Abstract
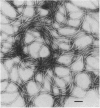
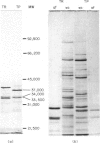
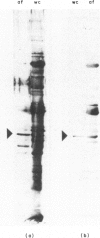
Axial filaments (flagella) of Treponema pallidum have been purified in large enough quantities to be analysed electrophoretically. They produced a characteristic linear precipitate in two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed three major polypeptides, the most prominent having an apparent molecular weight of 37,000, about 1500 less than the corresponding component of axial filaments of the Reiter treponeme. A doublet of less abundant polypeptides of 33,500-34,000 MW also differed slightly from those of the Reiter treponeme. Western blot analysis showed that the principal polypeptide of the T. pallidum axial filament was strongly antigenic, and antibody to it was prominent in sera from hyperimmunized, as well as acutely infected (orchitic), rabbits, and in soluble fractions from acutely infected rabbit testes from which large numbers of viable treponemes had been extracted. This indicated that antibody to this component was ineffective in eliminating treponemes from the tissue.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bharier M., Allis D. Purification and characterization of axial filaments from Treponema phagedenis biotype reiterii (the Reiter treponeme). J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1434–1442. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1434-1442.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy P. H., Jr, Fredericks W. R., Nell E. E. Isolation and antigenic characteristics of axial filaments from the Reiter Treponeme. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):380–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.380-386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hranitzky K. W., Mulholland A., Larson A. D., Eubanks E. R., Hart L. T. Characterization of a flagellar sheath protein of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):597–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.597-603.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Gubish E. R., Jr Identification of Treponema pallidum antigens: comparison with a nonpathogenic treponeme. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):833–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nell E. E., Hardy P. H., Jr Counterimmunoelectrophoresis of Reiter Treponeme Axial filaments as a diagnostic test for syphilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):148–152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.148-152.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. G., Ashman L. K. Application of the nitrocellulose transfer technique and alkaline phosphatase conjugated anti-immunoglobulin for determination of the specificity of monoclonal antibodies to protein mixtures. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Oct 29;54(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Axelsen N. H., Jørgensen B. B., Petersen C. S. Antibodies in secondary syphilis against five of forty Reiter treponeme antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(6):629–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Axelsen N. H., Petersen C. S. Antigenic analysis of Treponema pallidum: cross-reactions between individual antigens of T. pallidum and T. Reiter. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(2):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Petersen C. S., Vejtorp M., Axelsen N. H. Serodiagnosis of syphilis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IgG antibodies against the Reiter treponeme flagellum. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Apr;15(4):341–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W. Avoidance of host defences by Treponema pallidum in situ and on extraction from infected rabbit testes. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Sep;126(1):69–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-126-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. S., Pedersen N. S., Axelsen N. H. A simple method for the isolation of flagella from Treponema Reiter. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Dec;89(6):379–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. W., Koffler H. Bacterial flagella. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6:219–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltani K., Aronson I. K., Brickman F., Lorincz A. L. Detection by direct immunofluorescence of antibodies to Treponema pallidum in the cutaneous infiltrates of rabbit syphilomas. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):222–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg Pedersen N., Sand Petersen C., Axelsen N. H., Birch-Andersen A., Hovind-Hougen K. Isolation of a heat-stable antigen from Treponema Reiter, using an immunoadsorbent with antibodies from syphilitic patients. Scand J Immunol. 1981 Aug;14(2):137–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]