Abstract
Immunoglobulin Fc-binding activity was detected by indirect immunofluorescence employing fluorochrome conjugated F(ab')2 antibody fragments on acetone-fixed cell cultures infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Using this method the Fc receptor-like activity seemed to be restricted to the IgG class of human immunoglobulins. While IgG1, IgG2, and IgG4 myeloma proteins bind to this putative Fc gamma receptor at a concentration of 0.002 mg/ml, IgG3 myeloma proteins were without activity at 0.1 mg/ml. The binding activity was associated with the Fc fragments of IgG, while the pFc' fragments of IgG appeared to be unable to bind in this assay system. The reactivity and specificity of the HSV-1 Fc receptor was independent of both the type of tissue culture cells used and the strain of HSV-1 inducing the Fc receptor-like activity. The HSV-1-induced Fc receptor has a similar specificity for human immunoglobulin class and subclasses as staphylococcal Protein A. However, these two Fc receptors exhibit at least one striking difference. The IgG3 G3m(st) protein which binds to Protein A does not bind to HSV-1-induced Fc receptor. A possible reaction site for the HSV-1 Fc receptor on IgG could be at or near Asp 276.
Full text
PDF


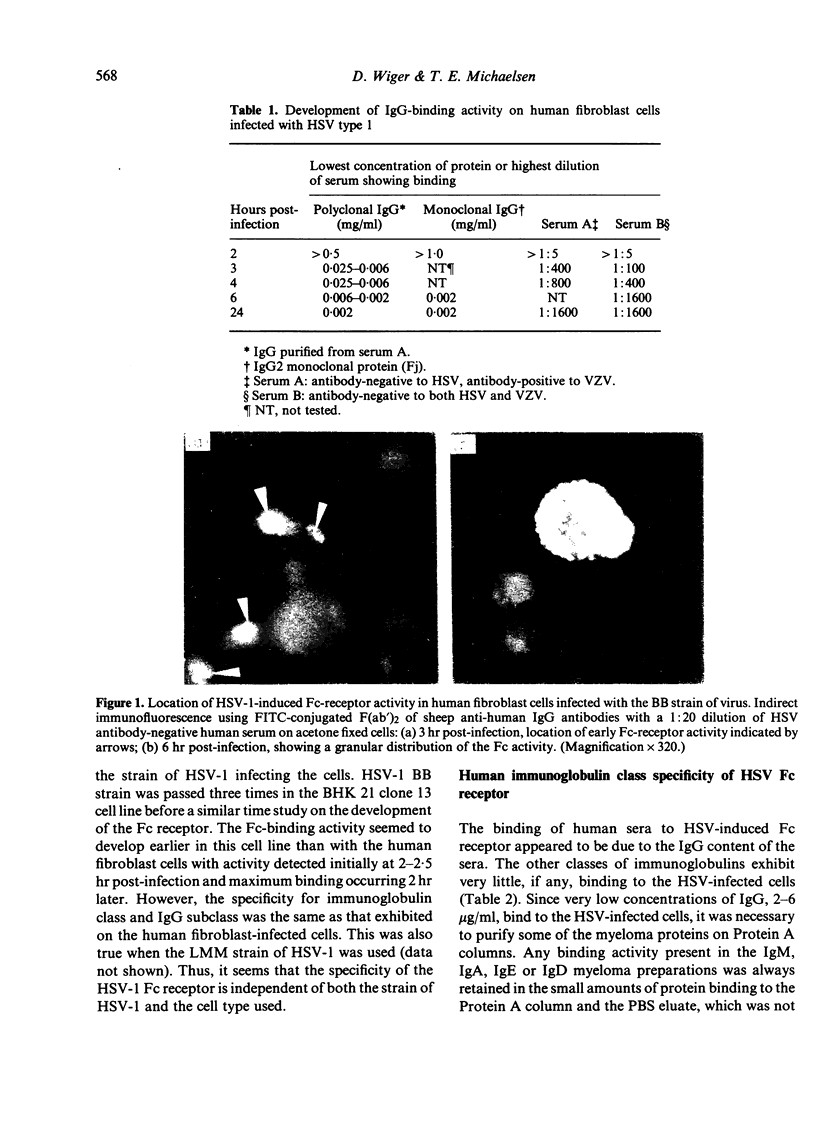
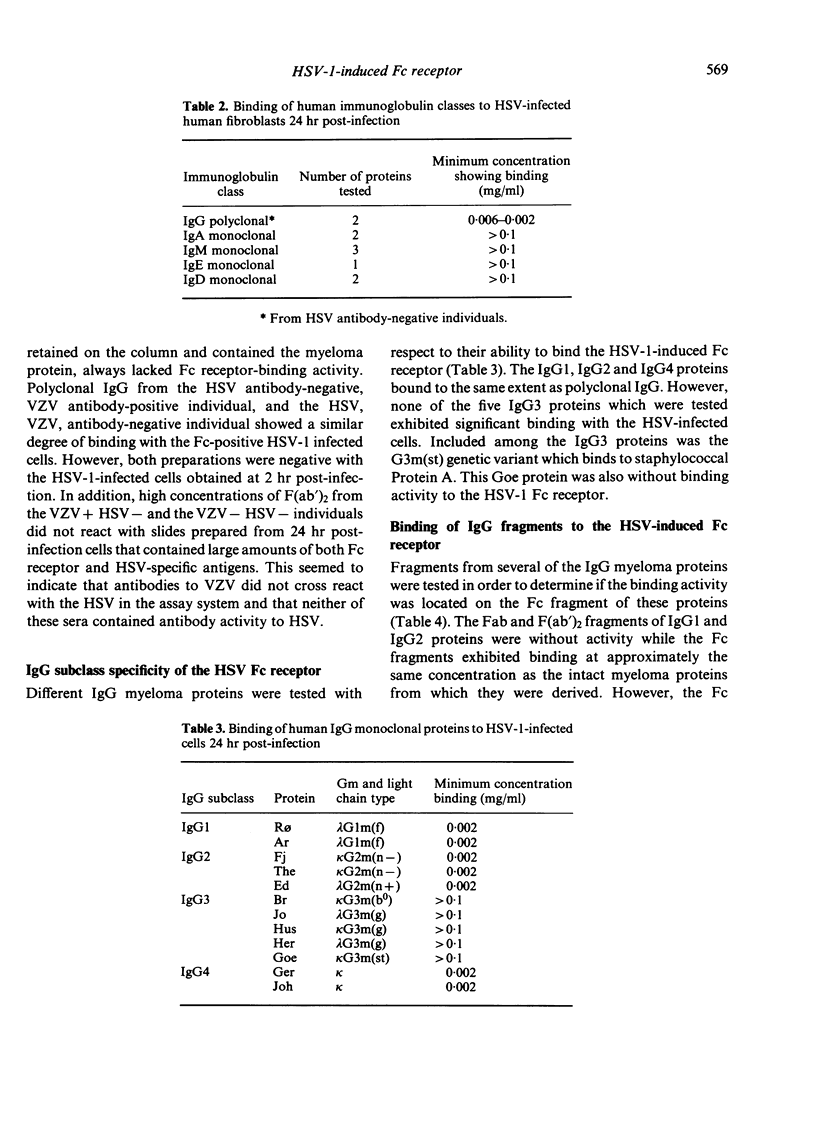


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Conjugates of immunoglobulin G with different fluorochromes. I. Characterization by anionic-exchange chromatography. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(3):273–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Jones T. A., Huber R., Sjödahl J., Sjöquist J. Crystallization, crystal structure analysis and atomic model of the complex formed by a human Fc fragment and fragment B of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Aug;359(8):975–985. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feorino P. M., Shore S. L., Reimer C. B. Detection by indirect immunofluorescence of Fc receptors in cells acutely infected with Herpes simplex virus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;53(3):222–233. doi: 10.1159/000231756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Wisloff F., Michaelsen T. E. Human lymphocytes with receptors for IgG. A population of cells distinct from T- and B-lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;47(1):124–138. doi: 10.1159/000231207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Hornberger E., Sakuma S., Plotkin S. A. Demonstration of immunoglobulin G receptors induced by human cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Oct;2(4):332–336. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.4.332-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergely J., Erdei A., Sándor M., Sármay G., Uher F. The Fc receptor model of membrane cytoplasmic signalling. Mol Immunol. 1982 Oct;19(10):1223–1228. