Abstract
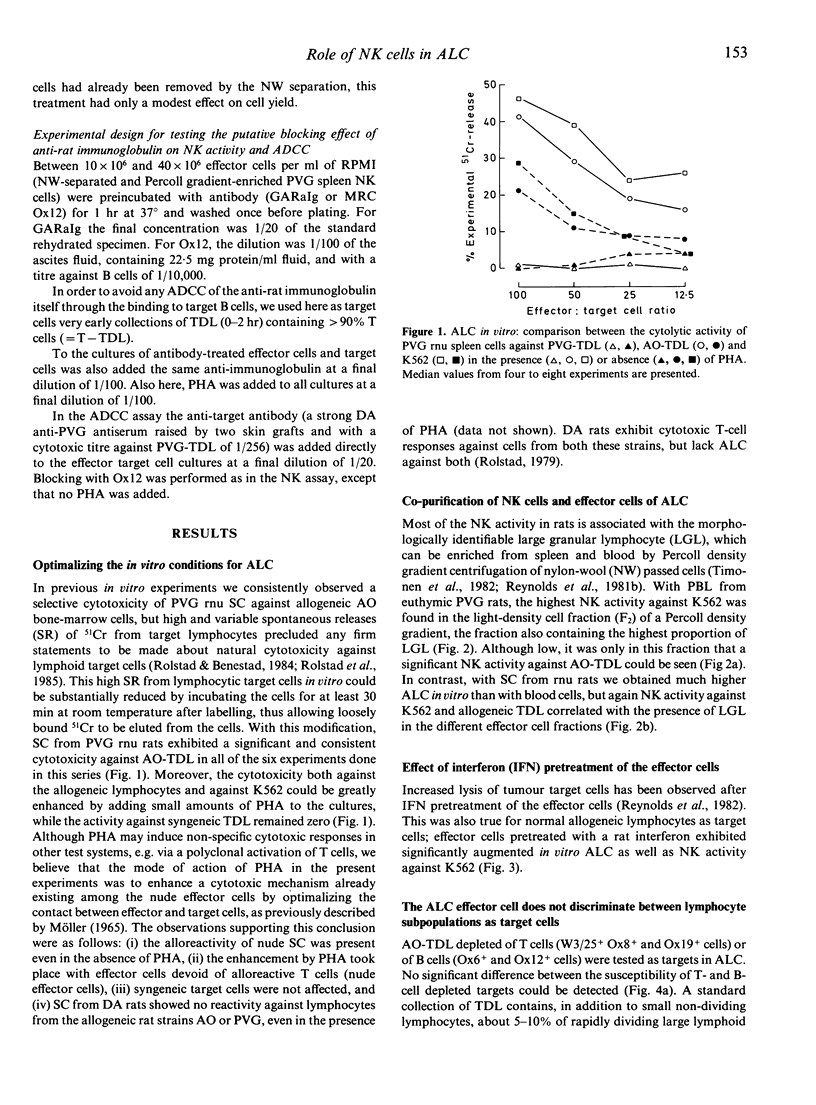
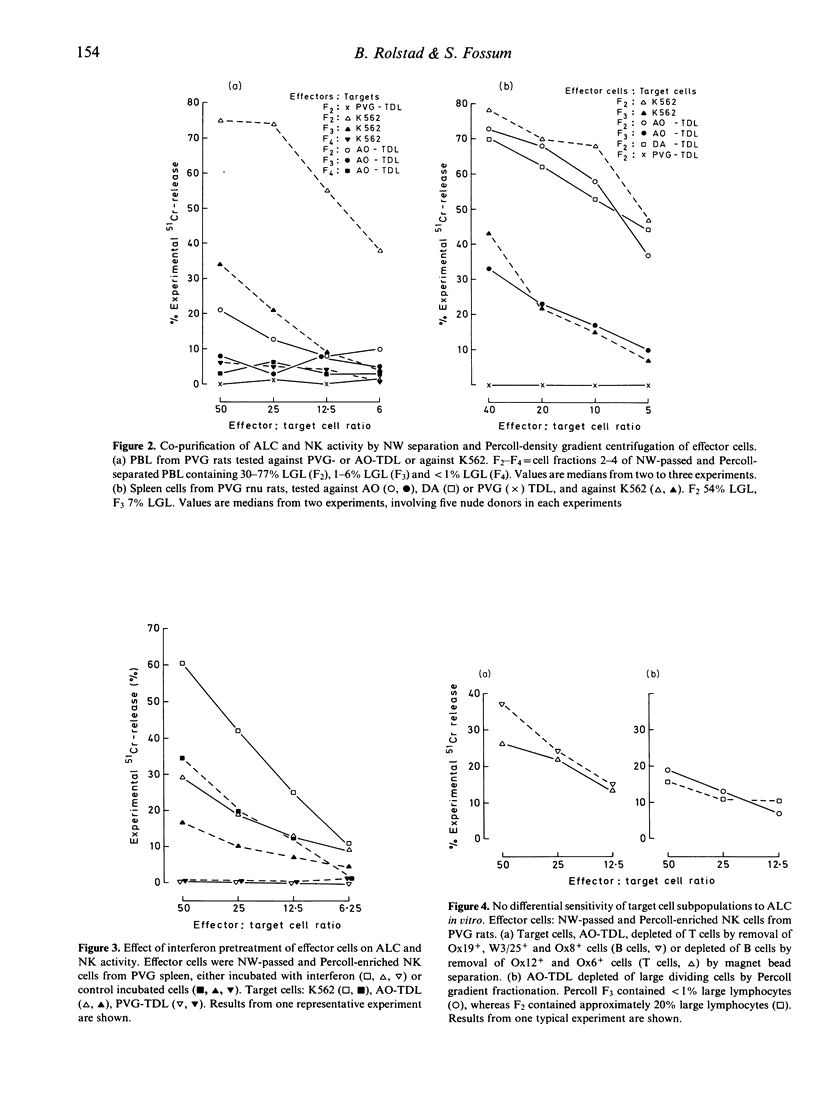
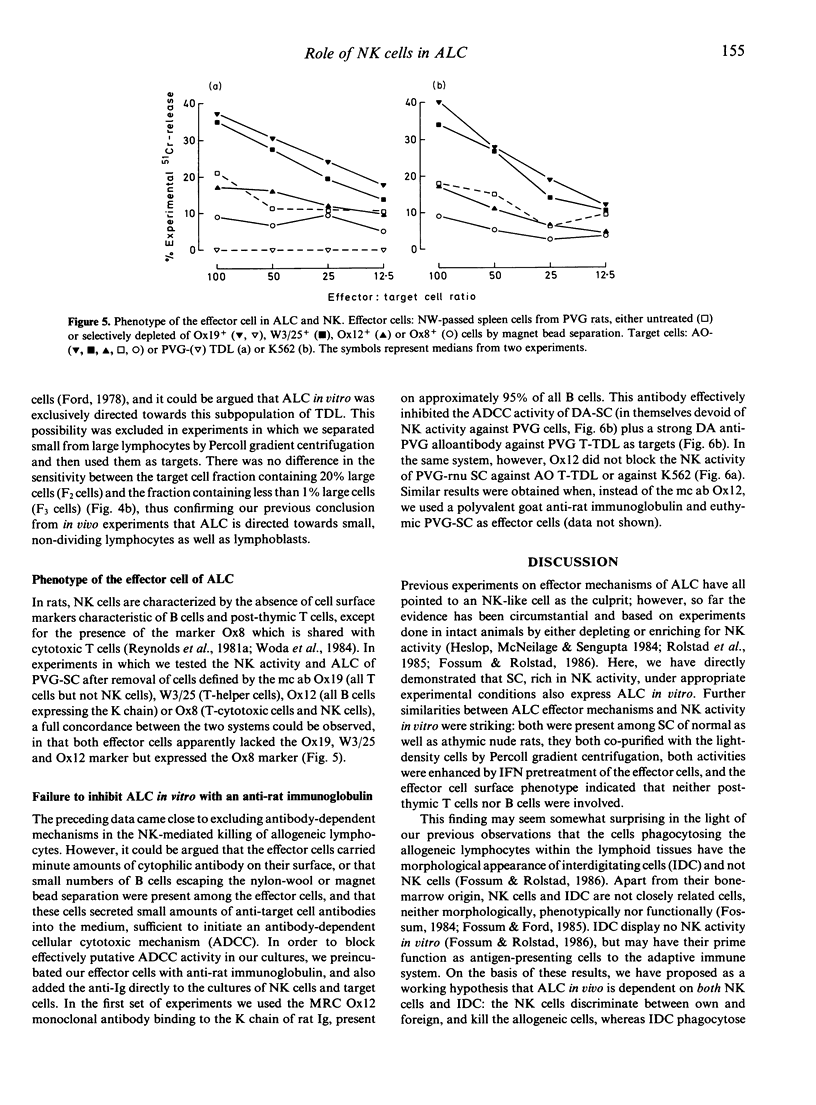
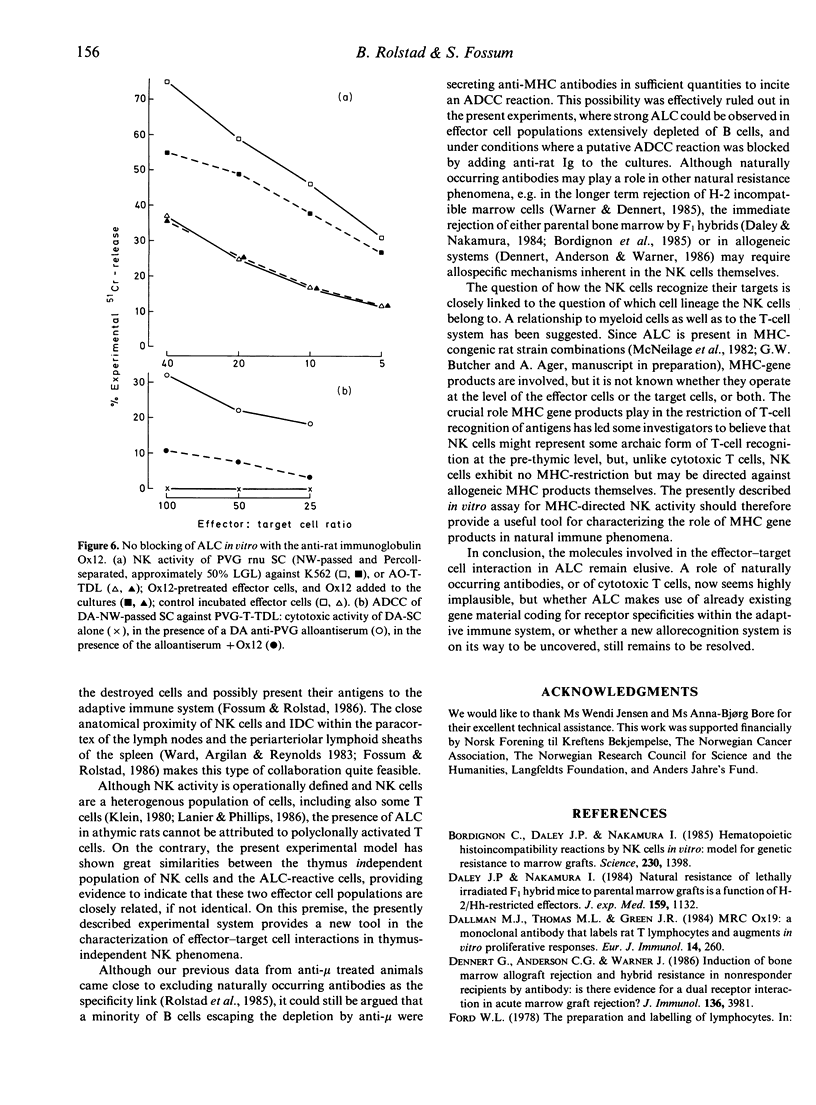
The evidence that NK cells can recognize and kill allogeneic lymphocytes has hitherto been based mainly on experiments in intact animals. Here we report results from an in vitro assay, showing allogeneic lymphocyte cytotoxicity in cell suspensions enriched for NK activity against tumour cells by Percoll gradient centrifugation of nylon-wool non-adherent cells. The addition of phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) to the NK-target cell cultures greatly enhanced the cytotoxic response against K562 and allogeneic, but not syngeneic, lymphocytes. The effector cells of ALC are present in the spleen of both euthymic and athymic nude rats, and to a lesser extent in the blood. ALC is augmented by interferon pretreatment of the effector cells, and by depleting the effector cell suspensions of all T cells and helper T cells with the monoclonal antibody MRC Ox19 and W3/25, respectively. Conversely, the activity was nearly abolished by depleting the cell suspensions of MRC Ox8+ cells reacting with rat cytotoxic T cells and NK cells. Furthermore, removal of residual B cells (Ox12+ cells) from the effector cells or attempts to block any putative antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic mechanism in vitro with the monoclonal antibody Ox12 did not inhibit the NK activity against allogeneic lymphocytes nor against tumour cells. ALC in vitro did not discriminate between T and B or large and small lymphocyte targets. These characteristics of the ALC effector cells substantiate that they are present within the thymus-independent population of cells with NK activity, and are dependent on neither B cells nor immunoglobulin for their recognition and destruction of the target.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bordignon C., Daley J. P., Nakamura I. Hematopoietic histoincompatibility reactions by NK cells in vitro: model for genetic resistance to marrow grafts. