Abstract
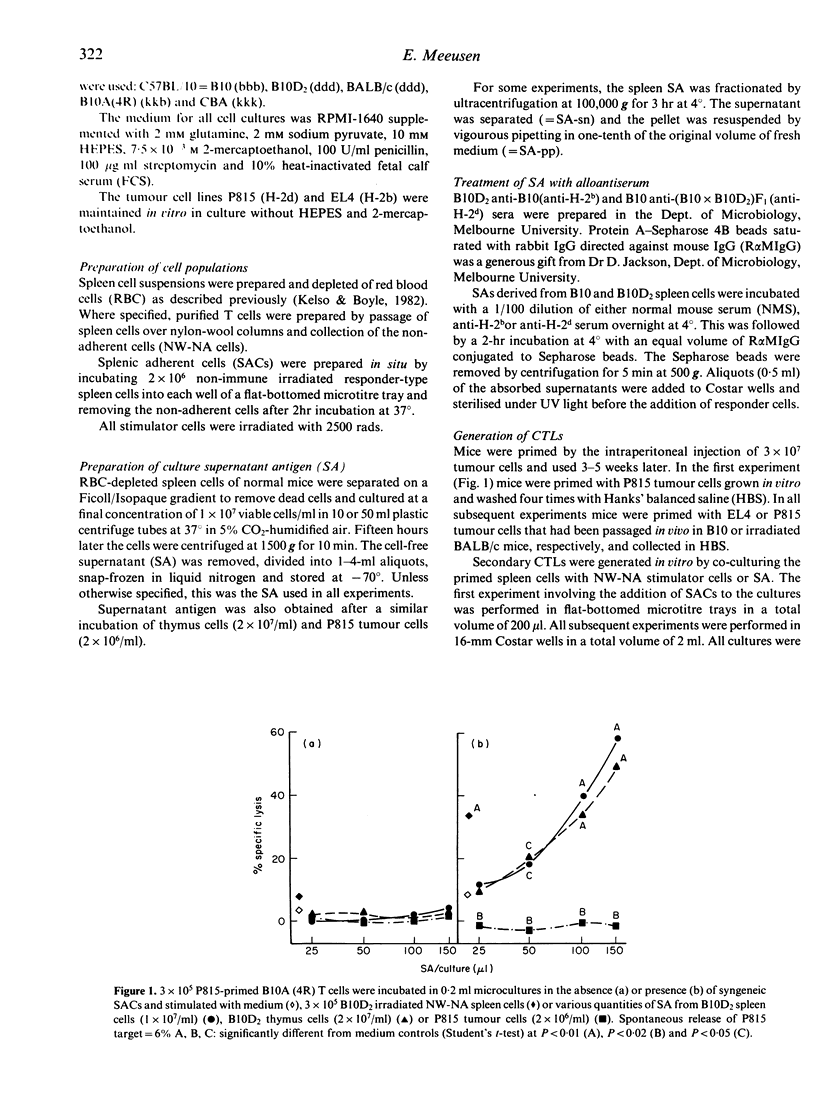
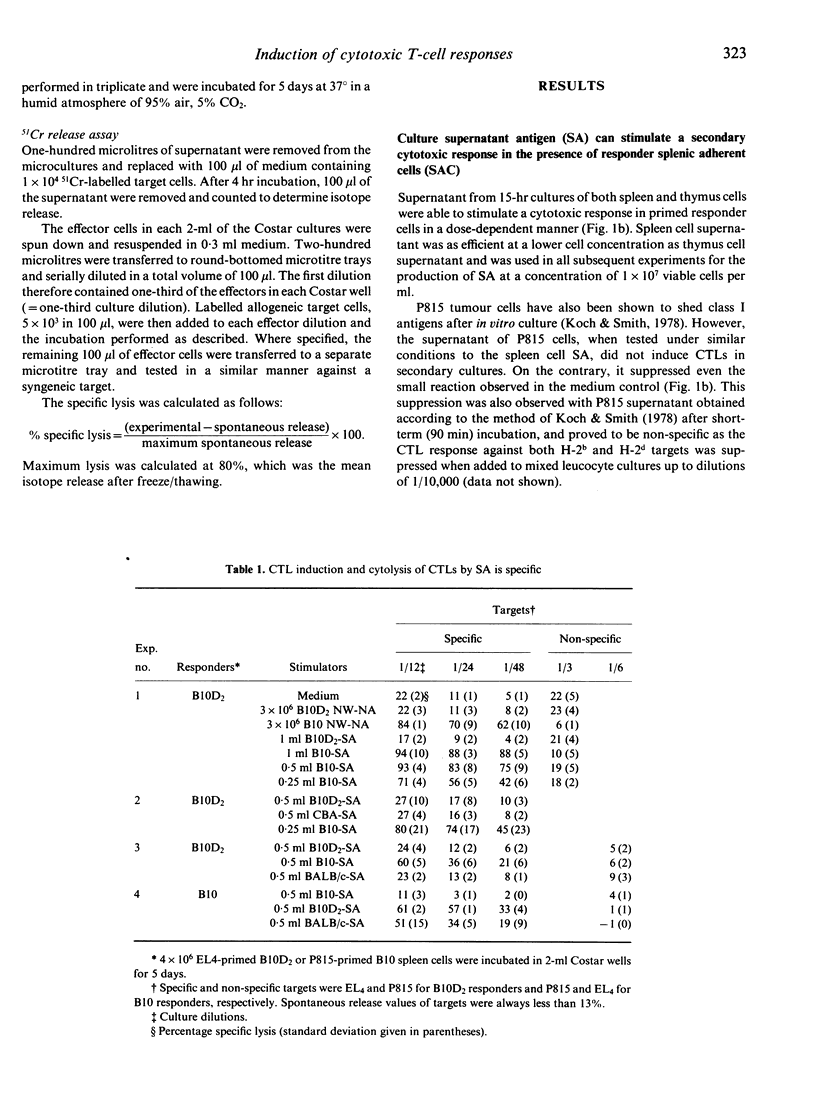
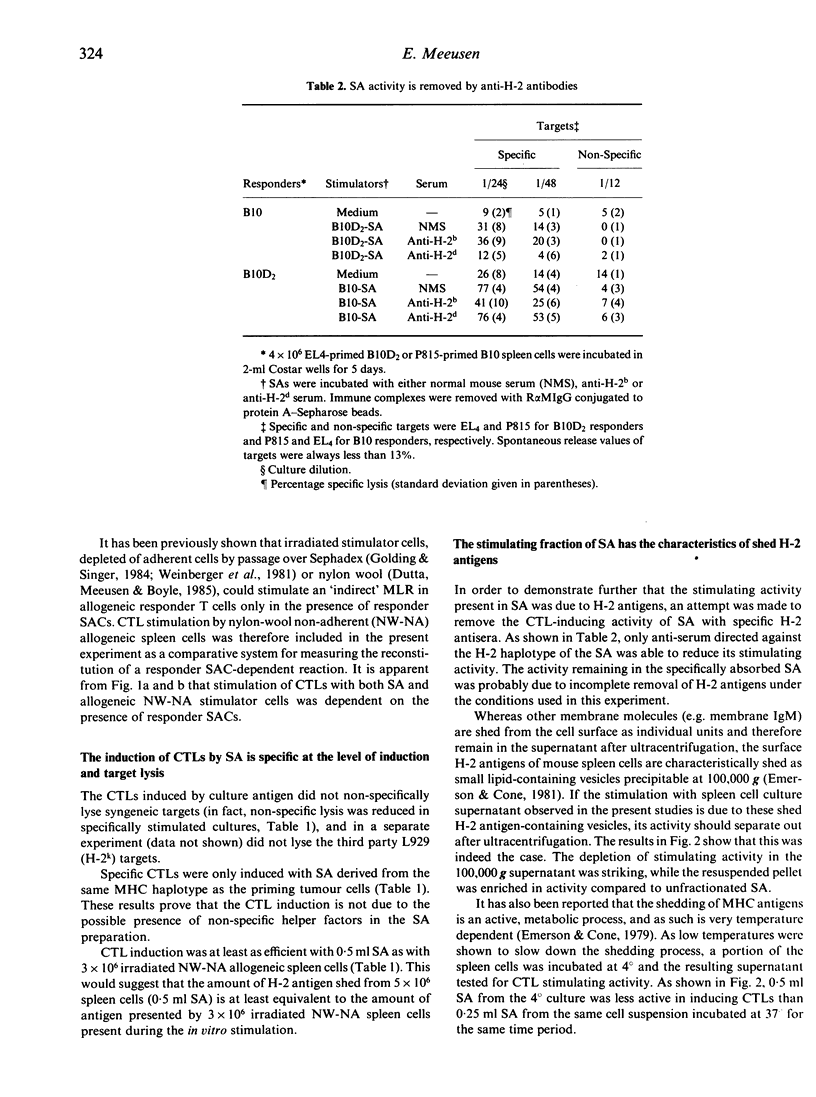
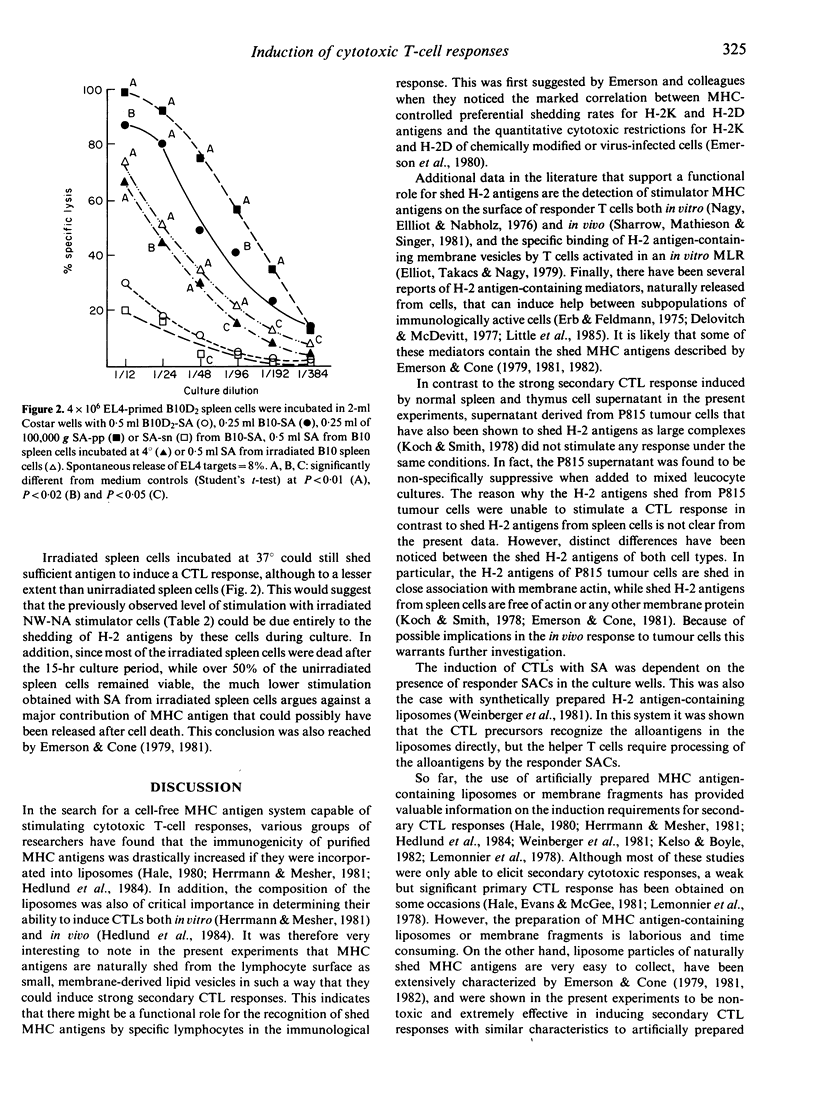
Supernatant derived from the incubation of normal, unstimulated spleen cells was able to stimulate a strong specific in vitro cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) response in allogeneic spleen cells primed with the corresponding haplotype. The supernatant antigen (SA) was as efficient in inducing secondary CTLs as equivalent numbers of irradiated, adherent cell-depleted spleen cell stimulators present during the culture period, and the CTL stimulation with both was dependent on the presence of responder splenic adherent cells. SA obtained from P815 tumour cells was unable to stimulate a similar response under the same conditions. The stimulating fraction of the SA showed the characteristics of lipid-associated major histocompatibility (MHC) antigens shed from viable lymphocytes, in that it was removed with specific H-2 antiserum, it was sedimented at 100,000 g and its activity was reduced if spleen cells were incubated at 4 degrees instead of 37 degrees. These results indicate a possible role for the shedding of MHC antigens in the general induction of a cytotoxic response.