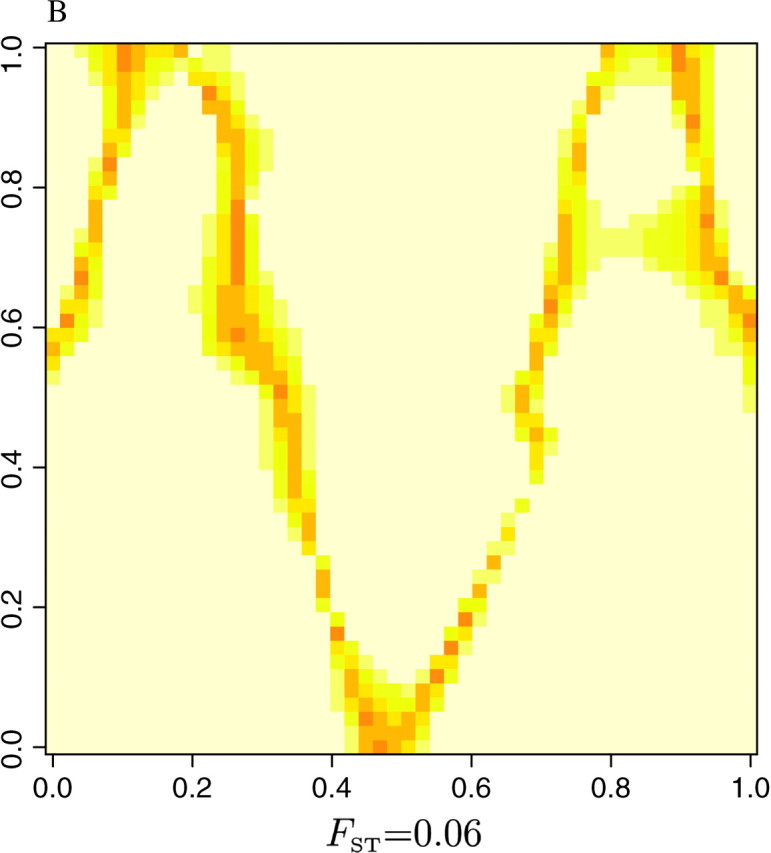
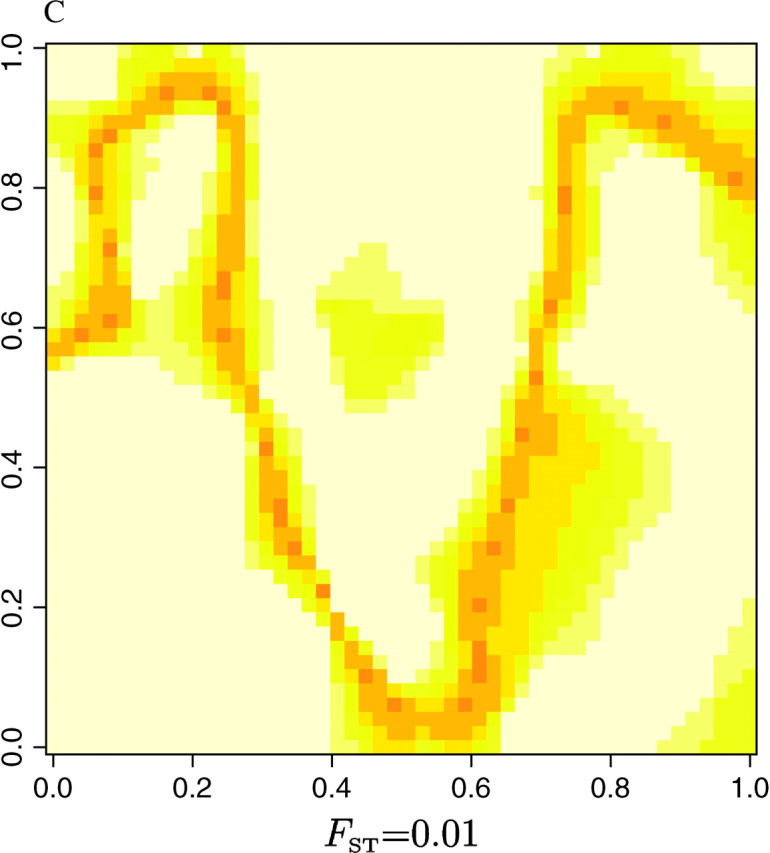
Delineation of lines of discontinuities from the dispersion δ(s) of the posterior probability π[c(s)|t, z].
Detection of migrants:
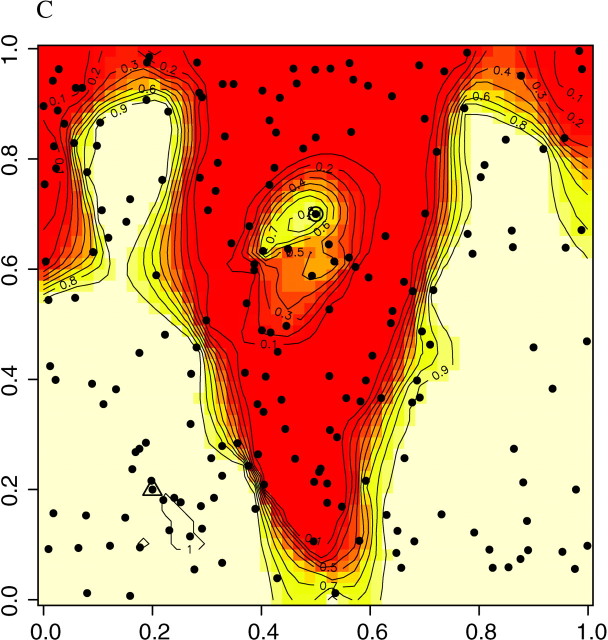
Since populations exchange migrants, it is sensible to assess whether the presence of such migrants would affect the spatial detection of genetic discontinuities and whether migrants could be detected and spatially located by our method, for different levels of differentiation between populations.
To address these points, we mimicked the presence of first-generation migrants in our previous data sets A, B, and C by moving one individual from the upper population to the lower population and another one in the opposite direction. Figure 9 shows that the presence of these first-generation migrants did not affect the accuracy of the method to detect the two populations and to spatially locate the genetic discontinuity. The figure also shows that the two migrants are easily detected (i.e., visualized) for data sets A, B, and C. The population of origin of each migrant could be easily deduced from its coloring pattern, including when more than two populations shared the domain (results not shown).
Figure 9.—
Maps of posterior probabilities π(c(s)|t, z) in the presence of one migrant on both sides of the line of discontinuity. The migrants from the upper to lower population and from the lower to upper population are depicted by triangles and circles, respectively.
Effect of errors on the locations of individuals:
We show here how errors on the locations of individuals may lead to poor results and how accounting for errors in the positioning of individuals allows us to retrieve most of the underlying signal. This question was addressed through the analysis of a new set of simulations.
