Abstract
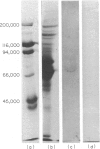
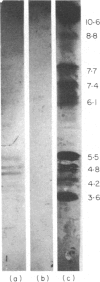
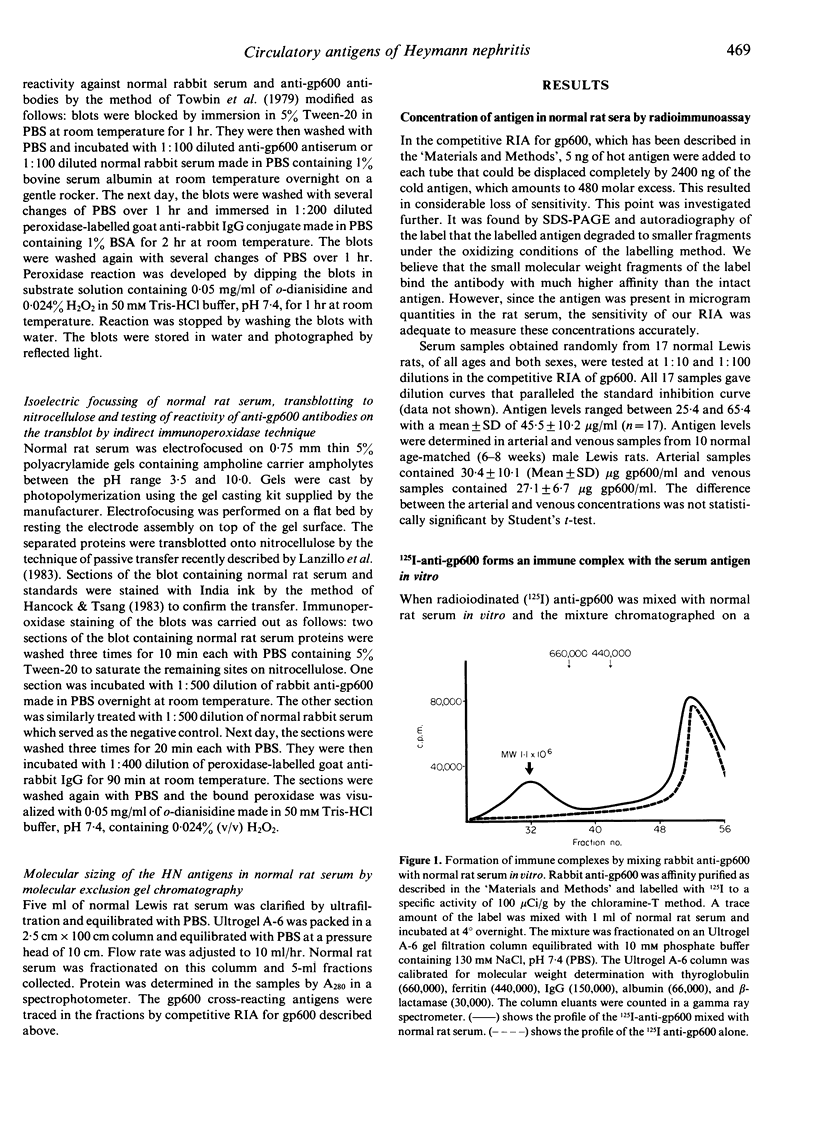
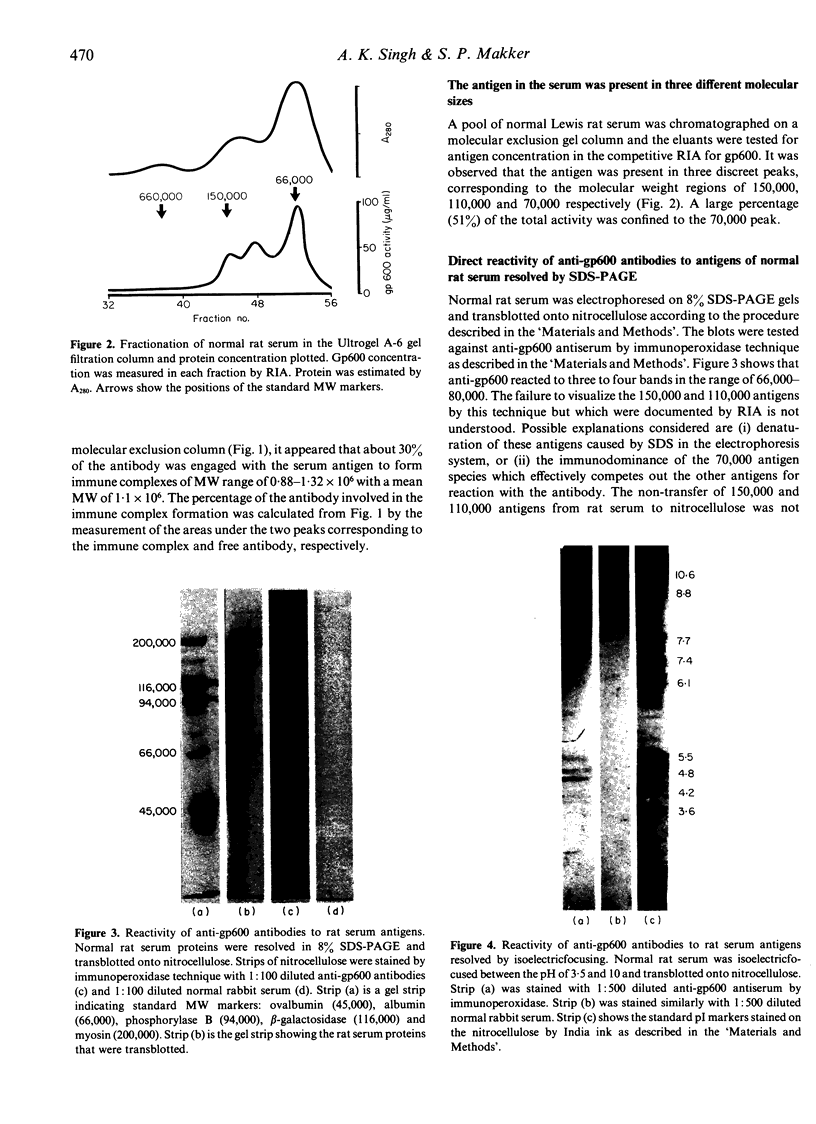
Previously, we have isolated and characterized a complex glycoprotein antigen (gp600) from the rat kidney that can induce Heymann nephritis (HN) in the rat. A monospecific antibody against the gp600 was used as a probe to document the existence of cross-reactive antigens in normal rat serum. A competitive radioimmunoassay measured the concentration in normal rat serum as being 45.5 +/- 10.2 micrograms/ml (n = 17). Molecular exclusion gel chromatography of normal rat serum identified gp600 activity in three distinct peaks corresponding to the molecular weights of 150,000, 110,000 and 70,000, respectively. Soluble immune complexes of mean molecular weight 1.1 X 10(6) were formed when normal rat serum was reacted with affinity-purified 125I anti-gp600. Normal rat serum, electrophoresed in 8% SDS-PAGE gels, transblotted to nitrocellulose membrane and reacted with anti-gp600 by indirect immunoperoxidase technique, identified three to four bands in the molecular weight region of 66,000-80,000. Isoelectric focusing revealed these antigens to be anionic (pI of 4.5-5.5) in nature. We conclude that normal rat serum contains antigens that cross-react with gp600. Further, these antigens are anionic in nature and form soluble immune complexes with anti-gp600 in vitro. The relevance of these findings to the pathogenesis of HN is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caulin-Glaser T., Gallo G. R., Lamm M. E. Nondissociating cationic immune complexes can deposit in glomerular basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1561–1572. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. I. Identification and isolation of the pathogenetic antigen. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):555–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. Nephritogenicity and differential distribution of glomerular immune complexes related to immunogen charge. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier V. J., Mannik M., Striker G. E. Effect of cationized antibodies in performed immune complexes on deposition and persistence in renal glomeruli. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):766–777. