Abstract
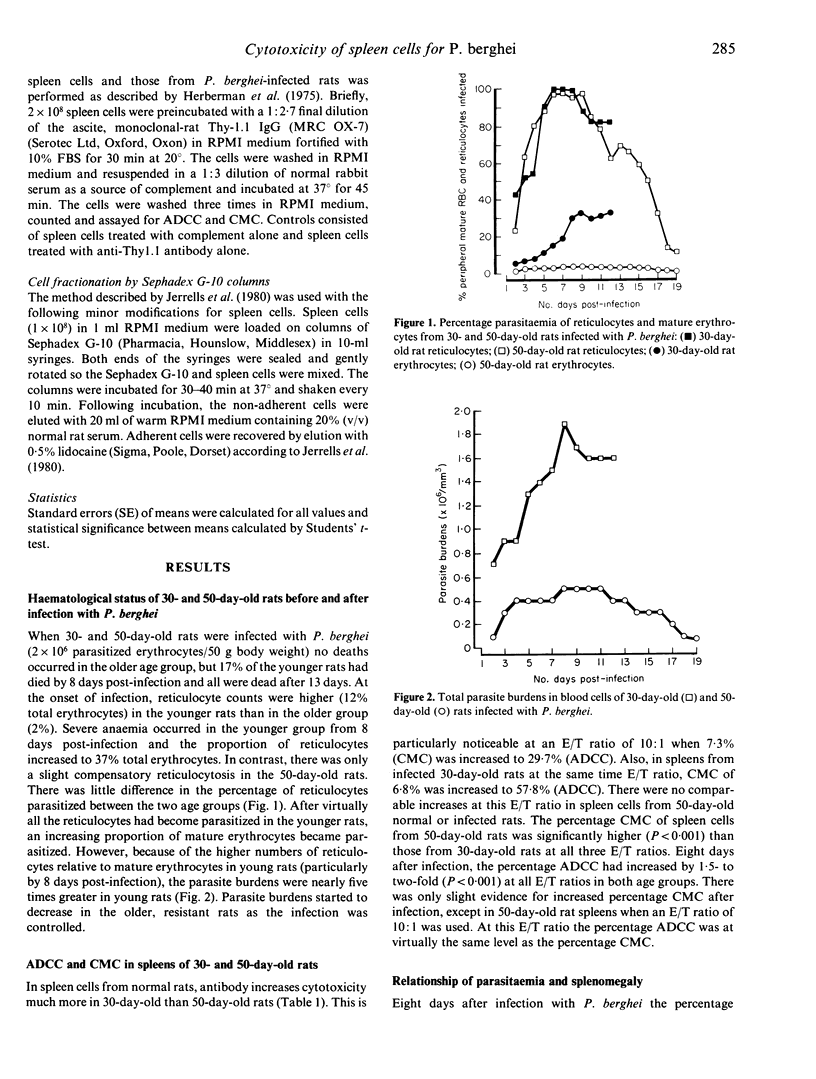
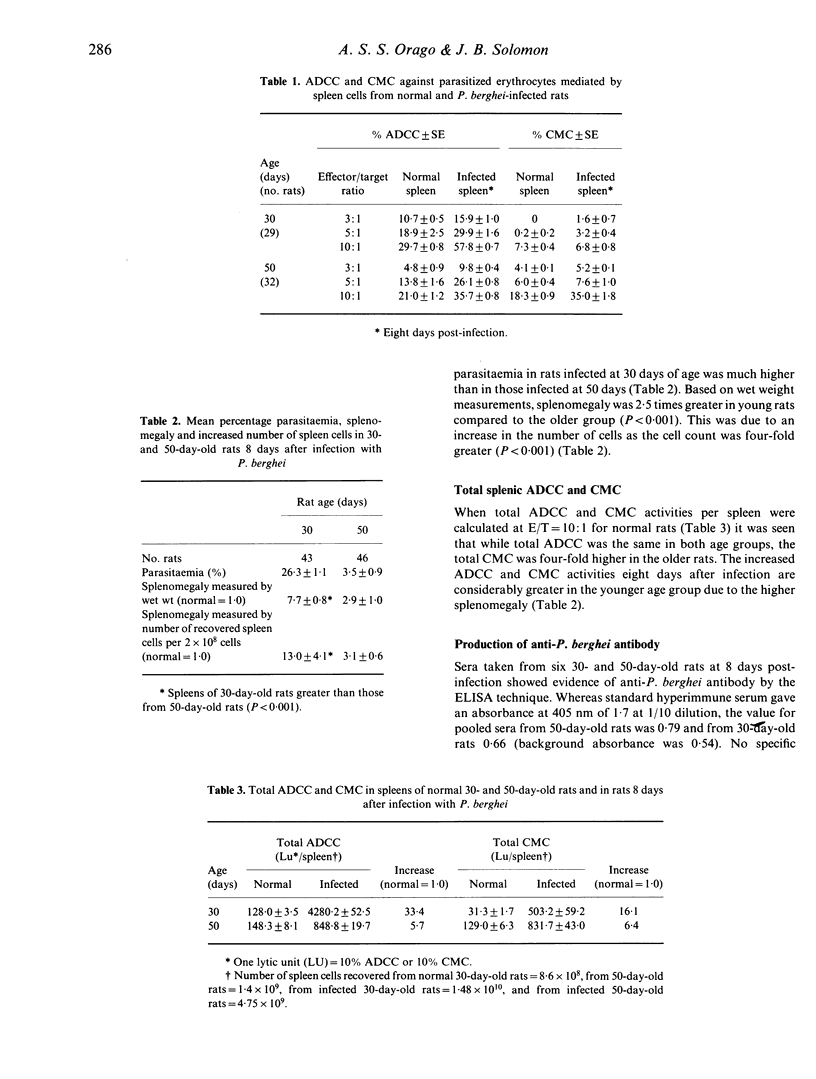
Antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) mediated by spleen cells from 30- or 50-day old rats against 51Cr-labelled rat erythrocytes parasitized by Plasmodium berghei in the presence of anti-P. berghei antibody showed only slight age differences. However, in the absence of specific antibody, the total cell-mediated cytotoxicy (CMC) per spleen was four times higher in the spleen cells from 50-day-old rats compared with those from 30-day-old rats. CMC accounted for about 50% of total cytotoxic activity in 50-day-old rat spleens. Spleen cells mediating ADCC and CMC are Thy-1.1 positive, and those mediating ADCC are nearly all non-adherent to Sephadex G-10 columns.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown I. N., Allison A. C., Taylor R. B. Plasmodium berghei infections in thymectomized rats. Nature. 1968 Jul 20;219(5151):292–293. doi: 10.1038/219292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J., Greenwood B. M. Cellular and humoral inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum growth in vitro and recovery from acute malaria. Parasite Immunol. 1985 May;7(3):265–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1985.tb00075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J., Smalley M. E. Specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in human malaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Sep;41(3):423–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Oduloju A. J., Stratton D. Lymphocyte changes in acute malaria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1977;71(5):408–410. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(77)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Lavrin D. H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumors. II. Characterization of effector cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):230–239. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Dean J. H., Richardson G. L., Herberman R. B. Depletion of monocytes from human peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes: comparison of the sephadex G-10 column method with other commonly used techniques. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(1):11–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khusmith S., Druilhe P. Cooperation between antibodies and monocytes that inhibit in vitro proliferation of Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):219–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.219-223.