Three independent populations separated by straight lines were positioned on the unit square. The number of individuals was n = 150 (50 individuals per population), L = Jl=1,…,L = 10, and the level of differentiation between populations was relatively low (FST = 0.08). The true positions si were blurred by an additive noise εi uniform on [−0.15, 0.15]2, so that the observed positions were ti = si + εi. The model was first run considering that the given positions were true (ε ≡ 0) and in a second run the uncertainty was accounted for by injecting the information that εi ∼ Uniform[−0.15, 0.15]2. We also considered the case where the true coordinates were used whereas wrong coordinates were assumed, and finally we give the results for true coordinates considered as true coordinates. The results are summarized in Figure 10. It can be clearly observed from the figure that accounting for uncertainty in the positioning of individuals substantially increases the precision in the detection of the true borders when some errors on the position of individuals exist (Figure 10, line 1 vs. line 2). Moreover, adding position noise in the model does not alter the results for data sets without position errors (Figure 10, line 3 vs. line 4).
Figure 10.—
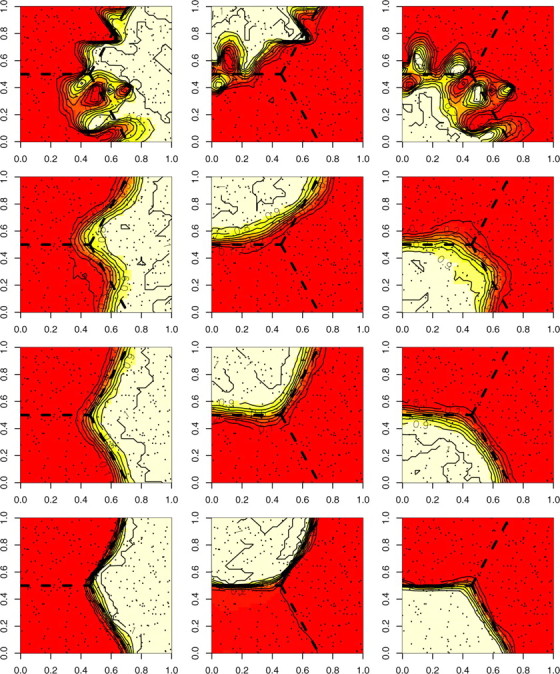
Maps of the posterior probability π[c(s) = k|t, z] when coordinates si are blurred by a uniform noise. First row, wrong coordinates, assumed true; second row, wrong coordinates, assumed wrong; third row, true coordinates, assumed wrong; fourth row, true coordinates, assumed true. FST = 0.08, L = Jl=1,…,L = 10. Dashed black lines are the true borders.
APPLICATION TO MONTANA WOLVERINES (GULO GULO)
We now analyze a previously published data set on wolverines (Gulo gulo), a medium-sized carnivore wildly distributed in North America. Wolverines are highly mobile, with the ability to disperse up to 300 km within a year, but are also highly sensitive to habitat disturbance by humans. Eighty-nine individuals were sampled in Montana and genotyped at 10 microsatellite loci Cegelski et al. (2003). Samples are nearly evenly distributed over an area that corresponds to a landscape highly fragmented by human development and disturbance. Using nonspatial Bayesian clustering procedures and assignment tests implemented in the programs Structure (Pritchard et al. 2000) and Geneclass (Cornuet et al. 1999), Cegelski et al. (2003) provided some evidence for the existence of three populations of wolverines in Montana, with FST values ranging from 0.08 to 0.10. The authors also provided some evidence for the identification of 11–22 migrants or offspring of migrants (depending on the method used for migrant detection).
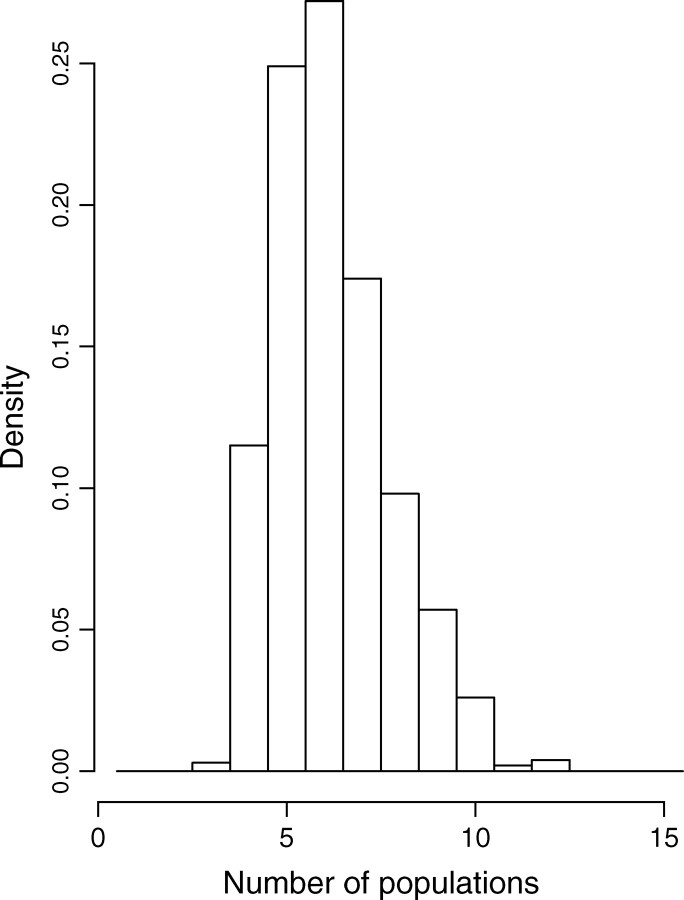
We reanalyzed the Wolverine data set (excluding one sample whose spatial coordinates were missing) by processing 10 independent MCMC runs of our spatial D-model. We used priors on K-uniform between 1 and 15 and on λ-uniform between 0 and 100. Each run includes 200,000 iterations and a short burn-in period. The posterior distribution gave a mode at K = 6, with a nonnegligible occurrence at K = 5 (Figure 11). Then the model was rerun along 50,000 iterations with a fixed value for K = 6. Maps of the posterior probability for any pixel of the domain to belong to each population could then be derived (Figure 12).
Figure 11.—
Posterior distribution of the number of populations for the wolverine data.
