Abstract
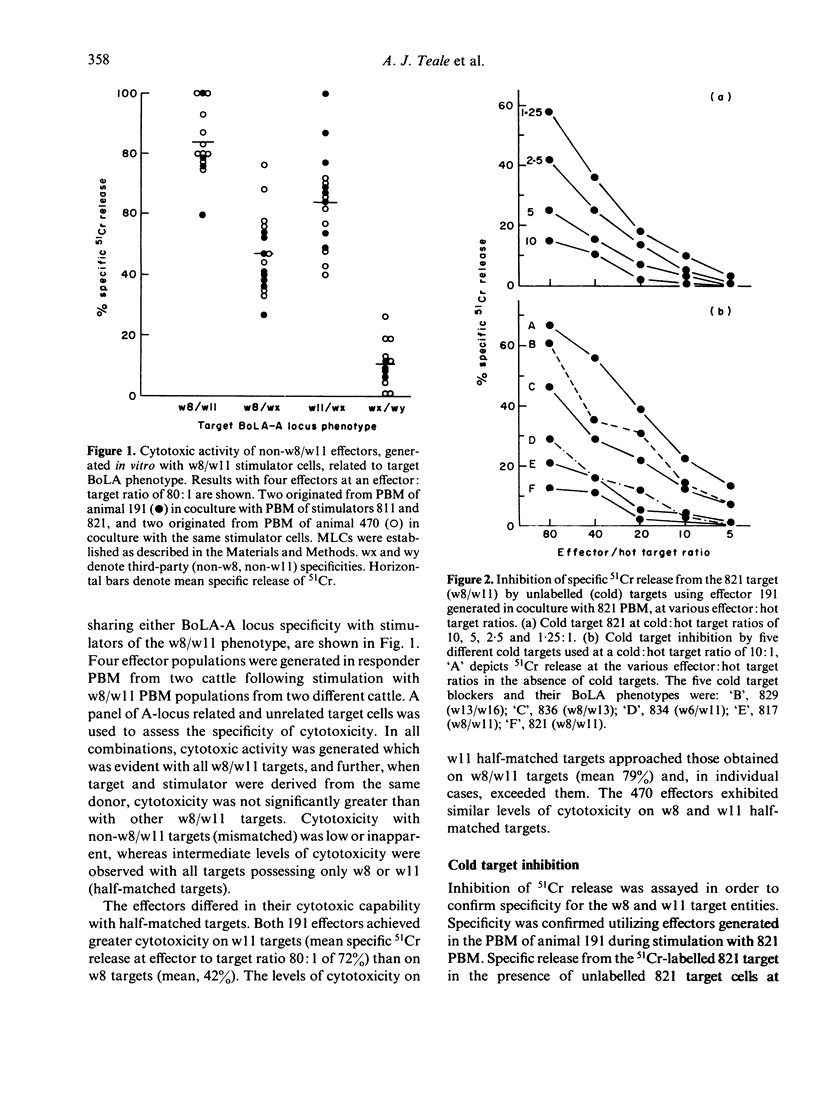
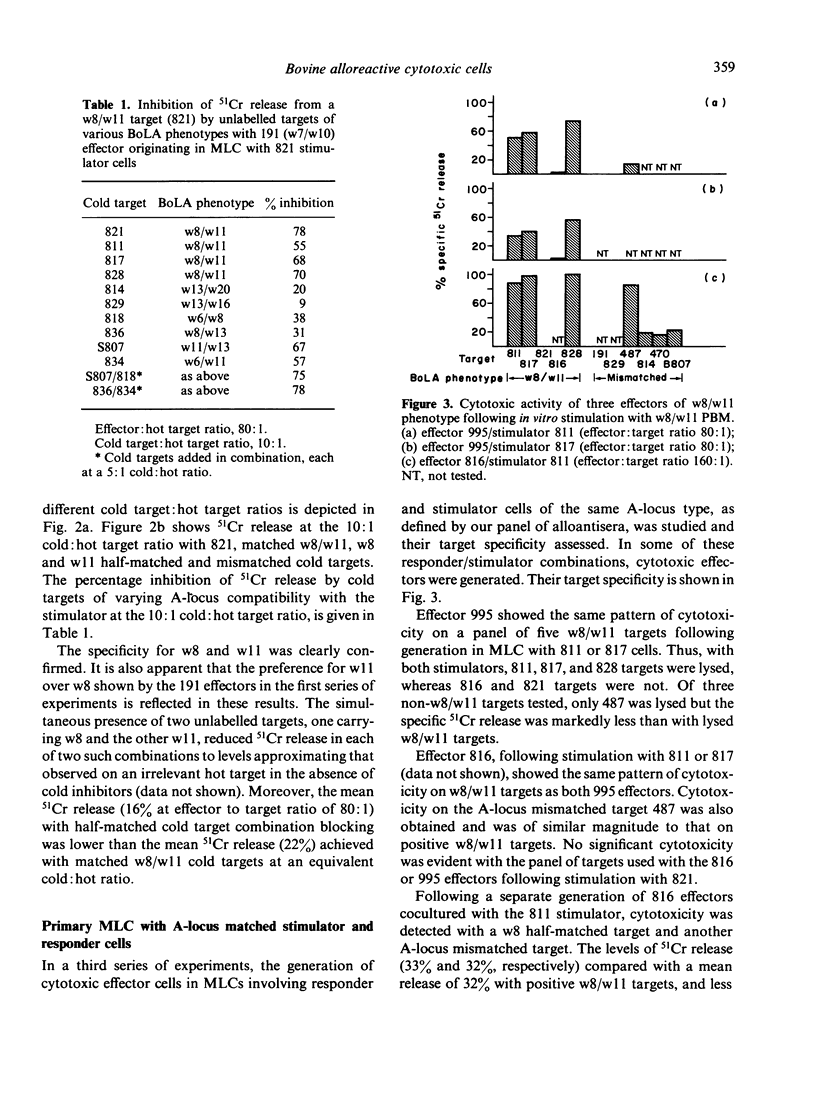
Cytotoxic cells of bovine origin were generated in primary MLC using stimulator cells of BoLA w8/w11 phenotype. Bovine lymphoblasts transformed by the protozoan parasite Theileria parva parva acted as target cells in studies of the specificity of cytotoxicity. When responder cells in MLC did not share w8 or w11 with stimulator cells, cytotoxicity was evident with all targets bearing w8 or w11, or both, and was almost entirely restricted to these products of the BoLA-A locus. When responder and stimulator cells shared both w8 and w11, cytotoxicity was also generated. Whether this was specific for the products of other putative Class I loci in cattle, or for the products of a Class II region, remains to be determined. These results suggest that the determinants recognized by appropriately generated bovine alloreactive cytotoxic cells are identical with, or closely related to, determinants characterized by BoLA w8 and w11 defining alloantisera.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amorena B., Stone W. H. Serologically defined (SD) locus in cattle. Science. 1978 Jul 14;201(4351):159–160. doi: 10.1126/science.663645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E., Ward F. E., Shearer G. M., Shaw S. The self determinants recognized by human virus-immune T cells can be distinguished from the serologically defined HLA antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):548–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickmeiss E., Soeberg B., Svejgaard A. Human cell-mediated cytotoxicity against modified target cells is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):526–528. doi: 10.1038/270526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eijsvoogel V. P., du Bois M. J., Meinesz A., Bierhorst-Eijlander A., Zeylemaker W. P., Schellekens P. T. The specificty and the activation mechanism of cell-mediated lympholysis (CML) in man. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1675–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulmy E., Termijtelen A., Bradley B. A., van Rood J. J. Y-antigen killing by T cells of women is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):544–545. doi: 10.1038/266544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULLIGER L., WILDE K. H., BROWN C. G., TURNER L. MODE OF MULTIPLICATION OF THEILERIA IN CULTURES OF BOVINE LYMPHOCYTIC CELLS. Nature. 1964 Aug 15;203:728–730. doi: 10.1038/203728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang-Xuan M., Charron D., Zilber M. T., Levy D. Biochemical characterization of class II bovine major histocompatibility complex antigens using cross-species reactive antibodies. Immunogenetics. 1982;15(6):621–624. doi: 10.1007/BF00347058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S., Biddison W. E., Strominger J. L. Comparative structural analysis of HLA-A2 antigens distinguishable by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. II. Variant DK1: evidence for a discrete CTL recognition region. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1856–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Ting A., Zweerink H. J., Askonas B. A. HLA restriction of cell-mediated lysis of influenza virus-infected human cells. