Abstract
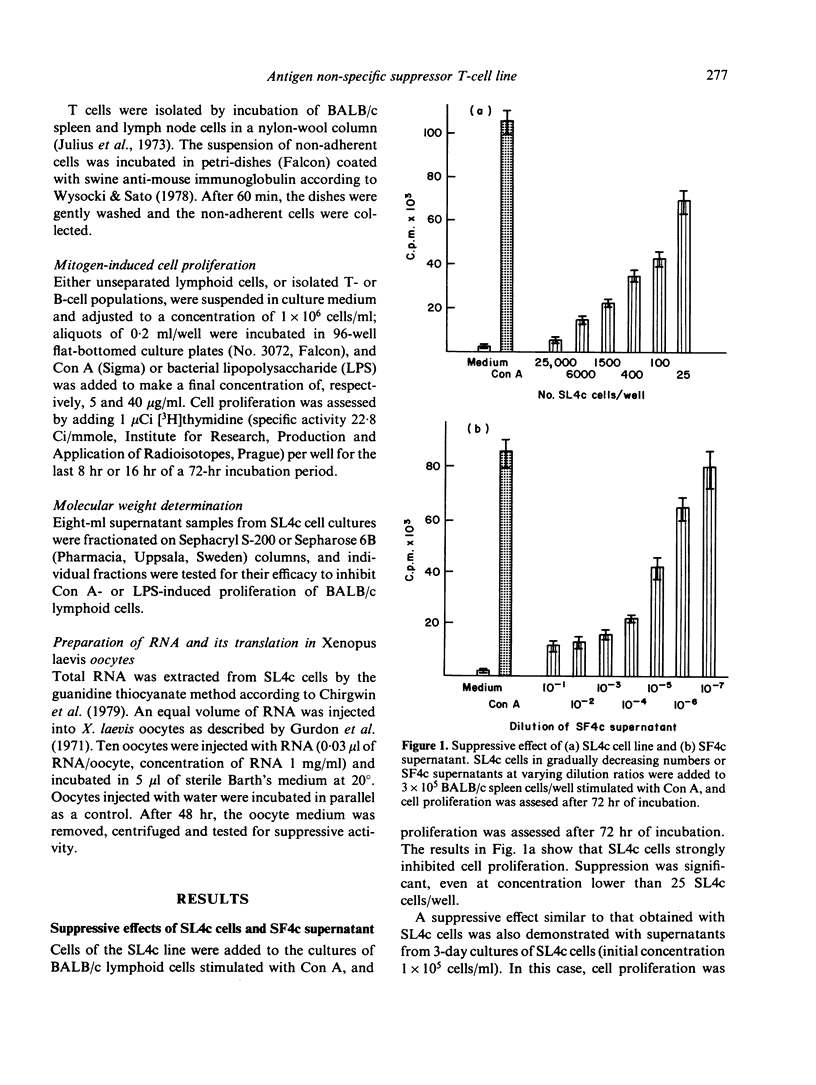
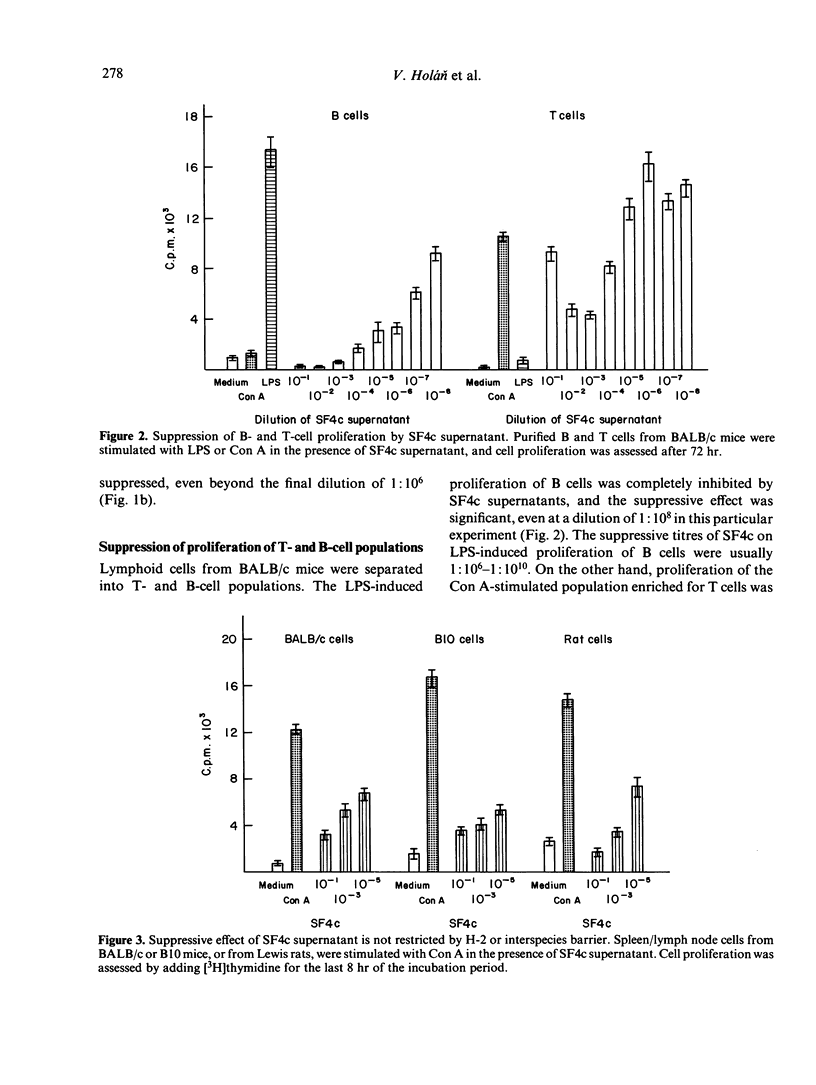
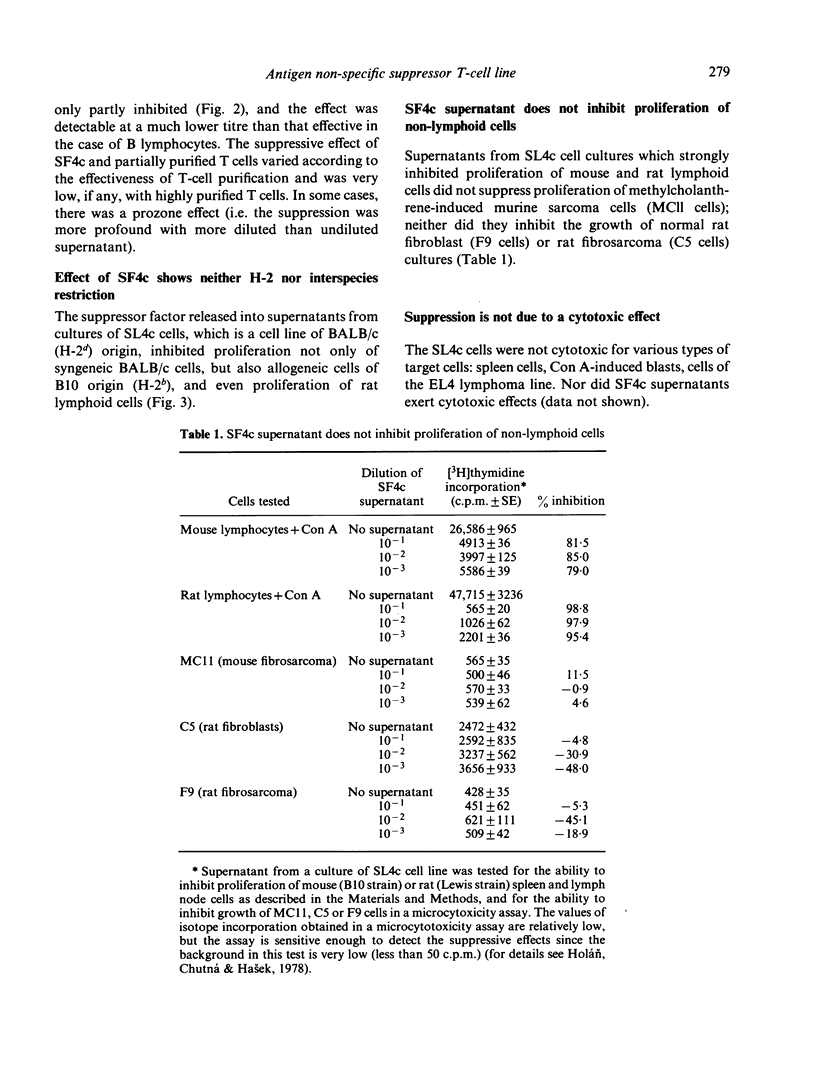
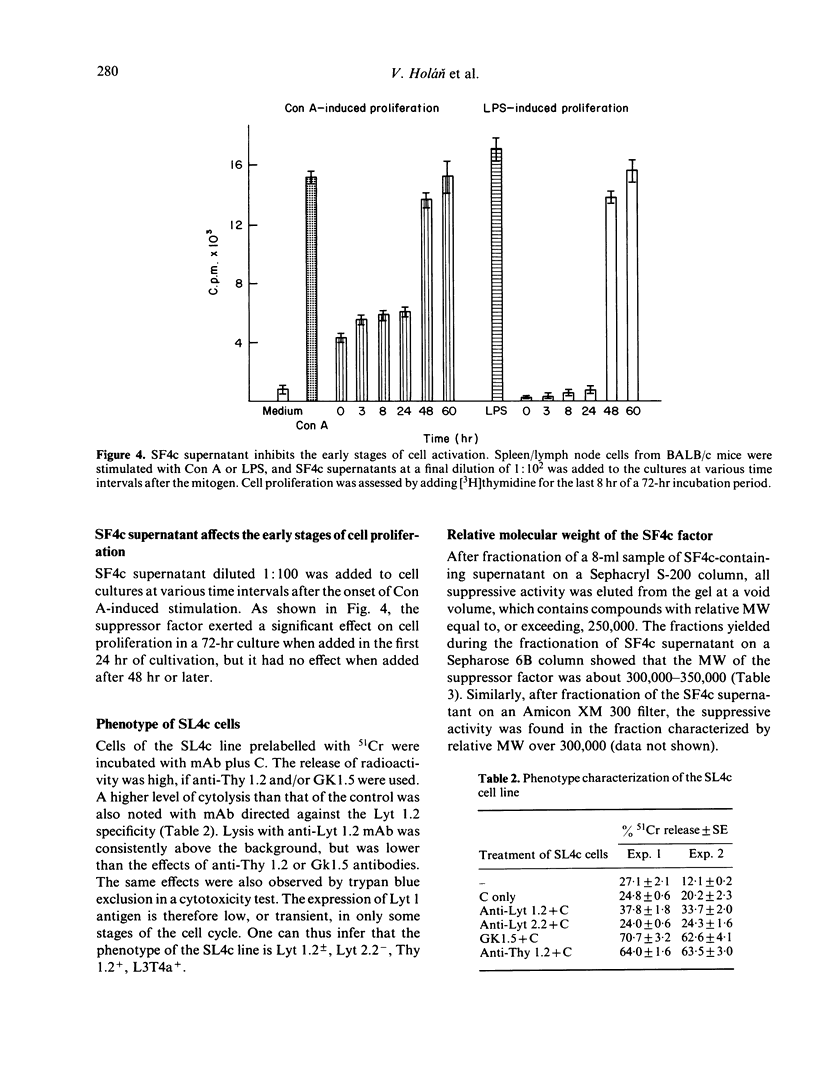
A permanent cell line designated SL4c has been established from a primary culture of murine BALB/c spleen cells regularly stimulated with large doses of irradiated allogeneic cells plus exogenous interleukin-2(IL-2). After 8 months of cultivation, the cells of the SL4c line proliferate spontaneously and do not respond with an increase in proliferation to alloantigenic stimulation. The cells have the Lyt 1.2+, Lyt 2.2-, L3T4a+, Thy 1.2+ phenotype and exert a strong suppressive effect upon stimulation with freshly explanted cells. The SL4c line produces a suppressor factor (SF4c), which inhibits the mitogen-induced proliferation of normal lymphoid cells but does not suppress the proliferation of fibroblasts and sarcoma cells. The suppression is antigen non-specific, is not limited by H-2 restriction nor by interspecies barrier, and is not due to cytotoxic effect. However, the suppression is only detectable if the SF4c is added to the stimulated cells during the early stages of mitogen-induced proliferation. A tentative characterization of the relative molecular weight (MW) of the suppressor molecule based upon fractionation of SF4c supernatant on a Sepharose 6B column shows that the inhibitory activity is confined to the high MW fractions (300,000-350,000). Translation material obtained from Xenopus laevis oocytes, which were injected with RNA preparations isolated from SL4c cells, also shows the suppressive effect.