Figure 12.—
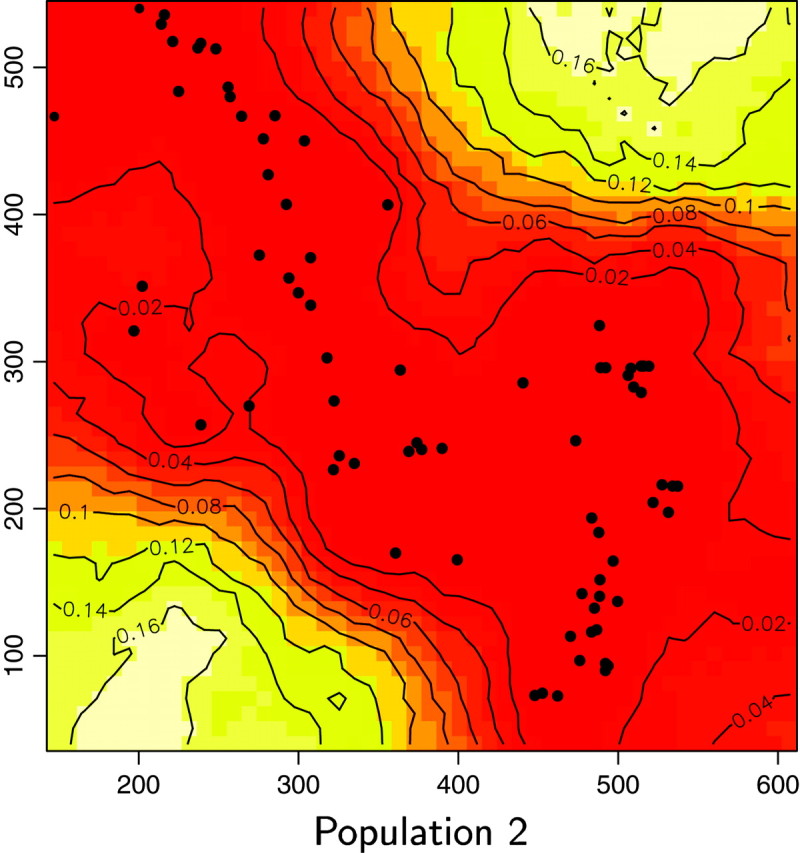
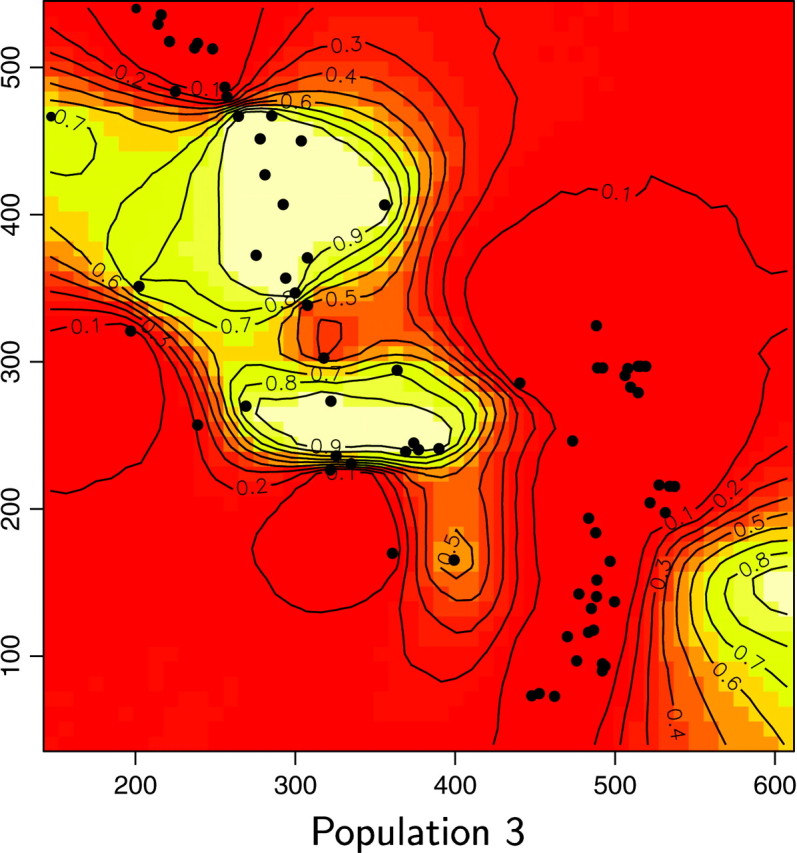
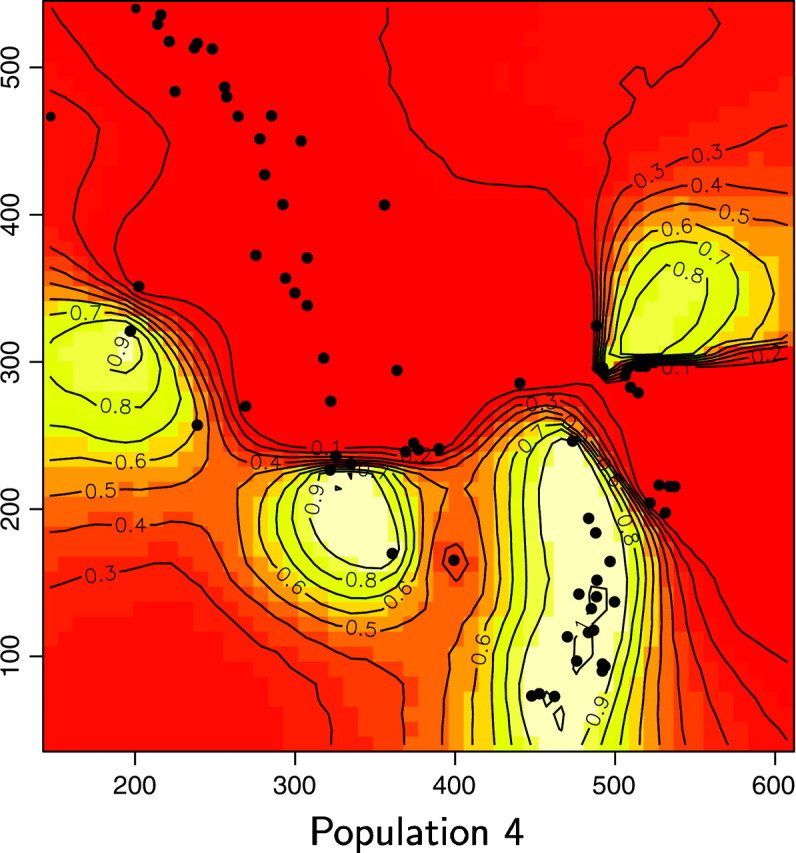
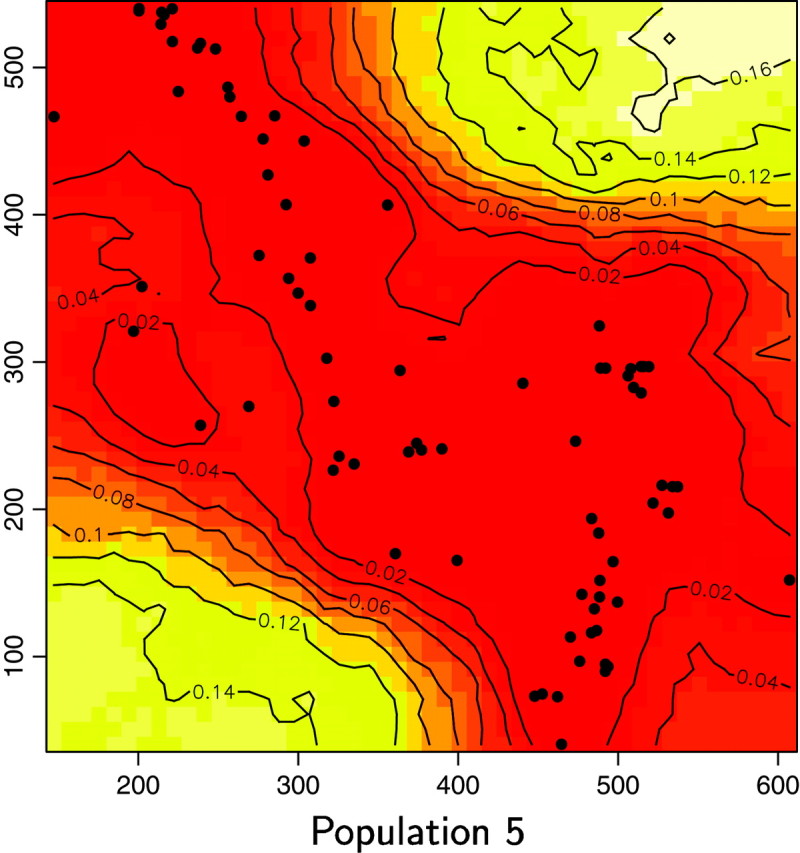
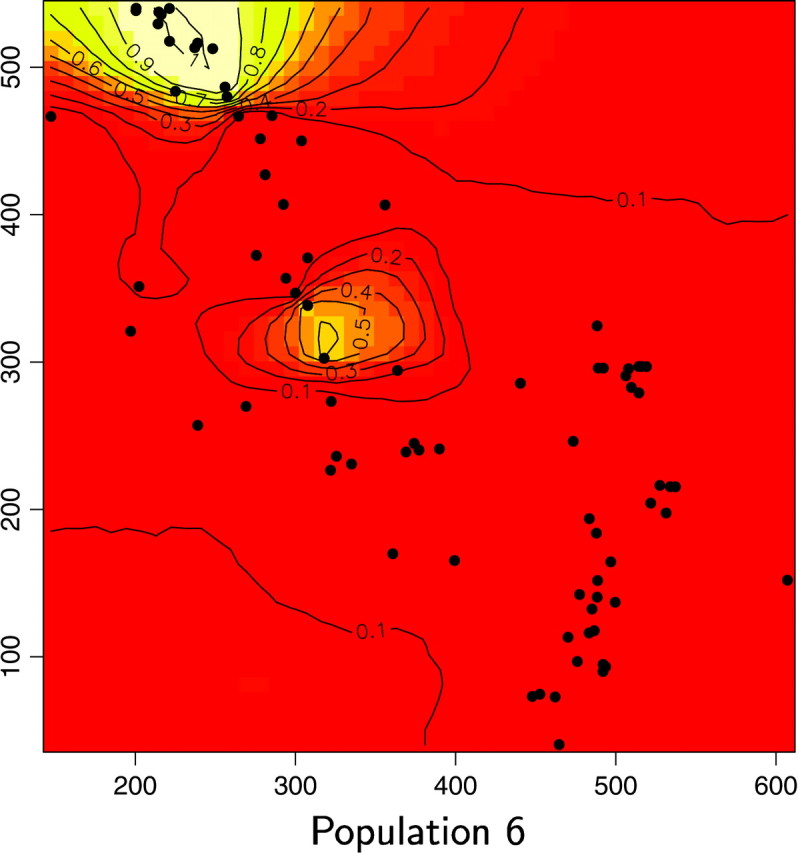
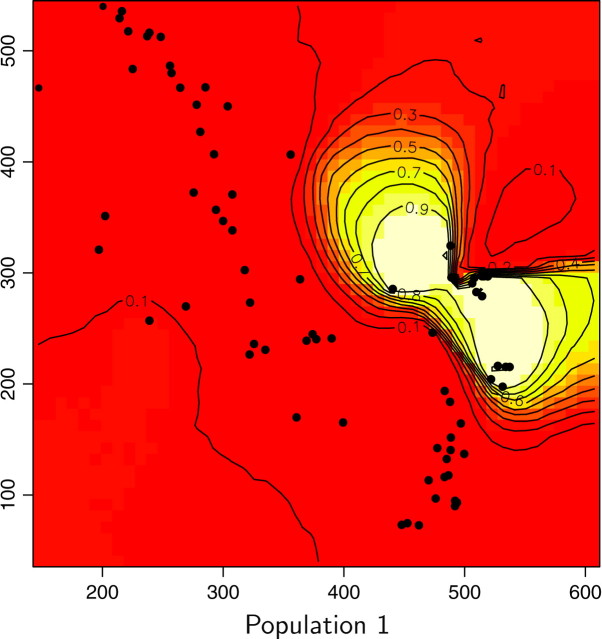
Maps of the posterior probability to belong to each population for the wolverine data. Unit of axis is kilometers.
We also computed for each pixel s the modal population, namely the population k for which π(c(s) = k|t, z) is maximum (Figure 13). Two of the six inferred populations (i.e., Figure 12, populations 2 and 5) do not appear to be the modal population for any pixel. Moreover, these