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassock R. J., Edgington T. S., Watson J. I., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. II. The pathogenetic mechanism. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):573–588. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupe W. E., Kaplan M. H. Demonstration of an antibody to proximal tubular antigen in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune nephrosis in rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Sep;74(3):400–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMANN W., HACKEL D. B., HARWOOD S., WILSON S. G., HUNTER J. L. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):660–664. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock K., Tsang V. C. India ink staining of proteins on nitrocellulose paper. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. In vitro demonstration of a particular affinity of glomerular basement membrane and collagen for DNA. A possible basis for a local formation of DNA-anti-DNA complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):428–443. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makker S. P., Singh A. K. Characterization of the antigen (gp600) of Heymann nephritis. Lab Invest. 1984 Mar;50(3):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse T., Fukasawa T., Hirokawa N., Oike S., Miyakawa Y. The pathogenesis of experimental membranous glomerulonephritis induced with homologous nephritogenic tubular antigen. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1347–1362. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. K., Makker S. P. A rapid tube ELISA for human IgG in body fluids using Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Apr 25;129(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. K., Makker S. P. The distribution and molecular presentation of the brush border antigen of Heymann nephritis in various rat tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jun;60(3):579–585. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J., Robbins J. B., Nieschlag E., Ross G. T. A method for producing specific antisera with small doses of immunogen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):988–991. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]