Abstract
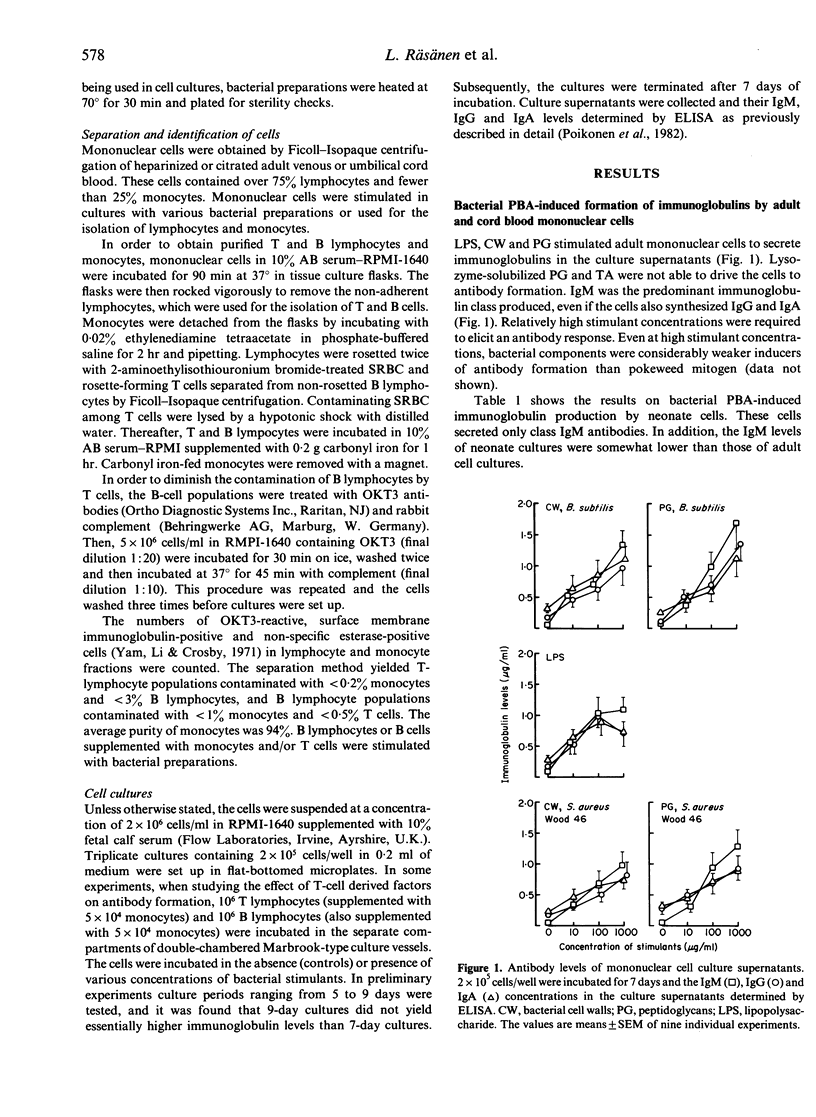
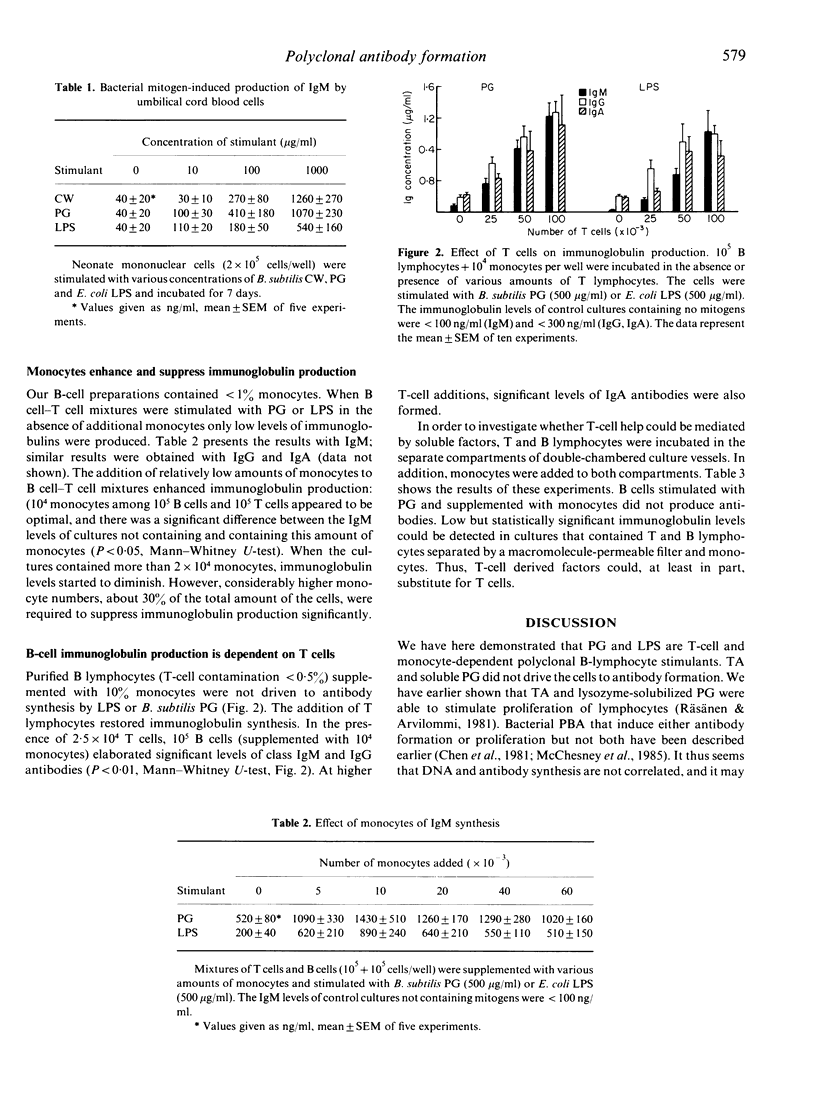
The capacity of various bacterial components to induce antibody formation in human lymphocyte cultures was studied in the present investigation. Antibody levels were determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), bacterial cell walls (CW, isolated from Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus Wood 46) and peptidoglycans (PG) appeared to stimulate IgM, IgG and IgA secretion, whereas lysozyme-solubilized PG and teichoic acids (TA) were ineffective. Also, umbilical cord blood lymphocytes produced IgM after stimulation with LPS, CW and PG. Coculture experiments with purified lymphocytes and monocytes indicated that B-cell differentiation was dependent on both T cells and monocytes, and that T-cell derived factors could derived factors could partially substitute for T cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen W. Y., Muñoz J., Fudenberg H. H., Tung E., Virella G. Polyclonal activation of human peripheral blood B lymphocytes by formaldehyde-fixed Salmonella paratyphi B. I. Immunoglobulin production without DNA synthesis. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):365–374. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clagett J. A., Engel D. Polyclonal activation: a form of primitive immunity and its possible role in pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Dev Comp Immunol. 1978 Apr;2(2):235–241. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(78)80066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R., Dziarski A., Levinson A. I. Mitogenic responsiveness of mouse, rat and human lymphocytes to Staphylococcus aureus cell wall, teichoic acid, and peptidoglycan. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;63(4):383–395. doi: 10.1159/000232654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkoff R. J., Zhu L. P., Fauci A. S. Separate signals for human B cell proliferation and differentiation in response to Staphylococcus aureus: evidence for a two-signal model of B cell activation. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Svedjelund A., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte stimulation by protein A of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):207–213. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmelig-Meyling F., Waldmann T. A. Human B cell activation in vitro: augmentation and suppression by monocytes of the immunoglobulin production induced by various B cell stimulants. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):529–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A. Selective triggering of B cell subpopulations by mitogens. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Nov;4(11):771–776. