Abstract
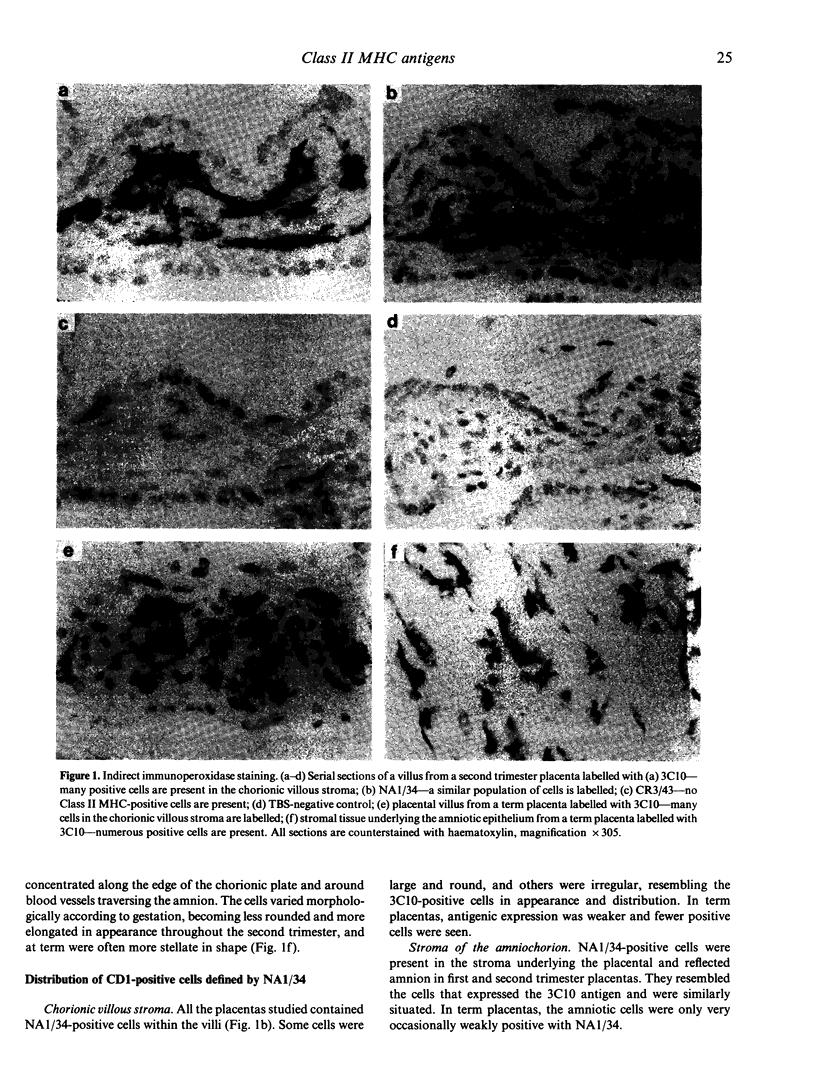
Immunohistological techniques have been used to study the stromal cells of the human placenta in both the chorionic villous mesenchyme and the connective tissue underlying the amnion. Throughout gestation many of these cells express an antigen (3C10) that is found on mononuclear phagocytes but not on dendritic cells or epidermal Langerhans cells. In the first and second trimesters the placental cells also react with a monoclonal antibody (NA1/34) to the human thymocyte antigen (CD1), a lymphocyte differentiation antigen expressed by cortical thymocytes and Langerhans cells; expression of this antigen diminishes as gestation advances. In contrast, an antibody to a different epitope of CD1 (OKT6) does not bind. Class II MHC antigens are not present in the first trimester but are acquired by increasing numbers of placental macrophages from the second trimester onwards. It is possible that the placenta has significant immune functions and that, by term, placental macrophages may be capable of antigen presentation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bulmer J. N., Johnson P. M. Macrophage populations in the human placenta and amniochorion. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):393–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellucci M., Zaccheo D., Pescetto G. A three-dimensional study of the normal human placental villous core. I. The Hofbauer cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;210(2):235–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00237612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotner T., Mashimo H., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Strominger J. L. Human T cell surface antigens bearing a structural relationship to HLA antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3858–3862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalchau R., Kirkley J., Fabre J. W. Monoclonal antibody to a human leukocyte-specific membrane glycoprotein probably homologous to the leukocyte-common (L-C) antigen of the rat. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Oct;10(10):737–744. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubertret L., Picard O., Bagot M., Tulliez M., Fosse M., Aubert C., Touraine R. Specificity of monoclonal antibody anti-T-6 for Langerhans' cells in normal human skin. Br J Dermatol. 1982 Mar;106(3):287–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb01725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. A., Jones D. B., Evans P. R., Smith J. L. Differential expression of HLA class II antigens on human fetal and adult lymphocytes and macrophages. Immunology. 1985 Jul;55(3):489–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders A. C., King B. F. The cytology of Hofbauer cells. Anat Rec. 1970 Jun;167(2):231–236. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091670211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fithian E., Kung P., Goldstein G., Rubenfeld M., Fenoglio C., Edelson R. Reactivity of Langerhans cells with hybridoma antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2541–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H. The incidence and significance of Hofbauer cells in the mature human placenta. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):710–717. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines K. A., Flotte T. J., Springer T. A., Gigli I., Thorbecke G. J. Staining of Langerhans cells with monoclonal antibodies to macrophages and lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3448–3451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Robinson A. P., MacPherson G. G., Gordon S. The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80. Relationship between macrophages, Langerhans cells, reticular cells, and dendritic cells in lymphoid and hematopoietic organs. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1522–1536. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Nogueira Araujo G. M. A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Trägårdh L., Lindblom J. B., Peterson P. A. Reactivity of a rabbit antiserum against highly purified HLA-DR antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1978 Mar;7(3):199–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch P. G., van de Rijn M., Schrier P., Terhorst C. Biochemical comparison of the T6 antigen and HLA-A,B antigens. Hum Immunol. 