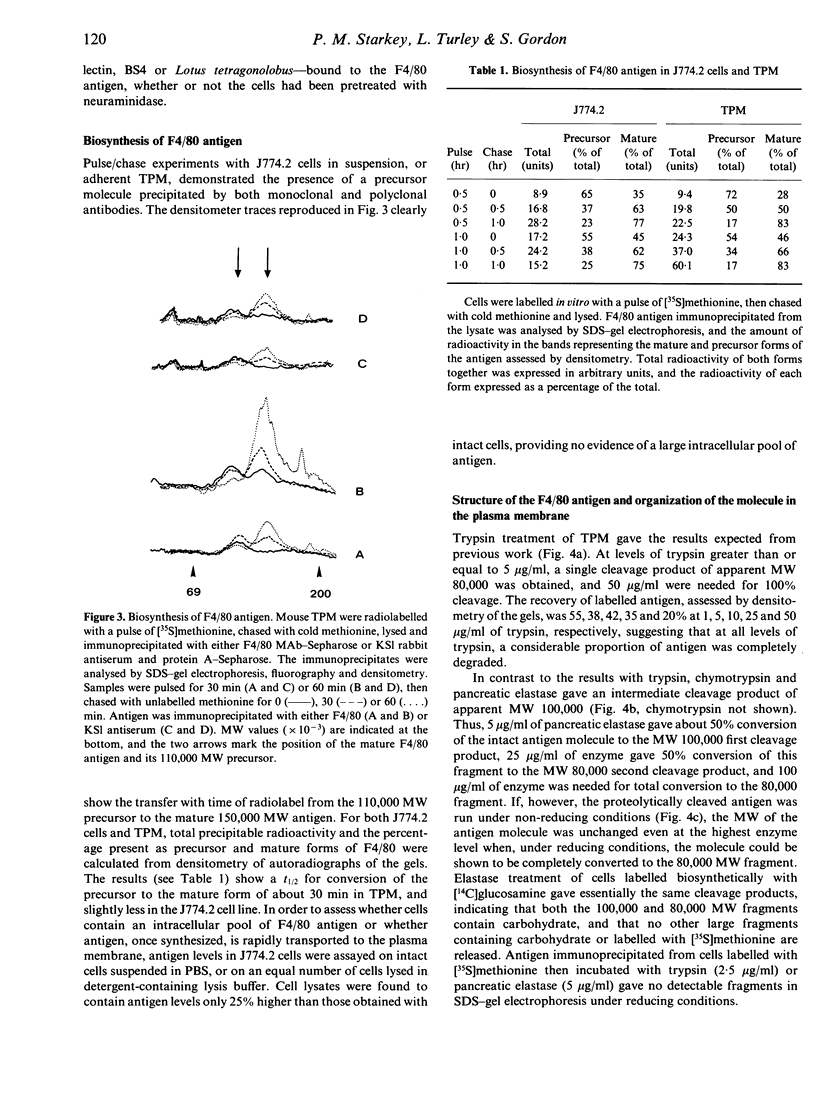
Abstract
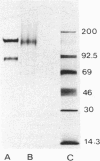
F4/80, a mouse macrophage-specific membrane marker defined by a rat monoclonal antibody, was precipitated by a rabbit antiserum raised against partially purified mouse antigen. The antiserum, when tested against a variety of mouse tissues and cells, bound only to, and was cytotoxic for, macrophages, and it precipitated a similar macrophage-specific protein from rat cells. The F4/80 antigen is a glycoprotein of apparent molecular weight (MW) 150,000, and was labelled biosynthetically with [14C]glucosamine. Neuraminidase treatment removed small amounts of sialic acid, and tunicamycin and 2-deoxyglucose both inhibited antigen synthesis. Pulse/chase labelling with [35S]methionine demonstrated a precursor of 110,000 MW. Proteinase treatment of intact cells cleaved the molecule to an initial 100,000, and then to an 80,000 MW fragment. Without reduction, the MW of the molecule was unchanged by proteinases. These studies indicate that the F4/80 antigen consists of at least two domains linked by disulphide bridges, of MW 80,000 and 20,000. Both domains are extracellular.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axén R., Ernback S. Chemical fixation of enzymes to cyanogen halide activated polysaccharide carriers. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb 1;18(3):351–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A., Sayers C. A. The electrophoretically 'slow' and 'fast' forms of the alpha 2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):401–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1810401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Williams A. F. Lymphocyte cell surface glycoproteins which bind to soybean and peanut lectins. Immunology. 1982 Aug;46(4):713–726. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings R. D., Kornfeld S., Schneider W. J., Hobgood K. K., Tolleshaug H., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Biosynthesis of N- and O-linked oligosaccharides of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15261–15273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert L. J., Stanley E. R. Specific interaction of murine colony-stimulating factor with mononuclear phagocytic cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;85(1):153–159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch S., Austyn J. M., Gordon S. Expression of the macrophage-specific antigen F4/80 during differentiation of mouse bone marrow cells in culture. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):713–725. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. K., Springer T. A. Tissue distribution, structural characterization, and biosynthesis of Mac-3, a macrophage surface glycoprotein exhibiting molecular weight heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):636–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. N., Colombatti A., August J. T. Murine cell surface glycoproteins. Purification of the polymorphic Pgp-1 antigen and analysis of its expression on macrophages and other myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1014–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Lampen J. O. Tunicamycin--an inhibitor of yeast glycoprotein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90925-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kürzinger K., Springer T. A. Purification and structural characterization of LFA-1, a lymphocyte function-associated antigen, and Mac-1, a related macrophage differentiation antigen associated with the type three complement receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12412–12418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Starkey P. M., Gordon S. Quantitative analysis of total macrophage content in adult mouse tissues. Immunochemical studies with monoclonal antibody F4/80. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):475–489. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Schwarz R. T. Formation of dolichol monophosphate 2-deoxy-D-glucose and its interference with the glycosylation of mannoproteins in yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I. S., Steinman R. M., Unkeless J. C., Cohn Z. A. Selective iodination and polypeptide composition of pinocytic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):712–722. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokoena T., Gordon S. Human macrophage activation. Modulation of mannosyl, fucosyl receptor activity in vitro by lymphokines, gamma and alpha interferons, and dexamethasone. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):624–631. doi: 10.1172/JCI111740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig M. C., Steinman R. M., Unkeless J. C., Witmer M. D., Gutchinov B., Cohn Z. A. Studies of the cell surface of mouse dendritic cells and other leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):168–187. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Prichard J., Cohn M. Reticulum cell sarcoma: an effector cell in antibody-dependent cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):898–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Lewandrowski K. Decrease of the major surface glycoprotein gp 160 in activated macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jun;70(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E. Macrophage component gp160, a major trypsin-sensitive surface glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1699–1708. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schwarz R. T., Scholtissek C. Nucleoside-diphosphate derivatives of 2-deoxy-D-glucose in animal cells. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):237–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]