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):524–526. doi: 10.1038/270524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabholz M., Vives J., Young H. M., Meo T., Miggiano V., Rijnbeek A., Shreffler D. C. Cell-mediated cell lysis in vitro: genetic control of killer cell production and target specificities in the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1974 May;4(5):378–387. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. J., Adams T. E., Brandon M. R. Serological and genetic identification of a bovine B lymphocyte alloantigen system. Anim Blood Groups Biochem Genet. 1982;13(2):123–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1982.tb01051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner R. L., Brown C. G. Bovine lymphocyte antigens (BoLA) of bovine lymphocytes and derived lymphoblastoid lines transformed by Theileria parva and Theileria annulata. Parasite Immunol. 1980 Autumn;2(3):163–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1980.tb00051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner R. L., Oliver R. A., Sales D. I., McCoubrey C. M., Millar P., Morgan A. G., Amorena B., Bailey E., Bernoco D., Brandon M. Analysis of alloantisera against bovine lymphocytes. Joint report of the 1st International Bovine Lymphocyte Antigen (BoLA) workshop. Anim Blood Groups Biochem Genet. 1979;10(2):63–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1979.tb01009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagg D. A., Dolan T. T., Leitch B. L., Young A. S. The initial stages of infection of cattle cells with Theileria parva sporozoites in vitro. Parasitology. 1981 Aug;83(Pt 1):191–197. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000050150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stear M. J., Newman M. J., Nicholas F. W. Two closely linked loci and one apparently independent locus code for bovine lymphocyte antigens. Tissue Antigens. 1982 Oct;20(4):289–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1982.tb00359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teale A. J., Kemp S. J., Young F., Spooner R. L. Selection, by major histocompatibility type (BoLA), of lymphoid cells derived from a bovine chimaera and transformed by Theileria parasites. Parasite Immunol. 1983 May;5(3):329–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistlethwaite J. R., Jr, Auchincloss H., Jr, Pescovitz M. D., Sachs D. H. Immunologic characterization of MHC recombinant swine: role of class I and II antigens in in vitro immune responses. J Immunogenet. 1984 Feb;11(1):9–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1984.tb01035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Götze D., Ptschelinzew L., Röllinghoff M. Induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against I-region-coded determinants: in vitro evidence for a third histocompatibility locus in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1477–1487. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. H-2 compatability requirement for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H-2K or H-2D;. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1427–1436. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


