Abstract
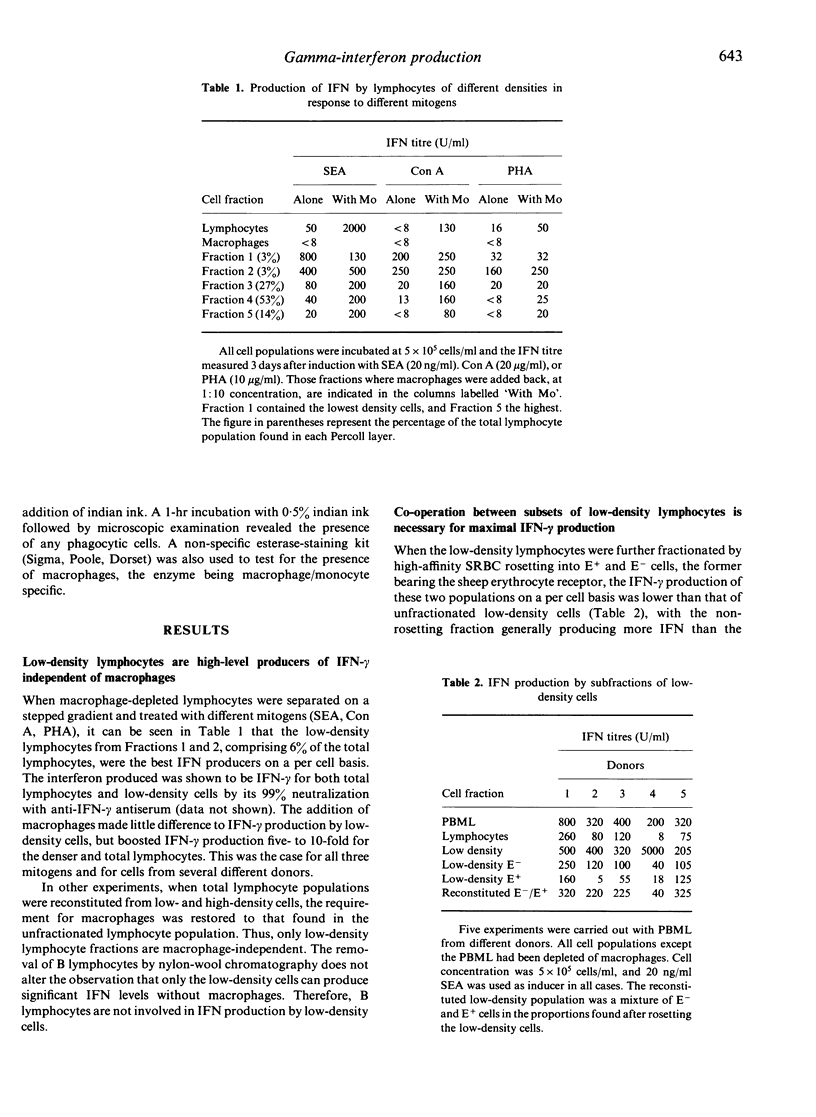
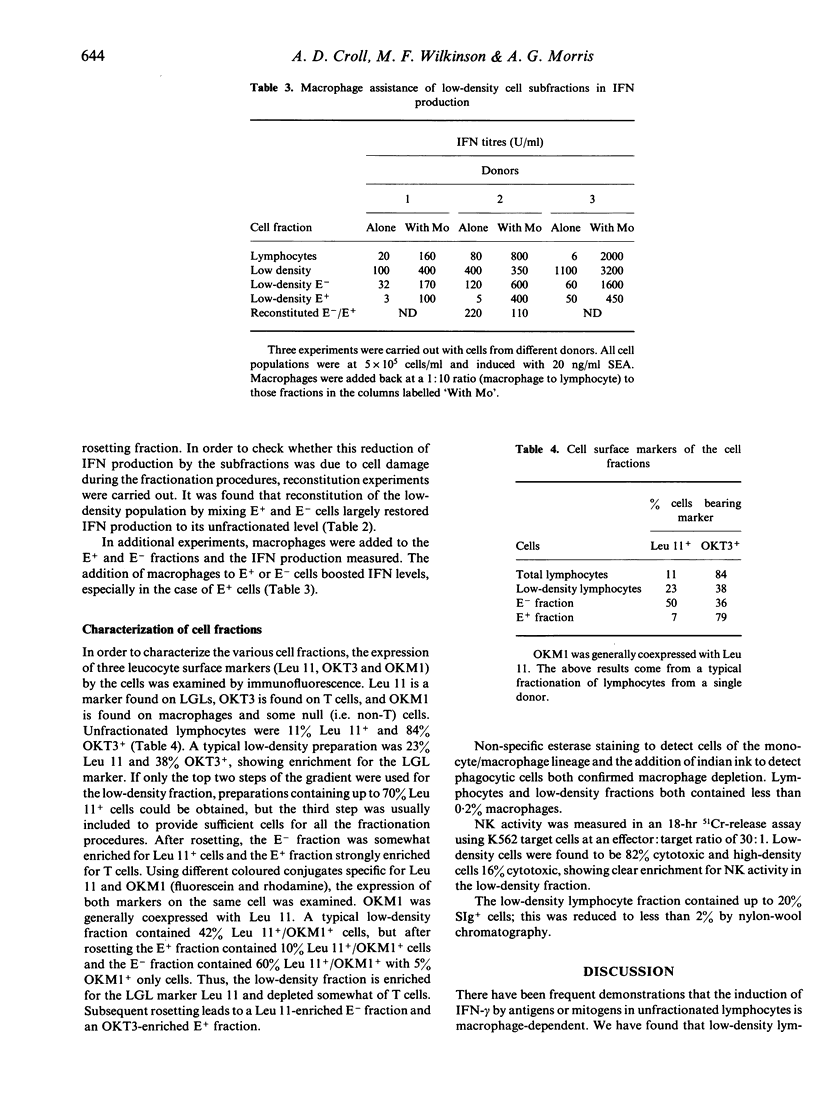
Low-density lymphocytes prepared by Percoll fractionation of human peripheral blood mononuclear leucocytes were found to produce large amounts of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in response to different T-cell mitogens in the absence of macrophages, whilst higher density lymphocytes were strongly dependent on the presence of macrophages for significant IFN-gamma production. The addition of macrophages to the low-density lymphocytes made little difference to their IFN-gamma production. Subsets of the low-density lymphocytes prepared by rosetting with sheep red blood cells produced markedly less IFN-gamma than did the original population; IFN-gamma production could be largely restored by recombining the two low-density fractions. This suggests that IFN-gamma production by low-density lymphocytes whilst macrophage-independent does require co-operation between different cell types. The low-density lymphocytes were enriched for cells bearing the Leu 11 and OKM1 antigens, and for natural killer cell activity. The rosetting fraction was enriched for OKT3 antigen-bearing cells, and the non-rosetting fraction was enriched for Leu 11, OKM1 antigen-bearing cells. Depletion of B cells (surface Ig-positive) by nylon-wool chromatography had no effect on IFN-gamma production by low-density lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Miller C. A., Balch C. M. Characterization of human granular lymphocyte subpopulations expressing HNK-1 (Leu-7) and Leu-11 antigens in the blood and lymphoid tissues from fetuses, neonates and adults. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jul;14(7):616–623. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer D. L., Smith B. G., Ulrich J. T., Johnson H. M. Immune interferon induction by T-cell mitogens involves different T-cell subpopulations. Cell Immunol. 1979 Dec;48(2):420–426. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins G. J., Johnston M. D., Westmacott L. M., Burke D. C. Department of Biological Sciences, University of Warwick, Coventry, CV47AL, England. J Gen Virol. 1974 Dec;25(3):381–390. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-3-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtzen K., Petersen J. Role of monocytes/macrophages and interleukin 1 in antigen-induced human lymphokine production. Cell Immunol. 1984 Jan;83(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruszewski W. B., Bruszewski J. A., Tonnu H., Ferezy S. L., O'Brien R. L., Parker J. W. Early mitogen-induced metabolic events essential to proliferation of human T lymphocytes: dependence of specific events on the influence of adherent accessory cells. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2837–2843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Testa D., Kung P. C., Perry L., Dreskin H. J., Goldstein G. Cellular origin and interactions involved in gamma-interferon production induced by OKt3 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):585–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croll A. D., Wilkinson M. F., Morris A. G. Interleukin 2 receptor blockade by anti-Tac antibody inhibits IFN-gamma induction. Cell Immunol. 1985 Apr 15;92(1):184–189. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Djeu J. Y., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Capacity of human large granular lymphocytes (LGL) to produce multiple lymphokines: interleukin 2, interferon, and colony stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Hooks J. J., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 2-mediated immune interferon (IFN-gamma) production by human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama M., Sugamura K., Kawade Y., Hinuma Y. Production of immune interferon by human cytotoxic T cell clones. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):450–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. G., Lin Y. L., Askonas B. A. Immune interferon release when a cloned cytotoxic T-cell line meets its correct influenza-infected target cell. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):150–152. doi: 10.1038/295150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Bevan M. J., Klein J. R. Release of discrete interferons by cytotoxic T lymphocytes in response to immune and nonimmune stimuli. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):277–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pistoia V., Cozzolino F., Torcia M., Castigli E., Ferrarini M. Production of B cell growth factor by a Leu-7+, OKM1+ non-T cell with the features of large granular lymphocytes (LGL). J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3179–3184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Allavena P., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B., Oppenheim J. J. Subsets of human large granular lymphocytes (LGL) exhibit accessory cell functions. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3049–3055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres B. A., Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M. Interleukin 2 regulates immune interferon (IFN gamma) production by normal and suppressor cell cultures. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2217–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Beller D. I., Lu C. Y., Allen P. M. Antigen presentation: comments on its regulation and mechanism. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. M., Ransil B. J., Shapiro H. M., Strom T. B. Accessory cell requirement for activation antigen expression and cell cycle progression by human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2986–2995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


