Abstract
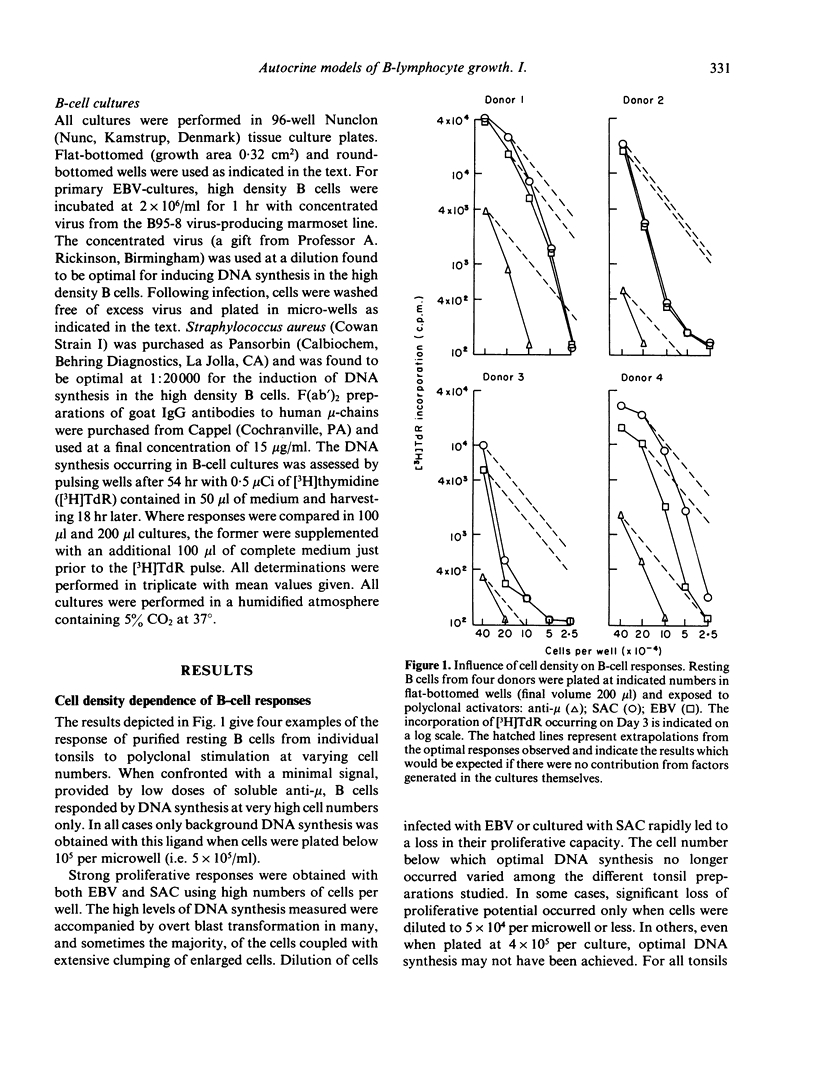
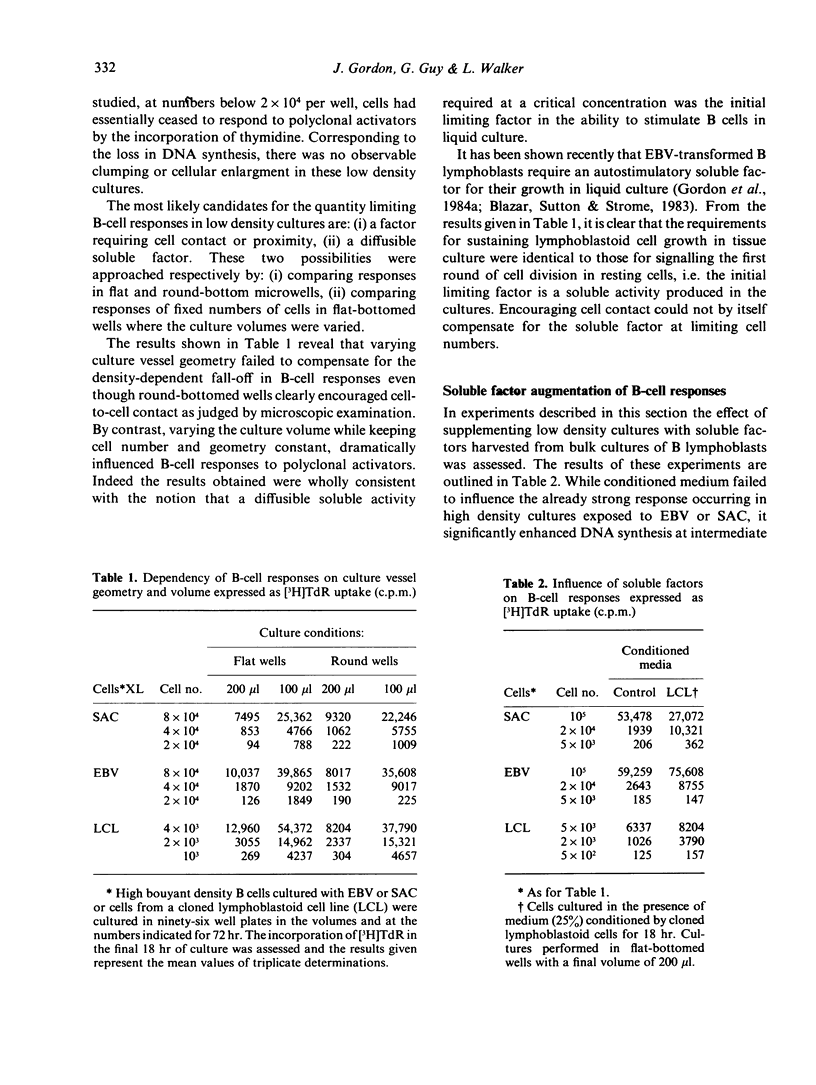
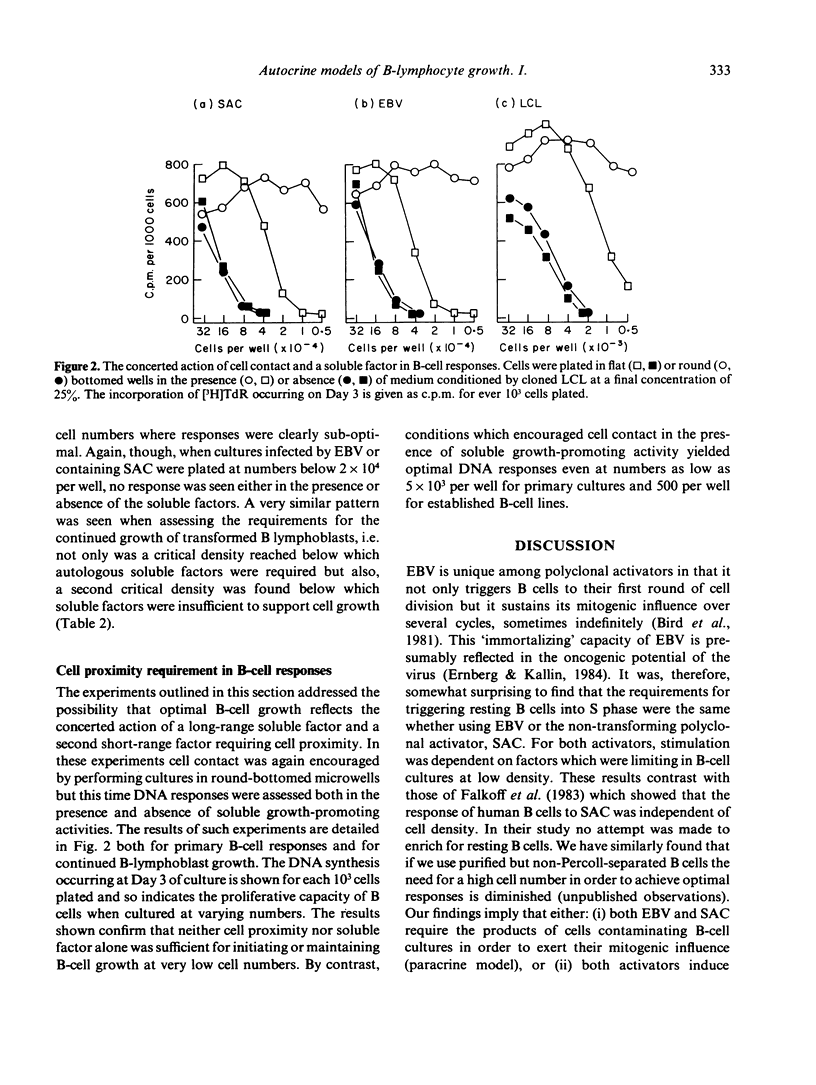
The requirements for triggering human B cells to DNA synthesis by T-independent polyclonal activators were examined. Optimal S phase entry of purified resting B cells infected with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) or confronted with killed particles of Staphylococcus aureus Cowan Strain I (SAC) required a high density of cells in culture. Experiments varying culture vessel geometry and culture volumes revealed that the initial limiting quantity was a soluble activity generated in the B-cell cultures. A parallel observation was noted in the requirements for the sustained growth of EBV-transformed lymphoblasts. Autostimulatory soluble factors harvested from such cultures were able to augment DNA synthesis in low density cultures of resting cells triggered by EBV or SAC. Below a critical cell number, however, soluble factors by themselves, were not sufficient either for supporting primary B-cell responses or for maintaining the proliferation of transformed lymphoblasts. By employing conditions which encouraged cell contact it was found that a second, non-harvestable factor requiring cell proximity for its action was also necessary to promote B-cell growth. The implications of these findings for autocrine and paracrine models of B-cell activation are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. G., Britton S., Ernberg I., Nilsson K. Characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus activation of human B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):832–839. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazar B. A., Sutton L. M., Strome M. Self-stimulating growth factor production by B-cell lines derived from Burkitt's lymphomas and other lines transformed in vitro by Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):4562–4568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel C., Melchers F. The synergism of accessory cells and of soluble alpha-factors derived from them in the activation of B cells to proliferation. Immunol Rev. 1984 Apr;78:51–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkoff R. J., Muraguchi A., Hong J. X., Butler J. L., Dinarello C. A., Fauci A. S. The effects of interleukin 1 on human B cell activation and proliferation. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):801–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fothergill J. J., Wistar R., Jr, Woody J. N., Parker D. C. A mitogen for human B cells: anti-Ig coupled to polyacrylamide beads activates blood mononuclear cells independently of T cells. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):1945–1949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Ley S. C., Melamed M. D., Aman P., Hughes-Jones N. C. Soluble factor requirements for the autostimulatory growth of B lymphoblasts immortalized by Epstein-Barr virus. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1554–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Ley S. C., Melamed M. D., English L. S., Hughes-Jones N. C. Immortalized B lymphocytes produce B-cell growth factor. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):145–147. doi: 10.1038/310145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Paul W. E. Regulation of B-cell growth and differentiation by soluble factors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:307–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed M. D., Gordon J., Ley S. J., Edgar D., Hughes-Jones N. C. Senescence of a human lymphoblastoid clone producing anti-Rhesus(D). Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):742–746. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Cantrell D. A., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Smith K. A., Reinherz E. L. Triggering of the T3-Ti antigen-receptor complex results in clonal T-cell proliferation through an interleukin 2-dependent autocrine pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1509–1513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Kehrl J. H., Butler J. L., Fauci A. S. Sequential requirements for cell cycle progression of resting human B cells after activation by anti-Ig. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):176–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock K. L., Benacerraf B., Abbas A. K. Antigen presentation by hapten-specific B lymphocytes. I. Role of surface immunoglobulin receptors. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1102–1113. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Kuang Y. D., Hall R. E., Muchmore A. V., Oppenheim J. J. Accessory cell function of human B cells. I. Production of both interleukin 1-like activity and an interleukin 1 inhibitory factor by an EBV-transformed human B cell line. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1637–1652. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizaki K., Nakagawa T., Fukunaga K., Kaieda T., Maruyama S., Kishimoto S., Yamamura Y., Kishimoto T. Characterization of human B cell growth factor (BCGF) from cloned T cells or mitogen-stimulated T cells. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1241–1246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