two populations have very low posterior probabilities and an analysis of a detailed map suggests that the areas of these populations are very similar. Although results from the Number of populations section suggest that one can be very confident in the spatial D-model to infer the right number of populations, we do not have straightforward interpretation of the “ghost” populations 2 and 5 (but see discussion section).
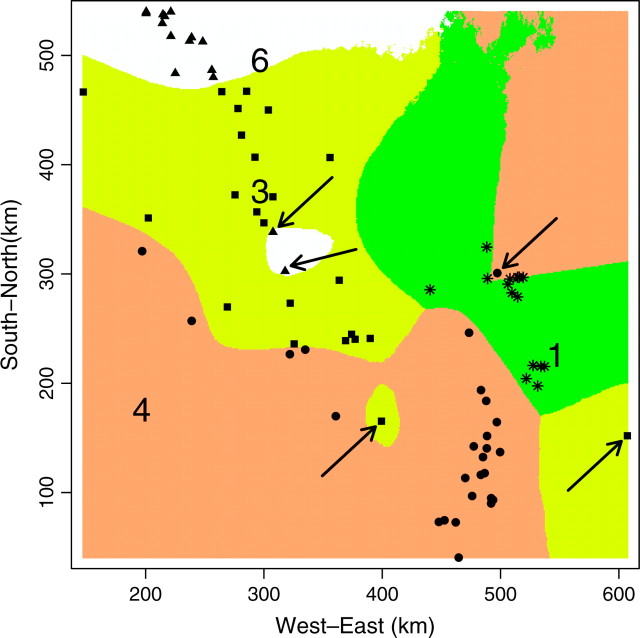
Figure 13.—
Map of the mode of the posterior probability to belong to each class for the wolverine data. Large character numbers indicate population labels. Arrows indicate putative migrants.
