Abstract
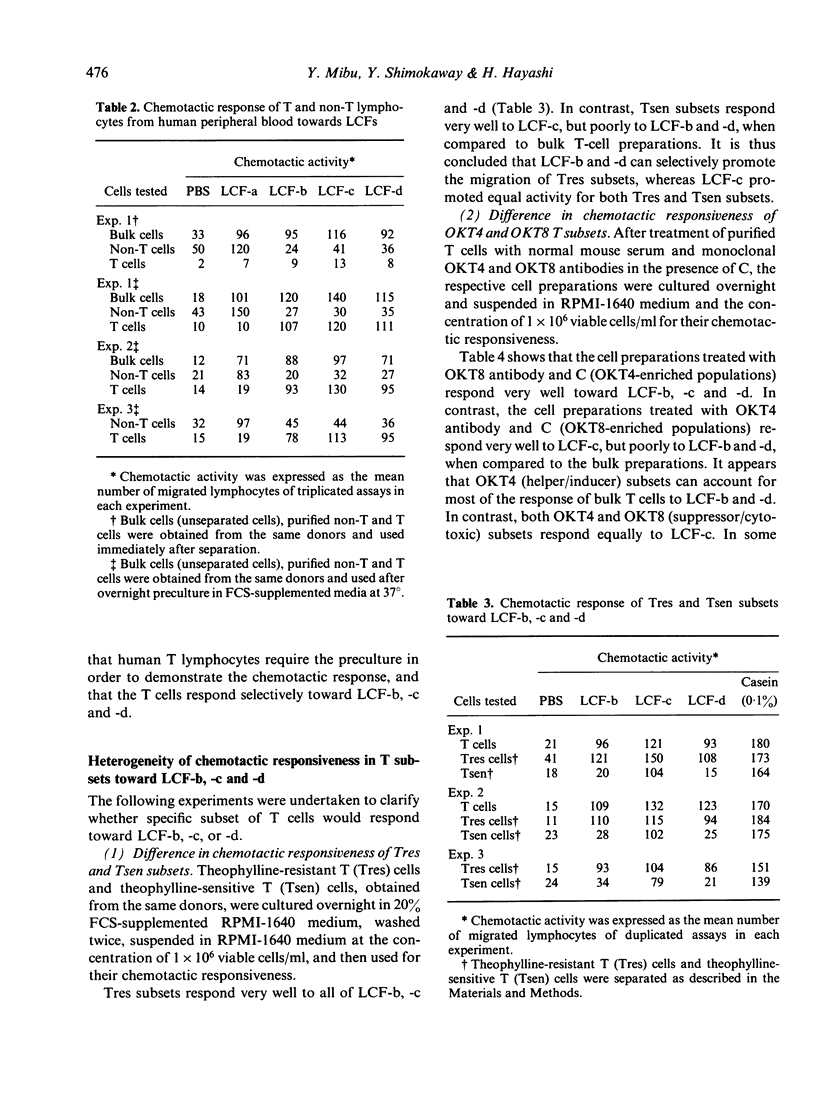
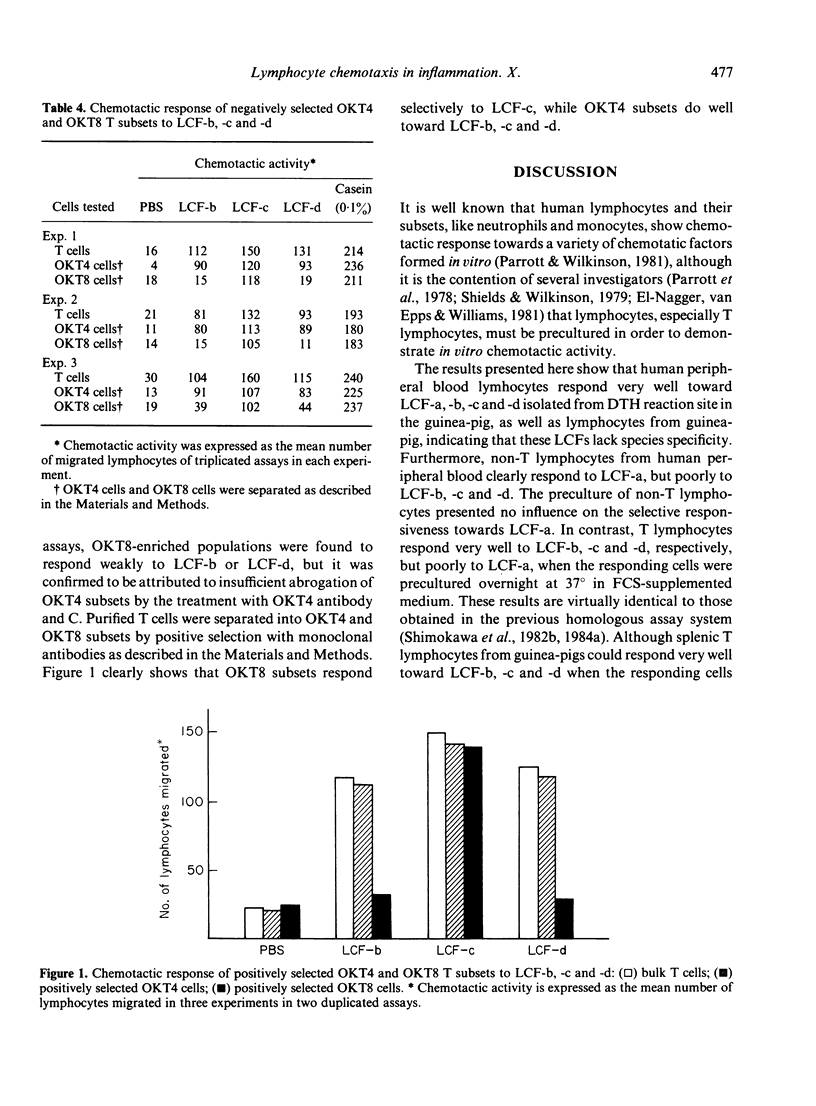
In previous studies, four lymphocyte chemotactic factors (LCF-a, -b, -c and -d) were isolated from delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) skin reaction sites of guinea-pig. In tests on guinea-pig lymphocytes, LCF-a attracted B cells, whereas LCF-b, -c and -d attracted T cells. We now report the chemotactic responses of human lymphocytes to the guinea-pig LCFs. LCF-a strongly attracted B lymphocytes and weakly attracted T lymphocytes, whereas LCF-b, -c and -d predominantly attracted T lymphocytes. In tests on T-lymphocyte subsets, LCF-b and -d selectively attracted OKT4 subsets and theophylline-resistant T cells with helper phenotype. In contrast, LCF-c attracted OKT4 and OKT8 subsets, and both theophylline-resistant and sensitive subsets (i.e. cells with both helper and suppressor phenotype). The results indicate that the different T-cell subsets migrate selectively into sites of inflammation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braathen L. R., Førre O., Natvig J. B. An anti-human T-lymphocyte antiserum: in situ identification of T cells in the skin of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, chronic photosensitivity dermatitis, and mycosis fungoides. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Jun;13(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudy A. L., Schmitt D., Viac J., Alario A., Staquet M. J., Thivolet J. Morphological, immunological and immunocytochemical identification of lymphocytes extracted from cutaneous infiltrates. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jan;23(1):61–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Naggar A., Van Epps D. E., Williams R. C., Jr Effect of culturing on the human lymphocyte locomotion response to casein, C5a, and fMet-Leu-Phe. Cell Immunol. 1981 May 1;60(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90246-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harita S., Shimokawa Y., Hayashi H. Production of two lymphocyte chemotactic factors by antigen-stimulated guinea pig lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;70(2):118–123. doi: 10.1159/000233308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harita S., Shimokawa Y., Mibu Y., Ishida M., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. IX. Further characterization of lymphocyte chemotactic lymphokines produced by purified protein derivative-stimulation in vitro and in vivo. Immunology. 1984 Feb;51(2):295–303. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Honda M., Shimokawa Y., Hirashima M. Chemotactic factors associated with leukocyte emigration in immune tissue injury: their separation, characterization, and functional specificity. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;89:179–250. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limatibul S., Shore A., Dosch H. M., Gelfand E. W. Theophylline modulation of E-rosette formation: an indicator of T-cell maturation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Sep;33(3):503–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen M., Johnsen H. E. A methodological study of E-rosette formation using AET-treated sheep red blood cells. J Immunol Methods. 1979 May 10;27(1):61–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage M. G., McHugh L. L., Rothstein T. L. Mouse lymphocytes with and without surface immunoglobulin: preparative scale separation in polystyrene tissue culture dishes coated with specifically purified anti-immunoglobulin. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Borel Y., Mantzouranis E., Steinberg A. D., Schlossman S. F. Autoantibody to an immunoregulatory inducer population in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):753–761. doi: 10.1172/JCI110092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. M., Good R. A., O'Neill G. J., Gupta S. Heterogeneity of locomotion in human T cell subsets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2392–2395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. M., Wilkinson P. C. Lymphocyte locomotion and migration. Prog Allergy. 1981;28:193–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Grant B. W., Eddy A. A., Michael A. F. Immune cell populations in cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1227–1242. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Seymour G. J., Duke O., Janossy G., Panayi G. Immunohistological analysis of delayed-type hypersensitivity in man. Cell Immunol. 1982 Dec;74(2):358–369. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields J. M., Wilkinson P. C. Relations between Fc receptor function and locomotion in human lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):598–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa Y., Harita S., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. VII. Isolation and purification of chemotactic factors for T lymphocytes from PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction site in the guinea-pig. Immunology. 1984 Feb;51(2):275–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa Y., Harita S., Higuchi Y., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. III. Demonstration of lymphocyte chemotactic activity in extract from PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction site in the guinea-pig. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Aug;63(4):355–361. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa Y., Harita S., Higuchi Y., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. IV. Isolation of lymphocyte chemotactic factors from PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction site in the guinea-pig, with special reference to a factor chemotactic for B cells. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Aug;63(4):362–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa Y., Harita S., Mibu Y., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. VIII. Demonstration of lymphocyte chemotactic lymphokines in PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction site in the guinea-pig. Immunology. 1984 Feb;51(2):287–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore A., Dosch H., Gelfand E. W. Induction and separation of antigen-dependent T helper and T suppressor cells in man. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):586–587. doi: 10.1038/274586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriram S., Solomon D., Rouse R. V., Steinman L. Identification of T cell subsets and B lymphocytes in mouse brain experimental allergic encephalitis lesions. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1649–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas Y., Sosman J., Irigoyen O., Friedman S. M., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Chess L. Functional analysis of human T cell subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies. I. Collaborative T-T interactions in the immunoregulation of B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2402–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Durant D. A., Potter J. W. Migration of human helper/inducer T cells in response to supernatants from Con A-stimulated suppressor/cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):697–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



