Abstract
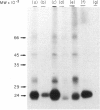
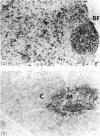
A panel of monoclonal antibodies have been produced which recognize monomorphic determinants of sheep MHC Class II antigens, including an allogenically derived murine monoclonal antibody specific for the I-E gene product. Immunoprecipitation and SDS-PAGE analyses indicates that these monoclonal antibodies recognize a non-covalently associated glycoprotein complex of molecular weight 30-32 kDa (alpha chain) and 24-26 kDa (beta chain). One and two colour immunofluorescence was used to measure the distribution of these 'Ia-like' antigens on mononuclear cells from various lymphoid organs. They were found almost exclusively on lymphocytes expressing surface immunoglobulin (B lymphocytes) and on a small population of surface immunoglobulin negative cells. Most thymocytes were negative for Class II molecules while thymic epithelial cells were positive. The tissue distribution of Class II molecules was found to be similar to that described in man. Individual monoclonal antibodies displayed no variations in reactivity with the different tissues studied.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay A. N. The localization of populations of lymphocytes defined by monoclonal antibodies in rat lymphoid tissues. Immunology. 1981 Apr;42(4):593–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Analysis of HLA-D region-associated molecules with monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen P. R., Bunch C., Brownlie J., Morris P. J. Sheep lymphocyte antigens: a preliminary study. Anim Blood Groups Biochem Genet. 1982;13(3):149–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1982.tb01577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of MHC Class II antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):293–298. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dausset J. The major histocompatibility complex in man. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1469–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.6792704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David C., Meo T., McCormick J., Shreffler D. Expression of individual Ia specificities on T and B cells. I. Studies with mitogen-induced blast cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):218–224. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk J. A., Addis J. B., Letarte M. Species cross-reactive Ia determinants: detection with a monoclonal antibody to human Ia of a murine Ia. 7 epitope. Hum Immunol. 1983 Jun;7(2):79–88. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(83)80008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrone S., Allison J. P., Pellegrino M. A. Human DR (Ia-like) antigens: biological and molecular profile. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1978;7:239–281. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0779-3_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolin-Ewens K. J., Mackay C. R., Mercer W. R., Brandon M. R. Sheep lymphocyte antigens (OLA). I. Major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Immunology. 1985 Dec;56(4):717–723. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Crumpton M. J. Isolation of glycoproteins from pig lymphocyte plasma membrane using Lens culinaris phytohemagglutinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):923–930. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90581-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F., Nagy Z. A. Genetics of the major histocompatibility complex: the final act. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:119–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. H-2 mutations: their genetics and effect on immune functions. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:55–146. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Maddox J. F., Gogolin-Ewens K. J., Brandon M. R. Characterization of two sheep lymphocyte differentiation antigens, SBU-T1 and SBU-T6. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):729–737. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M., McDevitt H. O. Several mechanisms can account for defective E alpha gene expression in different mouse haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):273–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millot P. The OLA major histocompatibility complex of sheep. Study of six new factors and evidence of a third locus of the complex: OLA-C. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1984;1(1):31–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. J., Barber P. C. Fixation of Thy-1 in nervous tissue for immunohistochemistry: a quantitative assessment of the effect of different fixation conditions upon retention of antigenicity and the cross-linking of Thy-1. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Feb;31(2):263–274. doi: 10.1177/31.2.6131917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy Z. A., Baxevanis C. N., Ishii N., Klein J. Ia antigens as restriction molecules in Ir-gene controlled T-cell proliferation. Immunol Rev. 1981;60:59–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P. G., De Martino C., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. Analysis of the expression of I-Ak-like antigens in murine fetal and adult tissues with the monoclonal antibody 10-2.16. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(6):541–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P. G., Segatto O., Ferrone S., Tosi R., Corte G. Differential tissue distribution and ontogeny of DC-1 and HLA-DR antigens. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(2):109–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00387853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Mann D. L., DeFranco A. L., Strominger J. L. Detergent solubilization, purification, and separation of specificities of HLA antigens from a cultured human lymphoblastoid line, RPMI 4265. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4682–4693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Robb R. J., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Submit and disulfide structure of monomeric and dimeric forms of detergent-soluble HLA antigens. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4694–4700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigaki N., Tosi R. Assessment of the specificity of human Ia alloantisera and alloantigens by the use of radioiodinated human Ia antigens. Tissue Antigens. 1982 Jul;20(1):1–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1982.tb00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. E., Reisfeld R. A. A high yield purification procedure for alpha and beta chains of HLA-DR antigens. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7940–7943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Galfrè G., Milstein C. Analysis of cell surfaces by xenogeneic myeloma-hybrid antibodies: differentiation antigens of rat lymphocytes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Shinohara N. Broad interspecies cross-reactions of anti-Ia murine alloantibodies. Dev Comp Immunol. 1983 Spring;7(2):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(83)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]