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1398–1401. doi: 10.1126/science.3906897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley J. P., Nakamura I. Natural resistance of lethally irradiated F1 hybrid mice to parental marrow grafts is a function of H-2/Hh-restricted effectors. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1132–1148. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. J., Thomas M. L., Green J. R. MRC OX-19: a monoclonal antibody that labels rat T lymphocytes and augments in vitro proliferative responses. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Mar;14(3):260–267. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Anderson C. G., Warner J. Induction of bone marrow allograft rejection and hybrid resistance in nonresponder recipients by antibody: is there evidence for a dual receptor interaction in acute marrow graft rejection? J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):3981–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum S. Characterization of Ia+ non-lymphoid cells in peripheral lymph from congenitally athymic nude rats. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Jan;19(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum S., Ford W. L. The organization of cell populations within lymph nodes: their origin, life history and functional relationships. Histopathology. 1985 May;9(5):469–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1985.tb02830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum S., Rolstad B. The roles of interdigitating cells and natural killer cells in the rapid rejection of allogeneic lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Apr;16(4):440–450. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönberg A., Kiessling R., Fiers W. Interferon-gamma is a strong modulator of NK susceptibility and expression of beta 2-microglobulin but not of transferrin receptors of K562 cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Oct 1;95(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop B. F., McNeilage L. J., Sengupta S. Allogeneic lymphocyte cytotoxicity in rats: the effects of various pharmacological agents. Immunology. 