Abstract
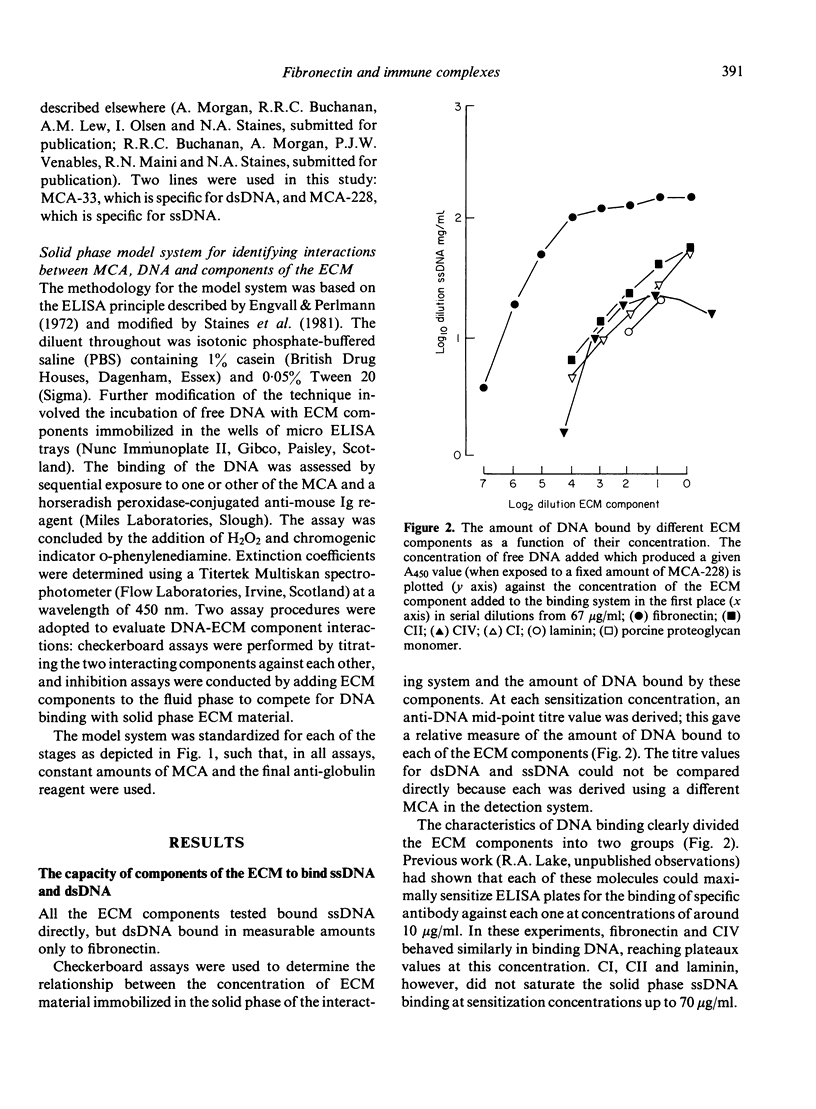
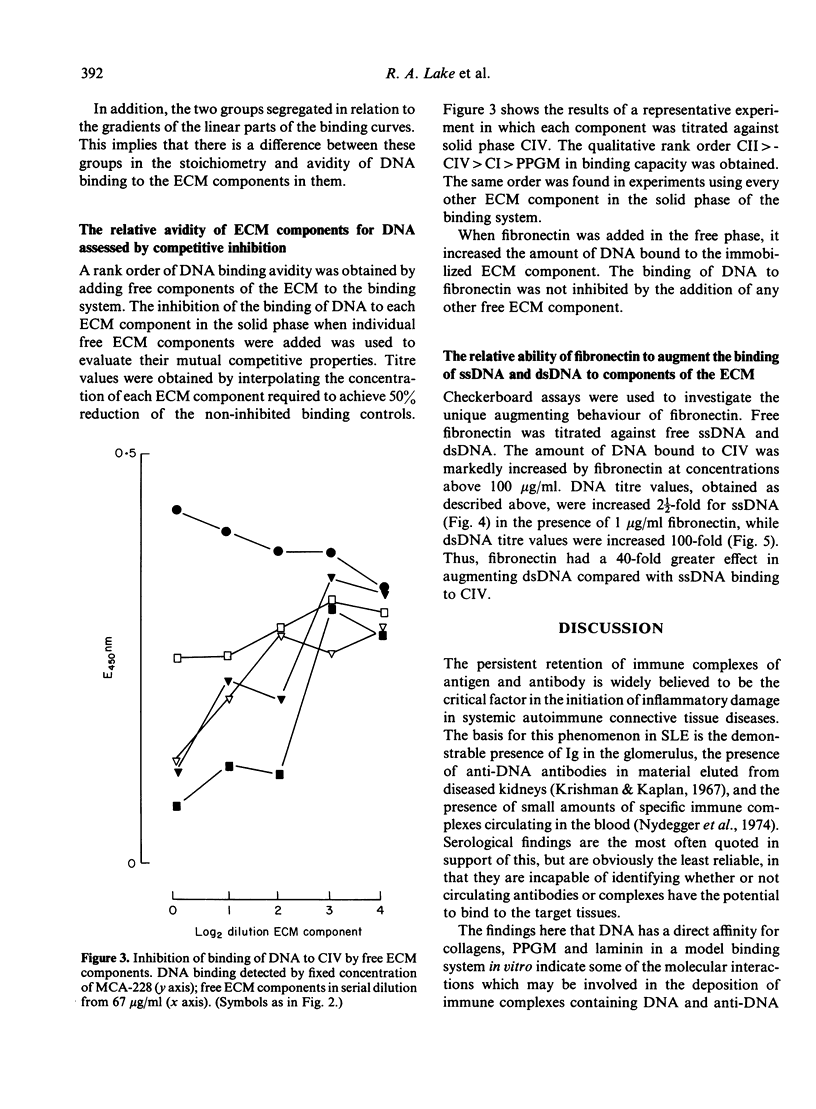
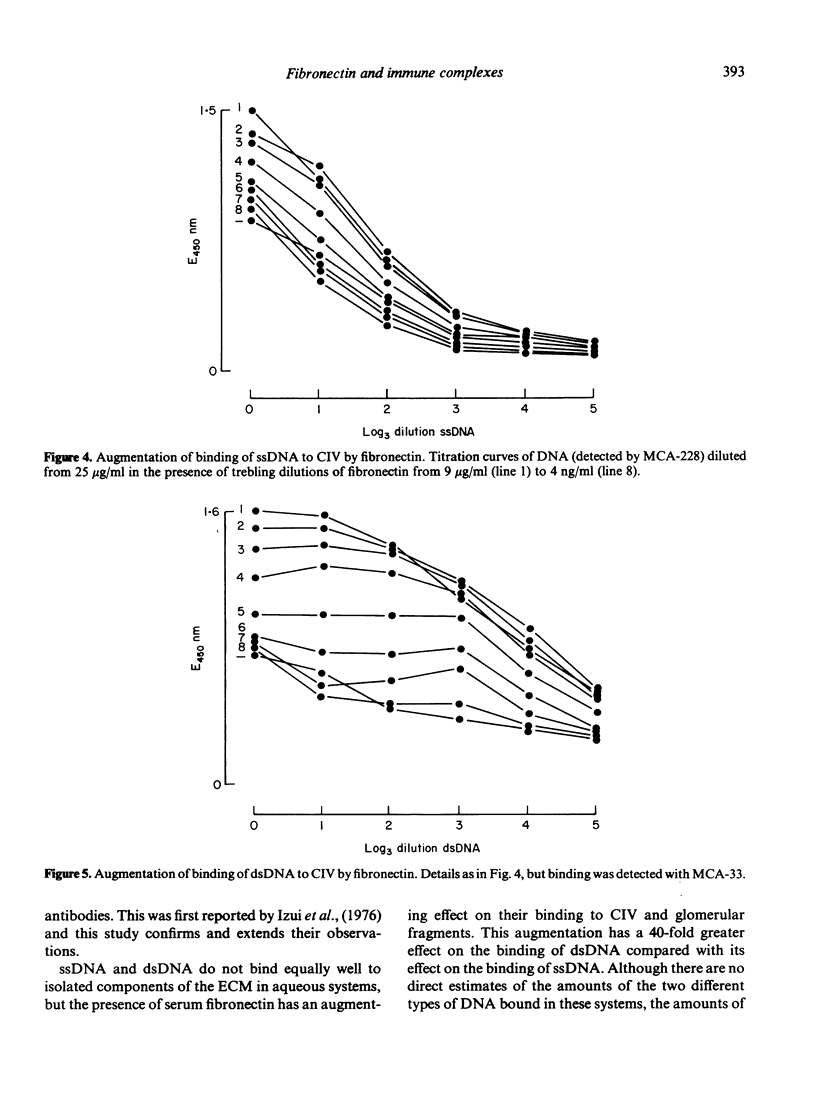
The interactions of DNA, monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibodies and isolated purified components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) were studied in a solid phase model system. Binding of DNA to each of the components was assessed using monoclonal antibody and enzyme conjugated antiglobulin in direct binding and inhibition assays. Each of the genetically distinct collagens (Types I-IV), proteoglycan monomer and laminin, bound ssDNA, but dsDNA bound significantly only to fibronectin. When used in an inhibition system, fibronectin linked DNA and anti-DNA antibodies to the collagens; it had a differential effect on the binding of ssDNA and dsDNA to a Type IV collagen matrix, the most striking feature being a 100 fold increase in dsDNA binding to Type IV collagen in the presence of fibronectin. It is likely that fibronectin binds dsDNA to collagen by separate binding domains for these molecules, and that this may be involved in the deposition of DNA in kidneys in some forms of glomerulonephritis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Couser W. G., Salant D. J. In situ immune complex formation and glomerular injury. Kidney Int. 1980 Jan;17(1):1–13. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon A. J., Burns J. Ultrastructural localisation of fibronectin in mouse kidney. J Pathol. 