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90287-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Fölling I. Recognition of two distinct groups of human IgM and IgA based on different binding to staphylococci. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(4):471–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson P. J., Hallberg T., Oxelius V. A., Grubb A., Blomberg J. Human immunoglobulin class and subclass specificity of Fc receptors induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.796-804.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Peitchel R., Goldman J. N., Goldman M. An IgG-Fc receptor induced in cytomegalovirus-infected human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):772–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonsdale D. M. A rapid technique for distinguishing herpes-simplex virus type 1 from type 2 by restriction-enzyme technology. Lancet. 1979 Apr 21;1(8121):849–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Ito S., Miyazaki T., Ohta T. Structural studies of a human gamma 3 myeloma protein (Jir) bearing the allotypic marker Gm(st). J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1865–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McTaggart S. P., Burns W. H., White D. O., Jackson D. C. Fc receptors induced by herpes simplex virus. I. Biologic and biochemical properties. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):726–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen T. E., Frangione B., Franklin E. C. The amino acid sequence of a human immunoglobulin G3m(g) pFc' fragment. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):558–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen T. E., Natvig J. B. Characterization of subclass-related F(ab)2, Fab-c and Fch fragments obtainined by short papain digestion of human IgG myeloma proteins. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(3):299–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen T. E., Natvig J. B. Isolation and characterization of IgG subclass proteins and Fc fragments from normal human IgG. A method for utilizing 'non a' and 'non g' as genetic markers. Immunochemistry. 1971 Mar;8(3):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen T. E., Natvig J. B. Three new fragments, F(ab) 2 , F(c) 2 , and Fab-c, obtained by papain proteolysis of normal human IgG. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(3):255–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen T. E., Natvig J. B. Unusual molecular properties of human IgG3 proteins due to an extended hinge region. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2778–2785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Costa J., Tralka T. S., Yee C. L., Rabson A. S. Properties of the cell surface Fc-receptor induced by herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1128–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Shigeta S. Appearance of immunoglobulin G Fc receptor in cultured human cells infected with varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):770–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.770-774.