1984 Sep;53(1):43–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. V., Fowler M. H. A repopulation assay for B and T lymphocyte stem cells employing radiation chimaeras. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1981 Jul;14(4):445–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1981.tb00551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kärre K., Ljunggren H. G., Piontek G., Kiessling R. Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):675–678. doi: 10.1038/319675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea T., Vartdal F., Davies C., Ugelstad J. Magnetic monosized polymer particles for fast and specific fractionation of human mononuclear cells. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(2):207–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilage L. J., Heslop B. F., Heyworth M. R., Gutman G. A. Natural cytotoxicity in rats: strain distribution and genetics. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 15;72(2):340–350. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90482-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Sharrow S. O., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Natural killer activity in the rat. II. Analysis of surface antigens on LGL by flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2204–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Timonen T. T., Holden H. T., Hansen C. T., Herberman R. B. Natural killer cell activity in the rat. Analysis of effector cell morphology and effects of interferon on natural killer cell function in the athymic (nude) rat. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jul;12(7):577–582. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolstad B., Benestad H. B. The "natural resistance" to bone marrow allografts in normal and athymic nude rats. Rapid cytotoxic reactions both in vivo and in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Sep;14(9):793–799. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolstad B., Ford W. L. The rapid elimination of allogeneic lymphocytes: relationship to established mechanisms of immunity and to lymphocyte traffic. Immunol Rev. 1983;73:87–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolstad B., Fossum S., Bazin H., Kimber I., Marshall J., Sparshott S. M., Ford W. L. The rapid rejection of allogeneic lymphocytes by a non-adaptive, cell-mediated mechanism (NK activity). Immunology. 1985 Jan;54(1):127–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolstad B., Herberman R. B., Reynolds C. W. Natural killer cell activity in the rat. V. The circulation patterns and tissue localization of peripheral blood large granular lymphocytes (LGL). J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2800–2808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolstad B. The influence of strong transplantation antigens (Ag-B) on lymphocyte migration in vivo. Cell Immunol. 1979 Jul;45(2):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90399-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell G. D. Recognition structures determined by the H-2 complex. Transplant Proc. 1976 Jun;8(2):147–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Reynolds C. W., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Isolation of human and rat natural killer cells. J Immunol Methods. 1982;51(3):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90393-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønnesen B., Rolstad B. In vivo elimination of allogeneic lymphocytes in normal and T-cell-deficient rats. Elimination does not require T cells. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Apr;17(4):303–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Argilan F., Reynolds C. W. Immunoperoxidase localization of large granular lymphocytes in normal tissues and lesions of athymic nude rats. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):132–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. F., Dennert G. Bone marrow graft rejection as a function of antibody-directed natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):563–576. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woda B. A., McFadden M. L., Welsh R. M., Bain K. M. Separation and isolation of rat natural killer (NK) cells from T cells with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2183–2184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