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B., Germain R. N. A single major pathway of T-lymphocyte interactions in antigen-specific immune suppression. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Hugenberger J., McVay-Boudreau L., Shen F. W., Gershon R. K., Cantor H. Immunoregulatory circuits among T-cell sets. I. T-helper cells induce other T-cell sets to exert feedback inhibition. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1106–1115. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresno M., McVay-Boudreau L., Nabel G., Cantor H. Antigen-specific T lymphocyte clones. II. Purification and biological characterization of an antigen-specific suppressive protein synthesized by cloned T cells. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1260–1274. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. R., Flood P. M., Gershon R. K. Immunoregulatory T-cell pathways. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:439–463. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Lane C. D., Woodland H. R., Marbaix G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):177–182. doi: 10.1038/233177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasek M., Holán V., Vancatová A. Suppressor factor from a permanent T cell line inhibits allotransplantation reactions in vivo. Folia Biol (Praha) 1985;31(2):185–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuer J., Brüner K., Opalka B., Kölsch E. A cloned T-cell line from a tolerant mouse represents a novel antigen-specific suppressor cell type. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):456–459. doi: 10.1038/296456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holán V., Chutná J., Hasek M. Individual variability and correlation of the in vitro tests in tolerant rats. Folia Biol (Praha) 1978;24(1):16–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holán V., Mitchison N. A. Allospecific suppression without requirement for participation of Ly 2+ cells. Immunology. 1984 Mar;51(3):469–475. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake P., Clark E. A., Khorshidi M., Sunshine G. H. Production and characterization of cytotoxic Thy-1 antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. Detection of T cell subsets. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Nov;9(11):875–886. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830091109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C. Y., Budz-Tymkewycz S., Wang E. Y., Ishaque A. A mutant human T-cell line producing immunosuppressive factor(s). Cell Immunol. 1984 Aug;87(1):35–52. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y. Specific suppression of responses to Leishmania tropica by a cloned T-cell line. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):630–632. doi: 10.1038/305630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseroff A., Okada S., Strober S. Natural suppressor (NS) cells found in the spleen of neonatal mice and adult mice given total lymphoid irradiation (TLI) express the null surface phenotype. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):101–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintáns J., Dick R. F. B cell destruction by T cell-derived factors. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1609–1610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Iscove N. N., Tees R., Aarden L., von Boehmer H. Clones of killer and helper T cells: growth requirements, specificity and retention of function in long-term culture. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:315–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Tokuhisa T., Kanno M., Yaoita Y., Shimizu A., Honjo T. Reconstitution of antigen-specific suppressor activity with translation products of mRNA. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):172–174. doi: 10.1038/298172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J., Corvalan J. R., Binns R. M., Holliman A. Production of an H--2-related suppressor factor by a hybrid T-cell line. Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):305–308. doi: 10.1038/277305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J., Holliman A. Structure of an antigen-specific suppressor factor produced by a hybrid T-cell line. Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):308–310. doi: 10.1038/277308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



