Abstract
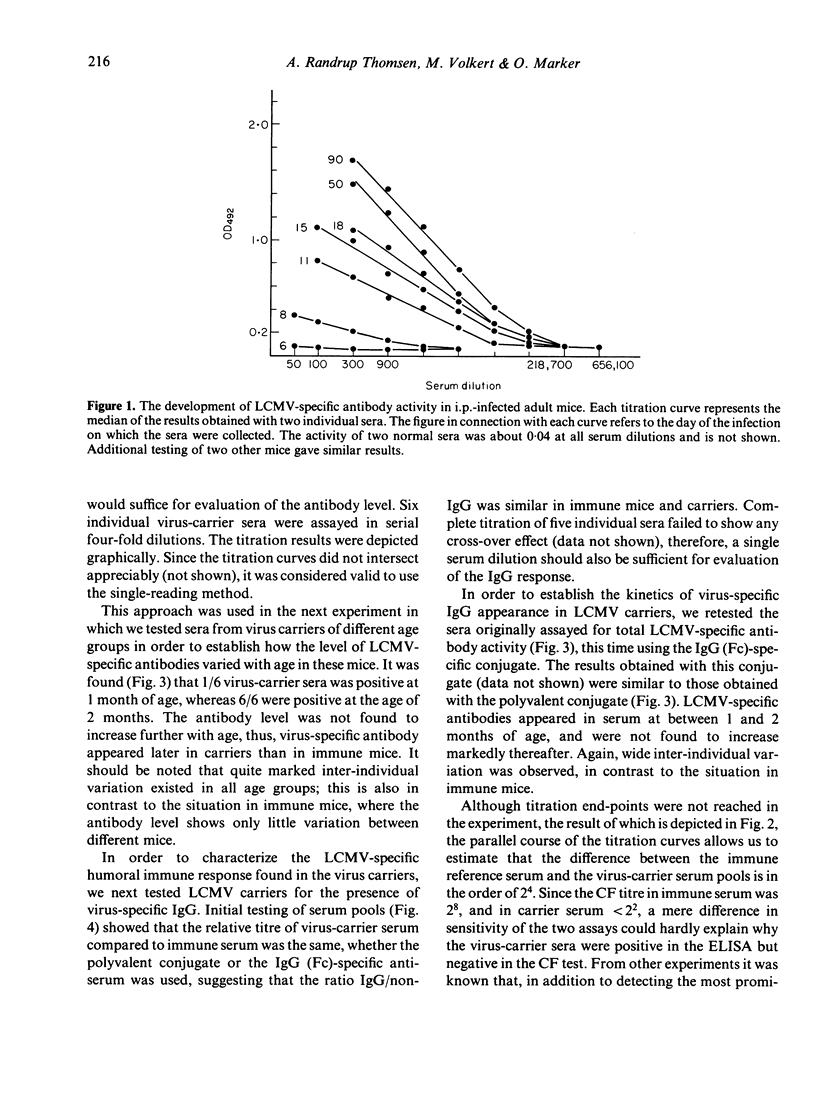
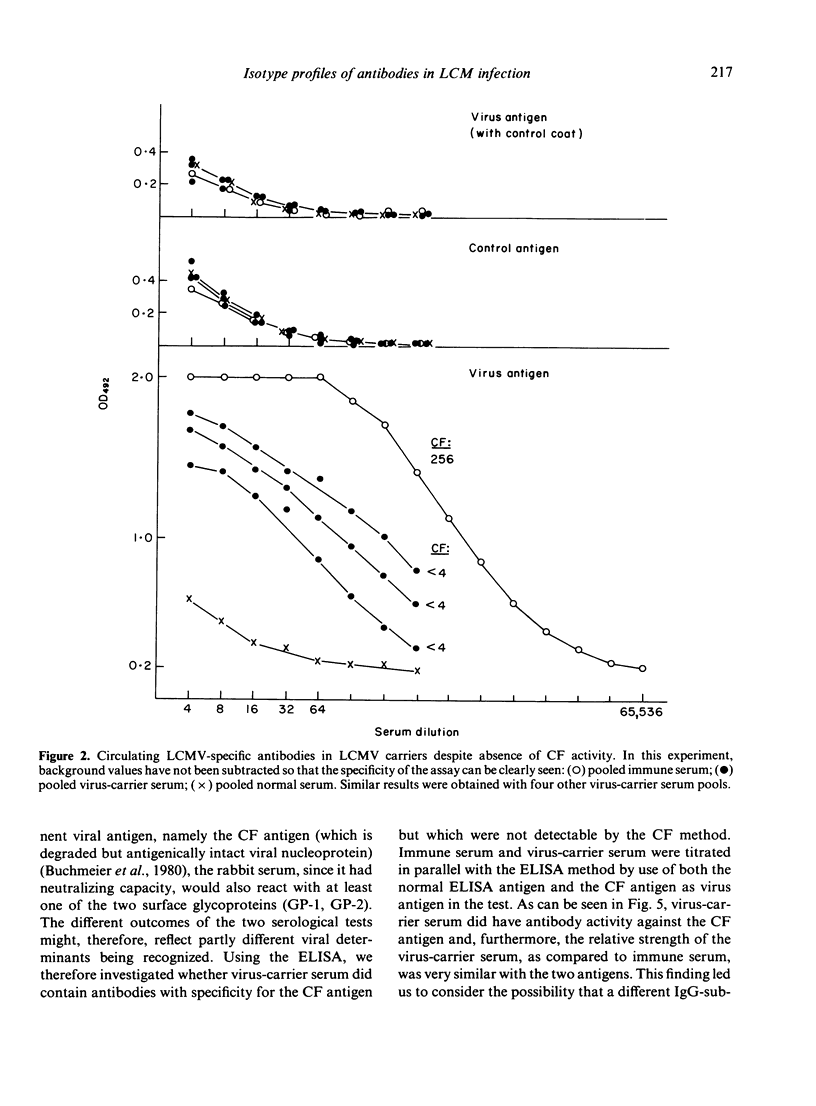
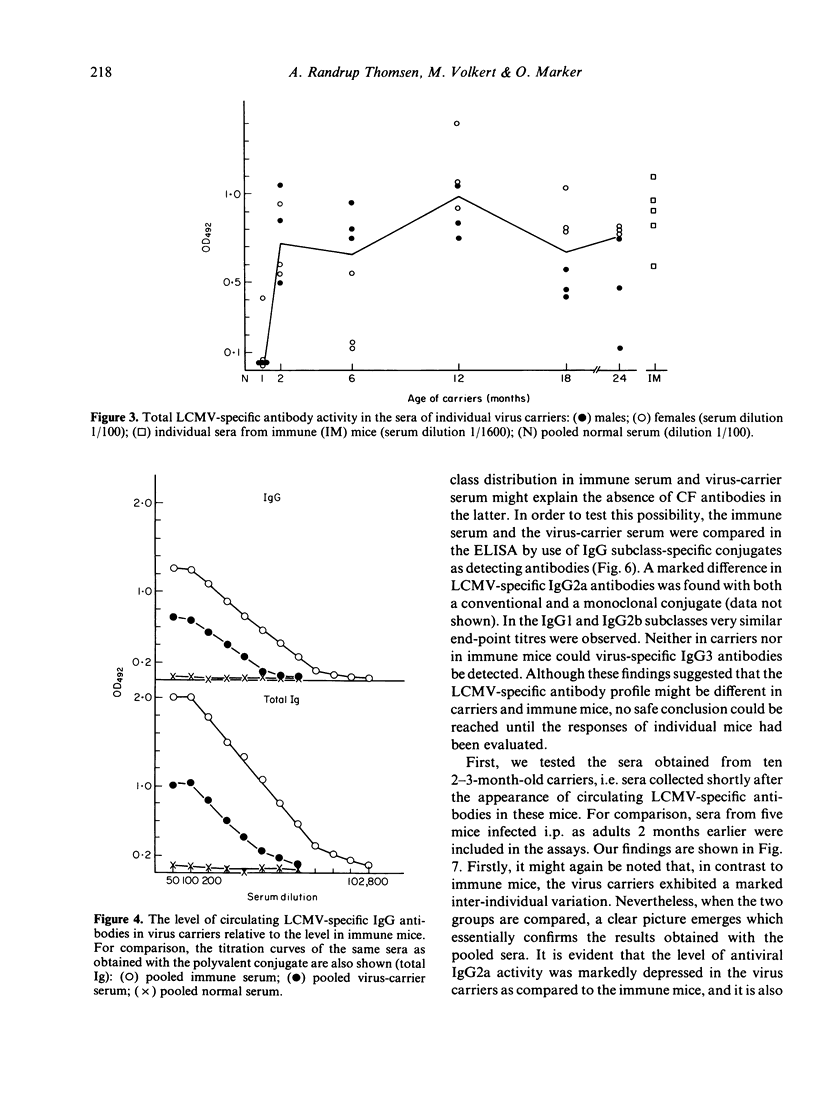
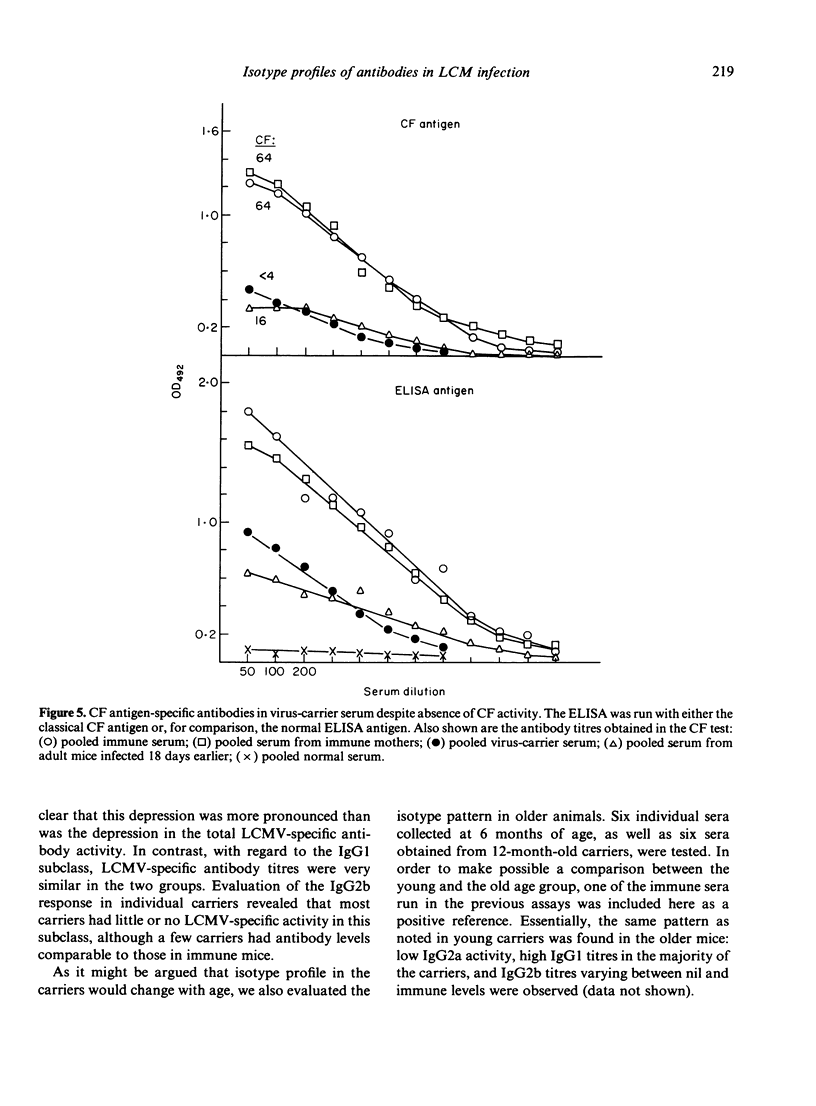
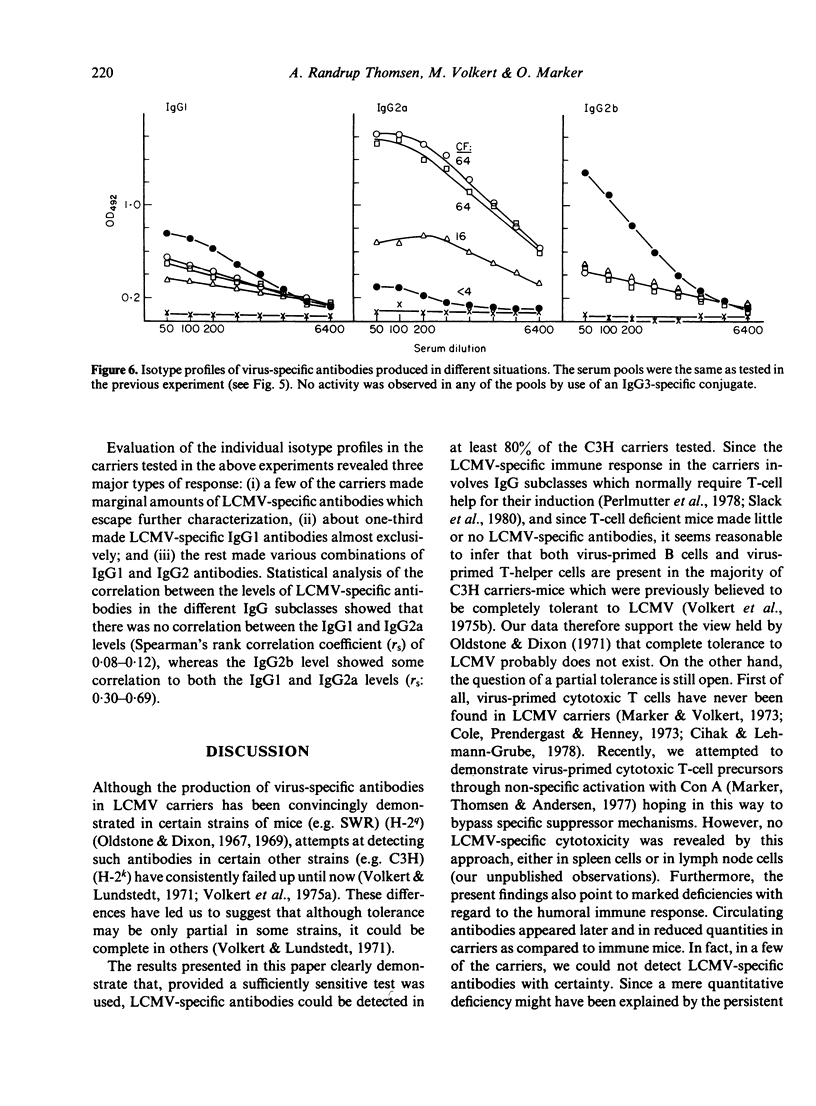
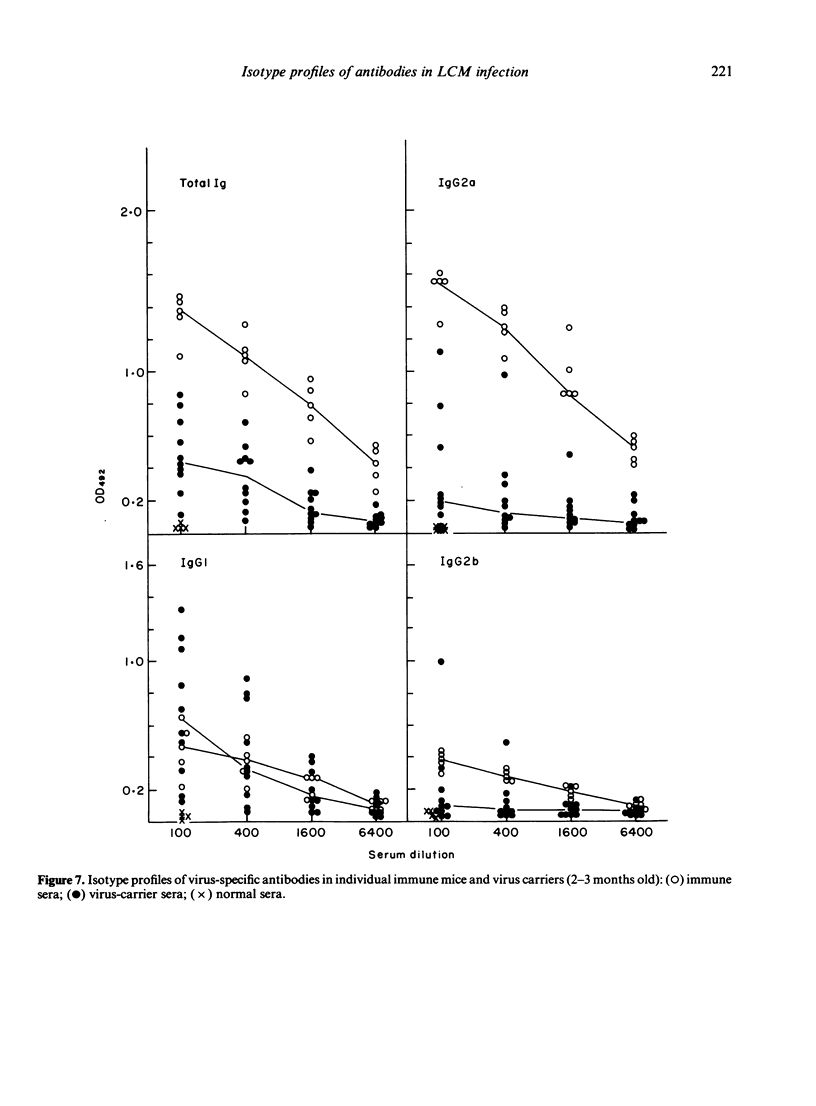
The humoral immune response to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) was analysed by the use of a sensitive ELISA. Our results show that LCMV carriers of the C3H strain, previously believed to be completely tolerant to the virus, do in fact produce LCMV-specific antibodies and, moreover, that a significant proportion of these antibodies belong to IgG subclasses which are considered T-cell dependent. This finding, together with the fact that T-cell deficient mice made little or no LCMV-specific antibodies, makes it reasonable to infer that C3H carriers have not only virus-primed B cells, but also virus-primed T-helper cells. However, the isotype profiles of the virus-specific antibodies detected were markedly different in carriers and in immune mice. Firstly, much greater inter-individual variation was observed in the carrier population than in the immune mice. Secondly, in immune mice IgG2a antibodies dominated the humoral response, whereas in carriers the virus-specific activity in this subclass was very low. In contrast, LCMV-specific antibodies of the IgG1 subclass were present in similar titres in immune mice and in the majority of the carriers. Evaluation of the IgG2b response revealed that most