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830041113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp W., Baumgartner G. Monocyte-mediated suppression of human B lymphocyte differentiation in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1177–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunori T., Ringdén O., Möller E. Optimal conditions for polyclonal antibody secretion and DNA synthesis in human blood and spleen lymphocytes by lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(5):451–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. I., Dziarski A., Zweiman B., Dziarski R. Staphylococcal peptidoglycan: T-cell-dependent mitogen and relatively T-cell-independent polyclonal B-cell activator of human lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):290–296. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.290-296.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Bach M. A. In vivo polyclonal stimulation of antibody secretion by two types of bacteria. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):621–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Duber-Stull D., Lawton A. R. T-cell-dependent and independent plasma cell differentiation induced by Escherichia coli Lipopolysaccharide in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Mar;18(3):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McChesney M. B., Froelich C. J., Cantrell J. L., Williams R. C., Jr Salmonella typhimurium mitogen induces proliferation of human B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jun;93(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Gartner S., Kaplan H. S. Stimulation of mitogenic responses in human peripheral blood lymphocytes by lipopolysaccharide: serum and T helper cell requirements. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2160–2164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit J. C., Unanue E. R. Effects of bacterial products on lymphocytes and macrophages: their possible role in natural resistance to listeria infetion in mice. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):984–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poikonen K., Oka M., Möttönen T., Jokinen I., Arvilommi H. Synthesis of IgM, IgG and IgA in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Dec;41(6):607–611. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.6.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringdén O. Induction of immunoglobulin secretion by protein A from Staphylococcus aureus in human blood and bone marrow B cells. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Jul;22(1):17–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Räsänen L., Arvilommi H. Cell walls, peptidoglycans, and teichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria as polyclonal inducers and immunomodulators of proliferative and lymphokine responses of human B and T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):712–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.712-717.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki O., Ralph P. Induction of human immunoglobulin secretion. I. Synergistic effect of B cell mitogen Cowan I plus T cell mitogens or factors. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1044–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley D. M., Choi Y. S. Characterization of the subpopulations of human peripheral blood B lymphocytes which react to staphylococcus aureus Cowan I and T-cell help. Cell Immunol. 1983 May;78(1):130–143. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