The spatial partition in four populations with high posterior probabilities considerably (but not entirely) decreased genetic structure within samples from FIS = 0.180 to 0.088, with single-population FIS values ranging from 0.038 to 0.110. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium could not be rejected in two of the four inferred populations (Fisher's exact test, P > 0.05; Raymond and Rousset 1995). Hence, our spatial method gives strong evidence for the presence of (at least) one more population than previously detected using nonspatial statistical approaches (i.e., Figures 12 and 13, population 6). The three other populations occupy spatial domains rather similar to those previously determined by Cegelski et al. (2003). The main added value of our spatial approach is thus the delineation of a fourth population located north of population 3. Populations 3 and 6 were previously confounded using nonspatial methods. Pairwise FST between the four populations inferred by our method are FST1–3 = 0.151, FST1–4 = 0.13, FST1–6 = 0.174, FST3–4 = 0.108, FST3–6 = 0.079, and FST4–6 = 0.176. The FST-value between the previously confounded populations is thus the lowest of all pairwise FST.
Interestingly, a close examination of the land cover map in Figure 2 of Cegelski et al. (2003) shows that the spatial domains of our populations 3 and 6 are separated by a narrow extent of man-made habitats (i.e., grasslands and grazing lands) that may have reduced wolverine movements.
Our spatial approach also allows detection of five individuals that genetically differ considerably from their spatial neighbors (Figure 13). These individuals can be interpreted as first-generation migrants as suggested by our previous analysis of simulated data sets. Some of these putative individual migrants have been previously detected by Cegelski et al. (2003).
DISCUSSION
The two key steps of landscape genetics are the detection and location of genetic discontinuities and the correlation of these discontinuities with landscape and environmental features. Efficient methods to achieve the first step have been lacking so far; our method provides the first efficient tool for locating genetic discontinuities within a landscape from individual geo-referenced multilocus genotype data, without any a priori knowledge on the populational units and limits. Once genetic discontinuities have been detected and spatially located using the observed genetic data, accurate landscape descriptors implemented, for example, in a geographic information system (GIS) can be used to associate the inferred genetic discontinuities with landscape features and hence generate hypotheses about the cause of genetic boundaries; see Piertney et al. (1998) for an attempt in this direction.
Our spatial method appears well suited for revealing cryptic spatial genetic structure and also provides a suitable approach for the detection of migrants (i.e., individuals poorly genetically related to their spatial neighbors) and their assignment to their population of origin. This has been illustrated by the analysis of a set of wolverine individuals sampled in the northwestern United States and genotyped at microsatellite markers (Cegelski et al. 2003). In addition to the populations previously identified by Cegelski et al. (2003) using nonspatial methods, our spatial approach allowed us to delineate a fourth population separated from others by a narrow extent of human-made habitats. Our analysis hence strengthens the conclusion that, even for a highly mobile species, habitat disturbance by humans may considerably limit movements and creates spatial genetic structure. Our approach also allowed detection of migrants between populations that were not previously distinguished, using nonspatial approaches (e.g., Figure 13, two migrants originating from population 6). The overall larger number of potential migrants detected by Cegelski et al. (2003) using assignment methods implemented in the package Geneclass (Cornuet et al. 1999) may be due to: (i) a lower power of our spatial method for detecting migrants and offspring of migrants, although this remains to be assessed; (ii) some Wahlund effect in at least one population identified by Cegelski et al. (2003); and (iii) an excess of the first type of error (i.e., resident individuals identified as migrants) produced by most assignment methods, as previously shown from simulated and empirical data sets (Berry et al. 2004; Paetkau et al. 2004). The exact behavior of our spatial method with respect to old migrants (e.g., F1, F2, and backcross migrants) still has to be assessed. Note that these cases are explicitly treated in the admixture case of the Structure approach (Falush et al. 2003).
Although theoretically applicable to any type of qualitative variable, our method was more specifically designed for genetic codominant markers (e.g., allozymes, microsatellites, single nucleotide polymorphisms). It assumes that the marker loci are unlinked and at linkage equilibrium with one another within populations (the effect of deviations from the second assumption is discussed further in this section). The accuracy of our method increases with the sampling effort (number of individuals and loci) as well as the strength of the genetic discontinuity between populations. However, our analysis of both simulated and real data sets showed good performances of the method for data sets of standard size (e.g., 100 individuals genotyped at 10 loci with 10 alleles per locus), with mild to low levels of population differentiation (e.g., FST < 0.1). Regarding individual sampling strategy, efficient inference in landscape genetics implies random sampling across the entire study area and not just sampling some individuals in each of several a priori defined populations (Manel et al. 2003). This also holds for our spatial method. Because methods to treat spatially approximately evenly distributed individual genetic data sets have not been available so far, such a sampling design has been rarely applied. We anticipate that our spatial method will stimulate population geneticists and ecologists interested in determining landscape and environmental factors influencing population genetic structure to modify their sampling strategy. The effect of a traditional sampling scheme (i.e., several groups of individuals collected on a limited area) on the performance of our method still needs to be assessed using simulated data sets. However, preliminary tests suggest that this effect may be small if enough of such sampling groups have been collected.
An interesting feature of our method is its propensity to infer that several spatial domains that may be apparently unconnected within the sampling window can belong to the same population unit. This represents a significant advantage in comparison to previous methods that aimed to define population (or individual) groups and hence genetic discontinuities. Hence our method is capable of treating complex spatial situations. In the meantime, we have demonstrated that our model does not artificially enforce a spatial substructure when it does not exist (see especially case K = 1 in Figure 4). Another major advantage of our approach as a whole compared to earlier methods (Pritchard et al. 2000; Dupanloup et al. 2002; Falush et al. 2003) is that the number of population units is treated here as an unknown parameter. Although Corander et al. (2003) also did so, their method is not spatially explicit and aims first at grouping populations rather than individuals. Regarding inference of the number of population units, the spatial D-model was found to perform better than the spatial F-model. The latter model tends to largely overestimate the number of population units, especially for low levels of population differentiation. To capture subtle genetic structures, the F-model gives a rather loose definition of what a population is. Embedding it in a fully Bayesian model where the number of these loosely defined populations is itself unknown seems to place too much flexibility in the algorithm. These results are in agreement with those of Falush et al. (2003), who found that, in a nonspatial context, the F-model was in general more permissive than the D-model (additional populations being fitted to a data set), as it permits the existence of two or more populations with very similar allele frequencies (particularly if the prior on the drift factor is chosen to favor small values).
We proposed a full Bayesian inference of the parameters of our spatial model through MCMC simulations. Estimation of parameters, uncertainty about the estimated values, and graphical outputs about all parameters involved can be derived from one single MCMC run. However, from a user point of view, it is more convenient to launch a first run processing all parameters in θ, from which only K̂ is derived, and then to launch a second run with K = K̂, and from which all remaining parameters will be investigated. All computations described in this article used the previous rule. It is worth mentioning that additional test computations performed on some other data sets for which some of the basic assumptions of our model were somewhat violated have shown that results from one single run could be misleading, as the Markov chain could get stuck to some local modes of the posterior. In this case we found, in agreement with Corander et al. (2003)(2004), that processing several independent runs and ranking them according to the posterior density could be an aid in the interpretation of results. We believe, however, that in such situations, more could be gained from model improvement than from inference algorithm improvement.
