Abstract
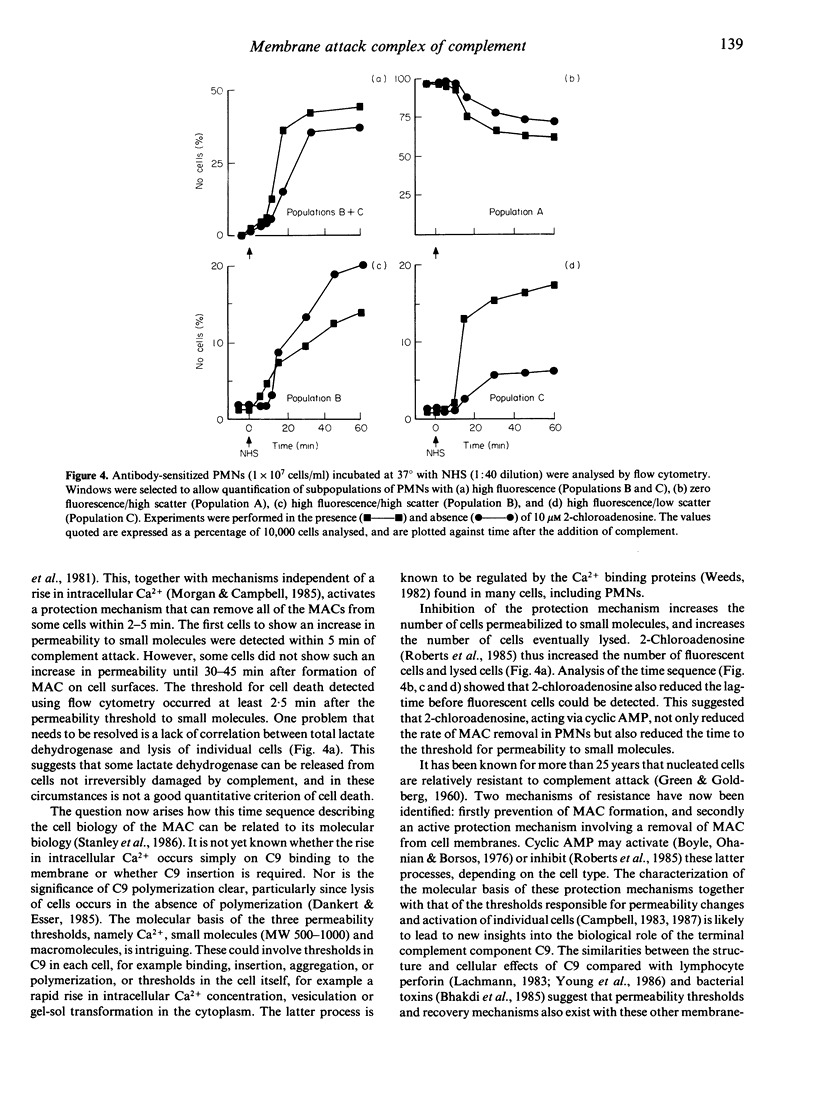
Flow cytometry was used to quantify the fluorescence of propidium iodide in rat polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN) attacked by the membrane attack complex (MAC) in order to establish the existence of permeability and lytic thresholds in individual cells, a 'threshold' being defined as a cellular event involving the rapid transition of cells from one state to another under physiological conditions. Activation of the complement pathway resulted in PMN being attacked by MAC within 5 min. Approximately 30-40% of the cell population subsequently became permeable to small molecules and macromolecules. Individual PMN passed through 'thresholds' of cell permeability and cell lysis, or recovered from complement attack at different times. In the flow cytometer, three distinct populations of PMN were identified: cells that had recovered before the permeability 'threshold', cells that had recovered after the permeability 'threshold' but before the lytic 'threshold', and cells that failed to recover from complement attack. Individual PMN attacked by MAC passed through permeability and lytic thresholds at different times after an initial lag of 7.5 +/- 2.5 min and 11.5 +/- 1.0 min, respectively. Adenosine, an activator of adenylate cyclase, inhibited removal of MAC from the cell surface. Consequently, more cells passed through the permeability and lytic 'thresholds', resulting in an increased percentage of lysed cells.