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiper J. B., Solomon J. B. Ontogeny of mitogenic responsiveness to PHA and sheep erythrocytes and lymphokine production in foetal guinea-pigs. Immunology. 1977 Mar;32(3):215–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald V., Phillips R. S. Increase in non-specific antibody mediated cytotoxicity in malarious mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Nov;34(2):159–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. S. Plasmodium berghei: passive transfer of immunity by antisera and cells. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Jun;27(3):479–495. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Wyler D. J. Resolution of acute malaria (Plasmodium berghei in the rat): reversibility and spleen dependence. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jan;29(1):1–4. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. W., Weidanz W. P. Splenomegaly, enhanced phagocytosis, and anemia are thymus-dependent responses to malaria. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):728–731. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.728-731.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER I., HADFIELD R., LAKONEN M. The influence of age on the intensity of infection with Plasmodium berghei in the rat. J Infect Dis. 1955 Jul-Aug;97(1):15–21. doi: 10.1093/infdis/97.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley M. E. The nature of age immunity to Plasmodium berghei in the rat. Parasitology. 1975 Oct;71(2):337–347. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000046771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B. Natural cytotoxicity for Plasmodium berghei in vitro by spleen cells from susceptible and resistant rats. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):277–281. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira D. T., Silverman P. H., Gaines C. Anti-thymocyte serum effects on Plasmodium berghei infection in rats. Immunology. 1970 Nov;19(5):759–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlgren M., Berzins K., Perlmann P., Björkman A. Characterization of the humoral immune response in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. I. Estimation of antibodies to P. falciparum or human erythrocytes by means of microELISA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):127–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