Postprocessing issues were also encountered when computing modal populations on the wolverine data as their number was smaller than the number of inferred populations. Such an issue has not been encountered with simulated data. The reason why this has been observed in the wolverine data set has to be further assessed. However, we may speculate that, as often in the MCMC algorithm for mixture models (Falush et al. 2003), some rarely visited states lead to inferred populations that do not appear to be the modal population for any individuals. Such populations may be interpreted as spurious populations that have not been successfully removed by the MCMC algorithm (and, hence, as a convergence flaw of the algorithm) or as populations standing for complex multimodality in the posterior. From a user point of view, these ghost populations have just to be ignored, and focus can be restricted to modal populations.
Some other forms of spatial dependence may occur in addition to that due to the presence of genetic discontinuities. These include isolation by distance between individuals, i.e., a regular increase of differentiation between individuals with geographic distance due to limited dispersal (Rousset 2000; Leblois et al. 2003); kin clustering, i.e., spatial clustering of highly related individuals at least before dispersal (e.g., Kelly 1994); and a certain rate of selfing reproduction for some species (Wolf and Takebayashi 2004). The problem of isolation by distance has been already mentioned by Dupanloup et al. (2002), who showed that under a stepping-stone migration model, their method found significant clustering of populations in the absence of any genetic boundary. It is expected that isolation by distance, kin-clustering, or selfing decrease the performance of our spatial method since the latter assumes Hardy-Weinberg and linkage equilibrium among loci within populations separated by genetic discontinuities. In particular, it is expected that deviations from random assortment that are not caused by genetic discontinuity will tend to overestimate the number of population units (Pritchard et al. 2000; Falush et al. 2003). However, to which extent additional forms of spatial dependence would affect the performance of our method to detect and locate genetic discontinuities between populations still needs to be assessed, analyzing simulated data sets. Given the complexity of genetic data sets at highly variable markers, our spatial model had to remain as simple as possible. A simple way to achieve spatial dependence was to assume a dependence on the class variable and an independence of z(s) within populations. However, this basic model might be improved in several ways. For instance, Allard and Guillot (2000) proposed in a different context a model where the population label variable is not spatially dependent (unlike here where the population variable c is spatially organized) and the data z are spatially dependent within populations. This model tended to cluster samples in a way very different from that of the current model. Although this model is not straightforwardly transposable to genetic data, the introduction of within-population dependence while keeping the spatial dependence of the class variable is certainly a promising way to improve spatial models for genetic data and, more specifically, to take into account other forms of spatial dependence such as isolation by distance, kin clustering, or selfing.
The whole computer code (including Fortran MCMC, postprocessing subroutines, and R data handling and graphical interfaces) used to carry out computations under our spatial model will be made available soon on the web page of G. Guillot and Comprehensive R Archive Network (Ihaka and Gentleman 1996; R Development Core Team 2004) as an R package called Geneland.
Acknowledgments
The wolverine data set was kindly provided by Chris Cegelski and Lisette Waits from the Department of Fish and Wildlife Resource, University of Idaho. We thank Stuart Baird for constructive comments on the manuscript and Mark Hewison for comments on an earlier draft. G. Guillot thanks Joël Chadœuf, Christian Robert, Eric Parent, Olivier François, Jesper Møller, and Rasmus Waagepetersen for stimulating comments at various stages of this work. We also thank two reviewers and Laurent Excoffier as associate editor for constructive remarks. This work was partly supported by a grant to the authors from Bureau des Ressources Génétiques.
APPENDIX
Description of simulation study:
The exact algorithm described in Number of populations is detailed in pseudo-code below:
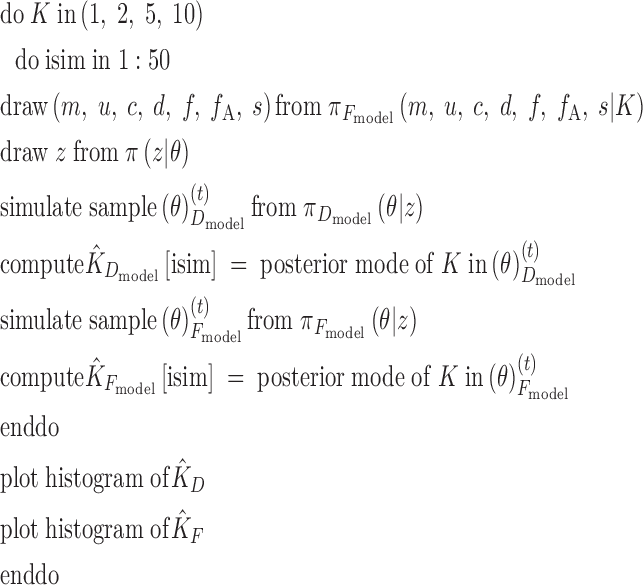 |
In words, we simulated spatialized data sets with various sets of parameters and tried to retrieve these parameters, considered as unknown, via our algorithm with a special emphasis on the number of populations.
Details of MCMC computations:
Six block updates (namely, those of u, c, p, f, fA, and s) do not change the dimensionality of θ, and two updates (K and m) are of jump type, increasing or decreasing the length of θ.
Update of drifts:
This is done through Metropolis-Hastings updates, as described by Falush et al. (2003).
Update of frequencies in the ancestral population:
This is done through Metropolis-Hastings updates, as described by Falush et al. (2003).
Update of frequencies in the present-time population:
This is done through Gibbs updates, as described by Falush et al. (2003).
Update of the colors of tile:
This is a Metropolis-Hastings update. We make componentwise updates of c: sequentially for each tile with color cj, we propose a new value c*j from the prior, namely 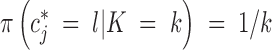 .
.
This proposal is accepted according to the usual M-H acceptance probability
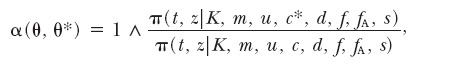 |
A1 |
where 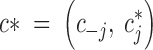 , c−j denoting the vector c deprived from its jth entry (the one currently updated).
, c−j denoting the vector c deprived from its jth entry (the one currently updated).
Update of the locations of tiles:
This is a Metropolis-Hastings random-walk update. We make a componentwise update of u: sequentially for each tile centered in uj, we propose a new value u*j obtained by a small random perturbation of the current position.
This proposal is accepted according to the usual M-H acceptance probability
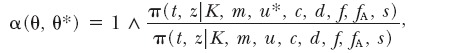 |
A2 |
where 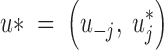 , u−j denoting the vector u deprived from its jth entry (the one currently updated).
, u−j denoting the vector u deprived from its jth entry (the one currently updated).