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Delovitch T. L., McDevitt H. O. In vitro analysis of allogeneic lymphocyte interaction. I. Characterization and cellular origin of an Ia-positive helper factor-allogeneic effect factor. J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):1019–1032. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta D., Meeusen E., Boyle W. Indirect presentation of allogeneic major histocompatibility complex antigens by syngeneic macrophages. Transplant Proc. 1985 Apr;17(2):1661–1663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott B. E., Takács B., Nagy Z. Specific binding of radiolabeled membrane vesicles by T cells activated in the mixed lymphocyte reaction. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):646–651. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. G., Cone R. E. I-Kk and H-2Kk antigens are shed as supramolecular particles in association with membrane lipids. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):482–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. G., Cone R. E. Turnover and shedding of Ia antigens by murine spleen cells in culture. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):892–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. G., Murphy D. B., Cone R. E. Selective turnover and shedding of H-2K and H-2D antigens is controlled by the major histocompatibility complex. Implications for H-2-restricted recognition. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):783–795. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale A. H., Evans D. L., McGee M. P. A study of the ability of H-2Kk-Iak containing subcellular fractions to elicit primary anti-H-2 cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jul 1;61(2):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale A. H. H-2 antigens incorporated into phospholipid vesicles elicit specific allogeneic cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1980 Oct;55(2):328–341. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann S. H., Mescher M. F. Secondary cytolytic T lymphocyte stimulation by purified H-2Kk in liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2488–2492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelso A., Boyle W. Cytolytic T lymphocyte responses to metabolically inactivated stimulator cells. II. Effect of a soluble "costimulator" factor(s) in primary and secondary mixed leukocyte culture. Cell Immunol. 1982 Mar 1;67(2):370–383. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemonnier F., Mescher T. M., sherman L., Burakoff S. The induction of cytolytic T lymphocytes with purified plasma membranes. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1114–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. A., Asherson G. L., Colizzi V., James B. M., Hraba T. Two-chain disulphide-bonded structure of antigen-specific T-helper factor: both chains are necessary for activity and their interaction is I-A restricted. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):713–719. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh D., Ross A. H., Hale A. H., Baltimore D., Eisen H. N. Synthetic phospholipid vesicles containing a purified viral antigen and cell membrane proteins stimulate the development of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1067–1074. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy Z., Elliott B. E., Nabholz M. Specific binding of K- and I-region products of the H-2 complex to activated thymus-derived (T) cells belonging to different Ly subclasses. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1545–1553. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrow S. O., Mathieson B. J., Singer A. Cell surface appearance of unexpected host MHC determinants on thymocytes from radiation bone marrow chimeras. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1327–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger O., Herrmann S., Mescher M. F., Benacerraf B., Burakoff S. J. Cellular interactions in the generation of cytolytic T lymphocyte responses. Analysis of the helper T cell pathway. Eur J Immunol. 1981 May;11(5):405–411. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