carriers had little or no LCMV-specific activity in this subclass, although a few had antibody levels comparable to those in immune mice. These findings are discussed in relation to the question of the state of immunity in LCMV carriers and its consequence for immune-complex disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christoffersen P. J., Volkert M., Rygaard J. Immunological unresponsiveness of nude mice to LCM virus infection. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Dec;84C(6):520–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cihak J., Lehmann-Grube F. Immunological tolerance to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in neonatally infected virus carrier mice: evidence supporting a clonal inactivation mechanism. Immunology. 1978 Feb;34(2):265–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daëron M., Couderc J., Ventura M., Liacopoulos P., Voisin G. A. Anaphylactic properties of mouse monoclonal IgG2a antibodies. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jun;70(1):27–40. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas A. I., Medgyesi G. A., Füst G., Miklós K., Gergely J. Immunogenicity of antigen complexed with antibody. I. Role of different isotypes. Immunology. 1982 Mar;45(3):483–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTCHIN J. The biology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis infection: virus-induced immune disease. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:479–499. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R., Tokuhisa T., Oi V. T., Herzenberg L. A. Molecular, cellular and systemic mechanisms for regulating IgCH expression. Immunol Rev. 1982;67:5–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb01053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marker O., Thomsen A. R., Andersen G. T. Concanavalin A-induced activation of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus memory lymphocytes into specifically cytotoxic T cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Dec;85C(6):483–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb03673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marker O., Volkert M. Studies on cell-mediated immunity to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in mice. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1511–1525. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Buchmeier M. J., Doyle M. V., Tishon A. Virus-induced immune complex disease: specific anti-viral antibody and C1q binding material in the circulation during persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):831–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis: production of antibody by "tolerant" infected mice. Science. 1967 Dec 1;158(3805):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3805.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of chronic disease associated with persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis viral infection. I. Relationship of antibody production to disease in neonatally infected mice. J Exp Med. 1969 Mar 1;129(3):483–505. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of chronic disease associated with persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis viral infection. II. Relationship of the anti-lymphocytic choriomeningitis immune response to tissue injury in chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis disease. J Exp Med. 1970 Jan 1;131(1):1–19. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Tishon A., Buchmeier M. J. Virus-induced immune complex disease: genetic control of C1q binding complexes in the circulation of mice persistently infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):912–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Hansburg D., Briles D. E., Nicolotti R. A., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine anti-carbohydrate antibodies. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):566–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J., Der-Balian G. P., Nahm M., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine antibodies. II. The IgG plaque-forming cell response to thymus-independent type 1 and type 2 antigens in normal mice and mice expressing an X-linked immunodeficiency. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):853–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teale J. M., Liu F. T., Katz D. H. A clonal analysis of the IgE response and its implications with regard to isotope commitment. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):783–792. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKERT M., LARSEN J. H., PFAU C. STUDIES ON IMMUNOLOGICAL TOLERANCE TO LCM VIRUS. 4. THE QUESTION OF IMMUNITY IN ADOPTIVELY IMMUNIZED VIRUS CARRIERS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1964;61:268–282. doi: 10.1111/apm.1964.61.2.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKERT M., LARSEN J. H. STUDIES ON IMMUNOLOGICAL TOLERANCE TO LCM VIRUS. 6. IMMUNITY CONFERRED ON TOLERANT MICE BY IMMUNE SERUM AND BY GRAFTS OF HOMOLOGOUS LYMPHOID CELLS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:172–180. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.2.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKERT M. Studies on immunological tolerance to LCM virus. A preliminary report on adoptive immunization of virus carrier mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1962;56:305–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M., Bro-Jorgensen K., Marker O. Persistent LCM virus infection in the mouse. Immunity and tolerance. Bull World Health Organ. 1975;52(4-6):471–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M., Bro-Jorgensen K., Marker O., Rubin B., Trier L. The activity of T and B lymphocytes in immunity and tolerance to the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in mice. Immunology. 1975 Sep;29(3):455–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