1982 Sep;138(1):25–31. doi: 10.1002/path.1711380104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emlen W., Mannik M. Effect of DNA size and strandedness on the in vivo clearance and organ localization of DNA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):185–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E., Miller E. J. Affinity of fibronectin to collagens of different genetic types and to fibrinogen. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1584–1595. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Ewins R. J., Muir H. Cartilage proteoglycans. Structure and heterogeneity of the protein core and the effects of specific protein modifications on the binding to hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):127–143. doi: 10.1042/bj1570127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch S. O. DNA-binding domains of fibronectin probed using Western blots. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1353–1358. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holian J., Griffiths I. D., Glass D. N., Maini R. N., Scott J. T. Human anti-DNA antibody: reference standards for diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Oct;34(5):438–443. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.5.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. In vitro demonstration of a particular affinity of glomerular basement membrane and collagen for DNA. A possible basis for a local formation of DNA-anti-DNA complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):428–443. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan C., Kaplan M. H. Immunopathologic studies of systemic lupus erythematosus. II. Antinuclear reaction of gamma-globulin eluted from homogenates and isolated glomeruli of kidneys from patients with lupus nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):569–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI105558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. M., Staines N. A., Steward M. W. Glomerulonephritis induced by pre-formed immune complexes containing monoclonal antibodies of defined affinity and isotype. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):413–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Lambert P. H., Gerber H., Miescher P. A. Circulating immune complexes in the serum in systemic lupus erythematosus and in carriers of hepatitis B antigen. Quantitation by binding to radiolabeled C1q. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staines N. A., Hardingham T., Smith M., Henderson B. Collagen-induced arthritis in the rat: modification of immune and arthritic responses by free collagen and immune anti-collagen antiserum. Immunology. 1981 Dec;44(4):737–744. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. The biology and detection of immune complexes. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:89–220. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Wick G., Gay S. Antibodies to distinct types of collagens and procollagens and their application in immunohistology. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(1-2):165–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuento M., Vaheri A. Purification of fibronectin from human plasma by affinity chromatography under non-denaturing conditions. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):331–337. doi: 10.1042/bj1830331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