Update of the true unknown locations of individuals:
This is a Metropolis-Hastings random-walk update. We make a componentwise update of s: sequentially for each tile individual sj, we propose a new value s*i obtained by a small random perturbation of the current position.
This proposal is accepted according to the usual M-H acceptance probability
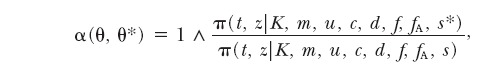 |
A3 |
where 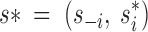 , s−i denoting the vector s deprived from its ith entry (the one currently updated).
, s−i denoting the vector s deprived from its ith entry (the one currently updated).
Birth or a death of a tile:
In step (7) we first randomly choose between a birth or a death of a tile with equal probability.
In the case where a birth is proposed, we have to propose a new random point to the current state u1, … , um, which we denote by u*m+1. This new proposed tile will also receive a color denoted by c*m+1. u*m+1 and c*m+1 are drawn from the prior. Namely, u*m+1 is uniform on the spatial domain and c*m+1 is uniform on the current set of colors {1, … , K}.
We denote by θ the current state and by θ* = (K, m*, u*, c*, d, fA, f, s) the proposed value. Since we consider the case of adding a tile, 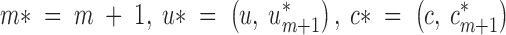 , and the reversible jump acceptance probability (see, e.g., van Lieshout 2000 or Roberts and Dellaportas 2003) takes the following form:
, and the reversible jump acceptance probability (see, e.g., van Lieshout 2000 or Roberts and Dellaportas 2003) takes the following form:
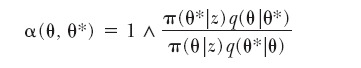 |
A4 |
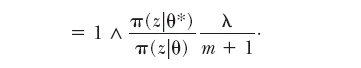 |
A5 |
In the case where a death is proposed, a tile is uniformly selected at random over (u1, … , um), and the acceptance probability takes a similar form (reverse expression, precisely; see Byers and Raftery 2002)).
Birth or death of a population:
The strategy used here to draw a new population or to discard an existing one is similar to the one described by Richardson and Green (1997), with three differences: we have to maintain a spatial consistency within the geometry of the current state and the one of the proposed state (hence, not all proposals will make sense), the data are categorical (there is no straightforward order between alleles), and they are also multivariate (which makes it impossible even to sort quantitative mean parameters, like frequencies).
The strategy to draw a new population consists of splitting an existing population into two distinct populations. Reversibly, a death of an existing population will be obtained by merging two existing ones. Thus, the first step consists of choosing between splitting and merging. This is done with equal probability.
Then a step of, say, split type involves the following:
Propose a new allocation of individuals (over K + 1 populations instead of K) through a new coloring c*, namely
propose the population k to be split with equal probability over the K existing populations (the split population will give birth to two new populations labeled as k and K + 1),
count the number of tiles νk belonging to population k (remember that their union forms the set Δk),
choose a uniform number of tiles ν between 0 and νk,
select randomly ν of those tiles in Δk that will be given a new color,
propose a new allocation of individuals c* by changing deterministically colors of the ν selected tiles of Δk from k to K + 1.
Then propose frequencies f*k, f*K+1 and drifts d*k, d*K+1.
The proposed state is denoted by θ* = (K*, m, u, c*, d*, fA, f*, s) with K* = K + 1, 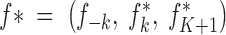 ,
, 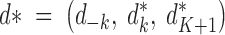 , where f−k (resp. d−k) denotes the set f (resp. d) deprived of parameters corresponding to population k.
, where f−k (resp. d−k) denotes the set f (resp. d) deprived of parameters corresponding to population k.
The drifts d*k and d*K+1 are sampled from the prior [Beta(2, 20) in the present case]. And to have a fairly high acceptance probability, the frequencies f*k and f*K+1 are sampled from the conditional distributions πf*k|d*, fA, m, c*, u, z, t and πf*K+1|d*, m, c*, u, z, t (in the spirit of a Gibbs sampler).
The acceptance ratio for the birth of a population is as usual
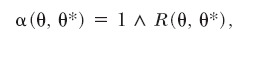 |
A6 |
where
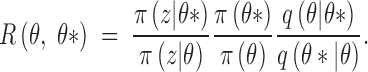 |
A7 |
Most of the terms in the ratio of the prior probabilities vanish, and we keep only
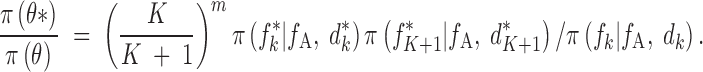 |
A8 |
The same applies in the ratio of proposals and we get
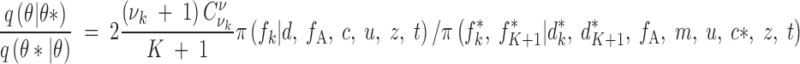 |
A9 |
while the last term in Equation A9 factorizes as
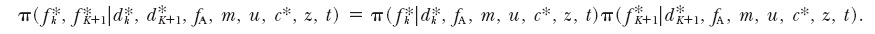 |
A10 |
The likelihood in Equation A7 has the expression given in Equation 4.
We have just to give more explicit expressions for the terms involving frequencies in Equations A8 and A9. These conditional distributions are Dirichlet by standard conjugacy properties. Denoting by nklj resp. n*klj the number of copies for locus l observed in population k for the current state (resp. the proposed state), we get
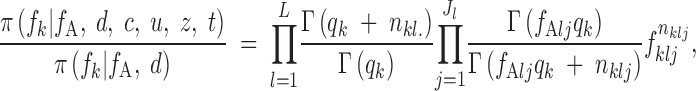 |
A11 |
where 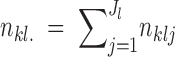 and
and 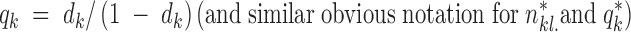 .
.
Combined with Equations A7–A9 we end up with
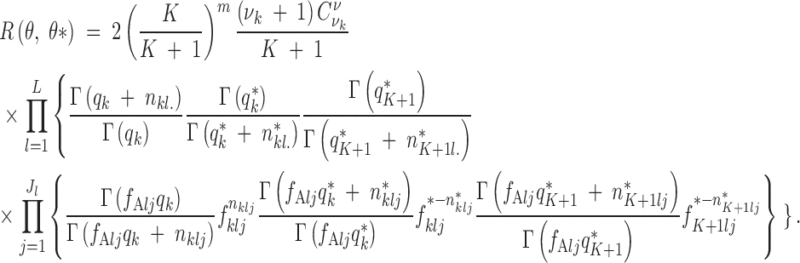 |
A12 |
Model nesting:
The same computer code can be used to make inference in spatial and nonspatial models (i.e., with i.i.d. class variable c) as well as in the F-model and D-model. The more general algorithm performs simulations of the posterior in the spatial F-model. The nonspatial version can be obtained with λ set to a very large value, but, more efficiently, by initializing the number of tiles to the number of individuals, with the center of the tiles at the position of the individuals (m = n and u = t), with εi to 0 (i = 1, … , n), and then by skipping steps (5)–(7).