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Immunoglobulin G(Fc)-binding receptors on virions of herpes simplex virus type 1 and transfer of these receptors to the cell surface by infection. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.512-520.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Goldstein L., Spear P. G. Similarities and differences in the Fc-binding glycoprotein (gE) of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and tentative mapping of the viral gene for this glycoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.137-144.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recht B., Frangione B., Franklin E., van Loghem E. Structural studies of a human gamma 3 myeloma protein (Goe) that binds staph protein A. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):917–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrasher S. G., Bigazzi P. E., Yoshida T., Cohen S. The effect of fluorescein conjugation on Fc-dependent properties of rabbit antibody. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):762–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Fleit H., Mellman I. S. Structural Aspects and Heterogeneity of Immunoglobulin Fc Receptors. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:247–270. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60922-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATKINS J. F. ADSORPTION OF SENSITIZED SHEEP ERYTHROCYTES TO HELA CELLS INFECTED WITH HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. Nature. 1964 Jun 27;202:1364–1365. doi: 10.1038/2021364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmoreland D., Watkins J. F. The IgG receptor induced by herpes simplex virus: studies using radioiodinated IgG. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):167–178. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams V., Gershon A., Brunell P. A. Serologic response to varicella-zoster membrane antigens measured by direct immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):669–672. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisloff F., Michaelsen T. E., Froland S. S. Inhibition of antibody-dependent human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity by immunoglobulin classes, IgG subclasses, and IgG fragments. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(1):29–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda J., Milgrom F. Hemadsorption by herpes simplex-infected cell cultures. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;33(2):151–170. doi: 10.1159/000229985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C., Costa J., Hamilton V., Klein G., Rabson A. S. Changes in the expression of Fc receptor produced by induction of Epstein-Barr virus in lymphoma cell lines. Virology. 1982 Jul 30;120(2):376–382. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]