1983 Jan;6(1):13–30. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(83)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loke Y. W., Eremin O., Ashby J., Day S. Characterization of the phagocytic cells isolated from the human placenta. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1982 Apr;31(4):317–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Pilch J. R., Galfré G., Mason D. Y., Fabre J. W., Milstein C. A human thymocyte antigen defined by a hybrid myeloma monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):205–210. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskalewski S., Czarnik Z., Ptak W. Demonstration of cells with igg receptor in human placenta. Biol Neonate. 1975;26(3-4):268–273. doi: 10.1159/000240738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. W., McMichael A. J., Stirrat G. M., Sunderland C. A., Ting A. Class 1 major histocompatibility complex antigens on human extra-villous trophoblast. Immunology. 1984 Jul;52(3):457–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G., Sullivan A. K. Ia antigen expression on human epidermal Langerhans cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):247–248. doi: 10.1038/268247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Steinman R. M. Murine epidermal Langerhans cells mature into potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):526–546. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding D. M., Koopman W. J., Eldridge J. H., McGhee J. R., Steinman R. M. Accessory cells in murine Peyer's patch. I. Identification and enrichment of a functional dendritic cell. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1646–1659. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Gutchinov B., Witmer M. D., Nussenzweig M. C. Dendritic cells are the principal stimulators of the primary mixed leukocyte reaction in mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):613–627. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Nussenzweig M. C. Dendritic cells: features and functions. Immunol Rev. 1980;53:127–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb01042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Clement L., Green I., Shevach E. M. Immunologic functions of Ia-bearing epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland C. A., Naiem M., Mason D. Y., Redman C. W., Stirrat G. M. The expression of major histocompatibility antigens by human chorionic villi. J Reprod Immunol. 1981 Dec;3(6):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(81)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton L., Mason D. Y., Redman C. W. HLA-DR positive cells in the human placenta. Immunology. 1983 May;49(1):103–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki K., Katz S. I. Ontogeny of Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jul;75(1):12–13. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhorst C., van Agthoven A., LeClair K., Snow P., Reinherz E., Schlossman S. Biochemical studies of the human thymocyte cell-surface antigens T6, T9 and T10. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):771–780. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90441-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Hair L. S., Steinman R. M., Kaplan G. Human dendritic cells. Enrichment and characterization from peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1172–1187. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Steinman R. M., Hair L. S., Luban J., Witmer M. D., Koide S., Cohn Z. A. Specific antimononuclear phagocyte monoclonal antibodies. Application to the purification of dendritic cells and the tissue localization of macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):126–145. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. W. Mononuclear phagocytes in the human placenta. Placenta. 1980 Apr-Jun;1(2):113–123. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(80)80019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Agthoven A., Terhorst C. Further biochemical characterization of the human thymocyte differentiation antigen T6. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):426–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn M., Lerch P. G., Knowles R. W., Terhorst C. The thymic differentiation markers T6 and M241 are two unusual MHC class I antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):851–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]