Simulations of the posterior in the D-model instead of the F-model can be made by initializing dk ≡ 0.5, fAlj ≡ 1 and skipping steps (1) and (2).
References
- Allard, D., and G. Guillot, 2000 Clustering geostatistical data, in Geostat 2000: Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Geostatistics, edited by W. J. Kleingeld and D. G. Krige. De Beers, Cape Town.
- Balloux, F., 2001. EASYPOP (version 1.7), A computer program for the simulation of population genetics. J. Heredi. 92 301–302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry, O., M. Tocher and S. Sarre, 2004. Can assignment tests measure dispersal? Mol. Ecol. 13 551–561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besag, J., 1986. On the statistical analysis of dirty pictures. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 48(3): 259–302. [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell, P., 2001. Bayesian inference for a random tesselation process. Biometrics 57(2): 502–507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers, S., and A. Raftery, 2002 Bayesian estimation and segmentation of spatial point processes using Voronoi tilings, pp. 109–121 in Spatial Cluster Modelling, edited by A. B. Lawson and D. G. T. Denison. Chapman & Hall, London/New York.
- Cegelski, C., L. Waits and J. Anderson, 2003. Assessing population structure and gene flow in Montana wolverines (Gulo, gulo) using assignment-based approaches. Mol. Ecol.y 12 2907–2918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celeux, G., 1997. Discussion of the paper by Richardson and Green “On Bayesian analysis of mixtures with an unknown number of components.” J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 59(4): 775–776. [Google Scholar]
- Celeux, G., M. Hurn and C. Robert, 2000. Computational and inferential difficulties with mixture posterior distributions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 95(451): 957–970. [Google Scholar]
- Corander, J., P. Waldmann and M. Sillanpää, 2003. Bayesian analysis of genetic differentiation between populations. Genetics 163 367–374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corander, J., P. Waldmann, P. Martinen and M. Sillanpää, 2004. BAPS2: enhanced possibilities for the analysis of genetic population structure. Bioinformatics 20(15): 2363–2369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornuet, J., S. Piry, G. Luikart, A. Estoup and M. Solignac, 1999. New methods employing multilocus genotypes to select or exclude populations as origins of individuals. Genetics 153 1989–2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, K., and K. Belkhir, 2001. A Bayesian approach to the identification of panmictic populations and the assignment of individuals. Genet. Res. 78 59–77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupanloup, I., S. Schneider and L. Excoffier, 2002. A simulated annealing approach to define genetic structure of populations. Mol. Ecol. 11 2571–2581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estoup, A., M. Beaumont, F. Sennedot, C. Moritz and J. Cornuet, 2004. Genetic analysis of complex demographic scenarios: spatially expanding populations of the cane toad, Bufo marinus. Evolution 58 2021–2036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falush, D., M. Stephens and J. Pritchard, 2003. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164 1567–1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurn, M., O. Husby and H. Rue, 2003 A tutorial in image analysis, pp. 86–141 in Spatial Statistics and Computational Methods (Lecture Notes in Statistics). Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany/New York.
- Ihaka, R., and R. Gentleman, 1996. R: a language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 5(3): 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, J., 1994. The effect of scale dependent processes on kin selection: mating and density regulation. Theor. Appl. Genet. 46 32–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantuéjoul, C., 2002 Geostatistical Simulation. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany/New York.
- Lawson, A., and D. Denison (Editors), 2002 Spatial Cluster Modelling. Chapman & Hall, London, New York.
- Leblois, R., A. Estoup and F. Rousset, 2003. Influence of mutational and sampling factors on the estimation of demographic parameters in a ‘continuous’ population under isolation by distance. Mol. Biol. Evol. 20 491–502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manel, S., M. Schwartz, G. Luikart and P. Taberlet, 2003. Landscape genetics: combining landscape ecology and population genetics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 18(4): 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, J., and Ø. Skare, 2001. Coloured Voronoi tesselations for Bayesian image analysis and reservoir modelling. Stat. Mod. 1 231–252. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, J., and R. Waagepetersen, 1998. Markov connected component fields. Adv. Appl. Probab. 30 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, G., 1997 Coloured continuum triangulation models in the Bayesian analysis of two dimensional change point problems, pp. 143–150 in The Art and Science of Bayesian Image Analysis: Leeds Annual Statistics Research Workshop, edited by K. V. Mardia and R. G. Aykroyd. Leeds University Press, Leeds, UK.
- Paetkau, D., R. Slade, M. Burdens and A. Estoup, 2004. Genetic assignment methods for the direct, real-time estimation of migration rate: a simulation-based exploration of accuracy and power. Mol. Ecol. 15 55–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piertney, S., A. MacColl, P. Bacon and J. Dallas, 1998. Local genetic structure in red grouse (Lagopus lagopus scoticus): evidence from microsatellite DNA markers. Mol. Ecol. 7(12): 1645–1654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, J., M. Stephens and P. Donnelly, 2000. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155 945–959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team, 2004 R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. (http://www.R-project.org).
- Rannala, B., and J. Moutain, 1997. Detecting immigration by using multilocus genotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94 9197–9201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, M., and F. Rousset, 1995. Genepop (version 1.2): a population genetic software for exact test and ecumenicism. J. Hered. 86 248–249. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, S., and P. Green, 1997. On Bayesian analysis of mixtures with an unknown number of components. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 59(4): 731–792. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C., and K. Mengersen, 1999. Reparameterisation issues in mixture modelling and their bearing on MCMC algorithms. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 29 325–343. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, G., and P. Dellaportas, 2003 Introduction to MCMC, pp. 1–86 in Spatial Statistics and Computational Methods (Lecture Notes in Statistics), edited by Jesper Møller. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany/New York.
- Rousset, F., 2000. Genetic differentiation between individuals. J. Evol. Biol. 13 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, M., 1997. Discussion of the paper by Richardson and Green “On Bayesian analysis of mixtures with an unknown number of components.” J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 59(4): 768–769. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, M., 2000. Dealing with label-switching in mixture models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 62 795–809. [Google Scholar]
- Tavaré, S., and O. Zeitouni, 2001 Proceedings of Saint Flour Summer School in Probability and Statistics (Lecture Notes in Statistics). Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany/New York.
- van Lieshout, M., 2000 Markov Point Processes and Their Applications. Imperial College Press, London.
- Vounatsou, P., T. Smith and A. Gelfand, 2000. Spatial modelling of multinomial data with latent structure: an application to geographical mapping of human gene and haplotype frequencies. Biostatistics 1(2): 177–189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir, B., and C. Cockerham, 1984. Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 38(6): 1358–1370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, D., and N. Takebayashi, 2004. Pollen limitation and the evolution of androdioecy from dioecy. Am. Nat. 163 122–137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]