Full text
PDF

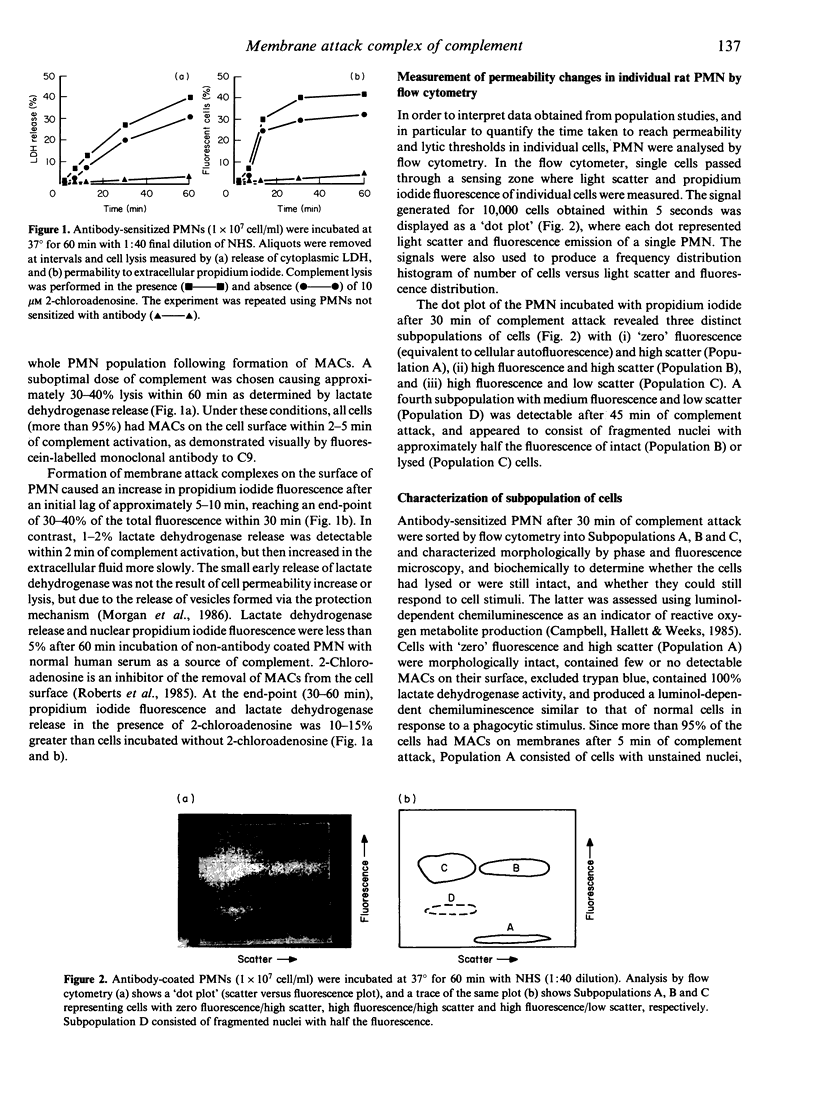


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biesecker G. Membrane attack complex of complement as a pathologic mediator. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):237–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Ohanian S. H., Borsos T. Studies on the terminal stages of antibody-complement-mediated killing of a tumor cell. II. Inhibition of transformation of T to dead cells by 3'5' cAMP. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1276–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. K., Daw R. A., Hallett M. B., Luzio J. P. Direct measurement of the increase in intracellular free calcium ion concentration in response to the action of complement. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):551–560. doi: 10.1042/bj1940551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. K., Hallett M. B., Weeks I. Chemiluminescence as an analytical tool in cell biology and medicine. Methods Biochem Anal. 1985;31:317–416. doi: 10.1002/9780470110522.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. K., Morgan B. P. Monoclonal antibodies demonstrate protection of polymorphonuclear leukocytes against complement attack. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):164–166. doi: 10.1038/317164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert J. R., Esser A. F. Proteolytic modification of human complement protein C9: loss of poly(C9) and circular lesion formation without impairment of function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2128–2132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards S. W., Morgan B. P., Hoy T. G., Luzio J. P., Campbell A. K. Complement-mediated lysis of pigeon erythrocyte ghosts analysed by flow cytometry. Evidence for the involvement of a 'threshold' phenomenon. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 15;216(1):195–202. doi: 10.1042/bj2160195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H., GOLDBERG B. The action of antibody and complement on mammalian cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 May 31;87:352–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb23205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett M. B., Campbell A. K. Two distinct mechanisms for stimulation of oxygen-radical production by polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):459–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2160459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett M. B., Luzio J. P., Campbell A. K. Stimulation of Ca2+-dependent chemiluminescence in rat polymorphonuclear leucocytes by polystyrene beads and the non-lytic action of complement. Immunology. 1981 Nov;44(3):569–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J. Are complement lysis and lymphocytotoxicity analogous? Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):473–474. doi: 10.1038/305473a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P., Campbell A. K. The recovery of human polymorphonuclear leucocytes from sublytic complement attack is mediated by changes in intracellular free calcium. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):205–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2310205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P., Daw R. A., Siddle K., Luzio J. P., Campbell A. K. Immunoaffinity purification of human complement component C9 using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 25;64(3):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90434-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P., Sewry C. A., Siddle K., Luzio J. P., Campbell A. K. Immunolocalization of complement component C9 on necrotic and non-necrotic muscle fibres in myositis using monoclonal antibodies: a primary role of complement in autoimmune cell damage. Immunology. 1984 May;52(1):181–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack complex. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):93–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01893017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschoop J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular organization of C9 within the membrane attack complex of complement. Induction of circular C9 polymerization by the C5b-8 assembly. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):268–282. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts P. A., Morgan B. P., Campbell A. K. 2-Chloroadenosine inhibits complement-induced reactive oxygen metabolite production and recovery of human polymorphonuclear leucocytes attacked by complement. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):692–697. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Edwards M. R., Luzio J. P. Subcellular distribution and movement of 5'-nucleotidase in rat cells. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):59–69. doi: 10.1042/bj1860059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Page M., Campbell A. K., Luzio J. P. A mechanism for the insertion of complement component C9 into target membranes. Mol Immunol. 1986 May;23(5):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Engel A., Podack E. R. Molecular weight of poly(C9). 12 to 18 C9 molecules form the transmembrane channel of complement. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1922–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. Actin-binding proteins--regulators of cell architecture and motility. Nature. 1982 Apr 29;296(5860):811–816. doi: 10.1038/296811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Hengartner H., Podack E. R., Cohn Z. A. Purification and characterization of a cytolytic pore-forming protein from granules of cloned lymphocytes with natural killer activity. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]